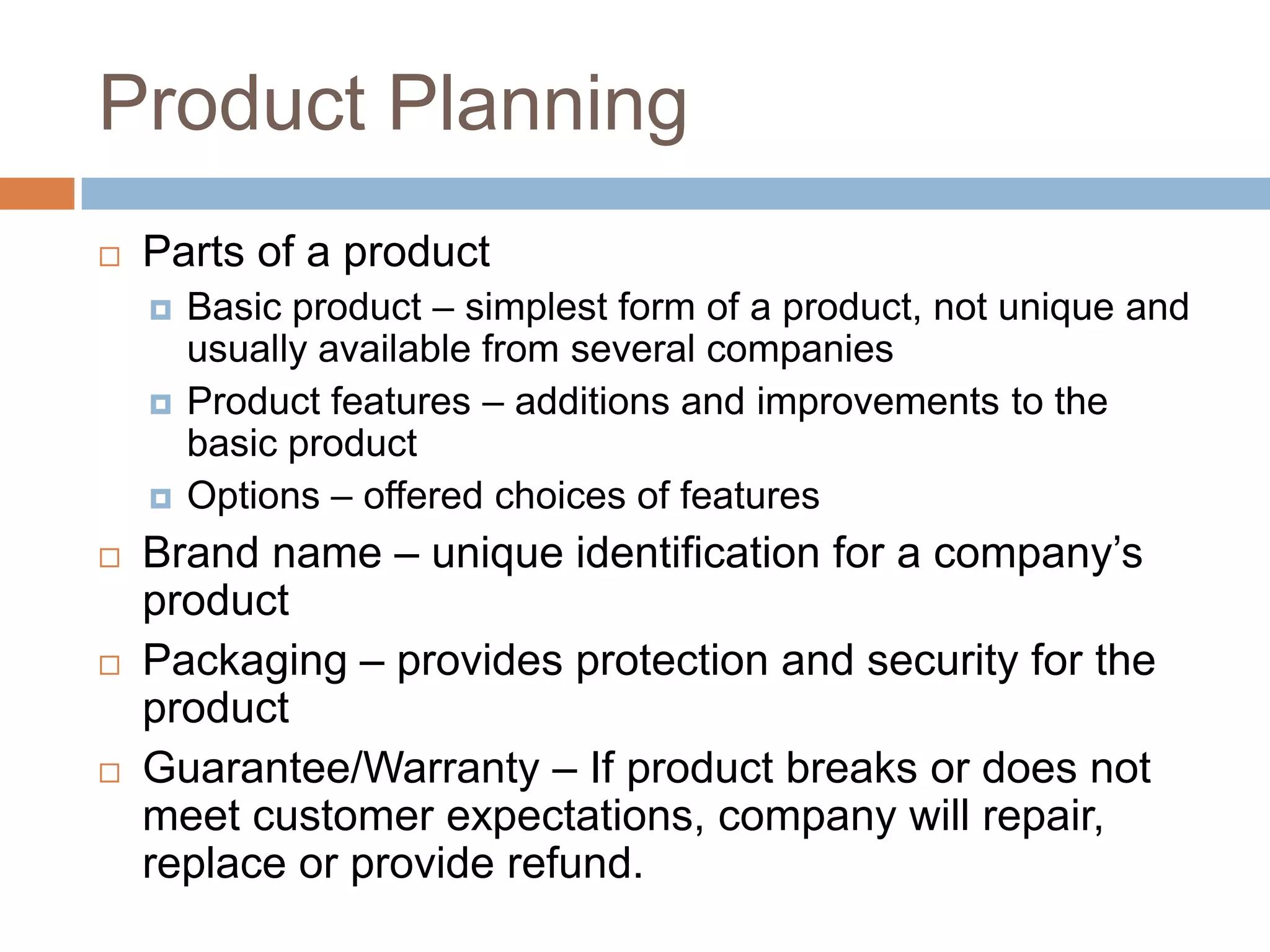
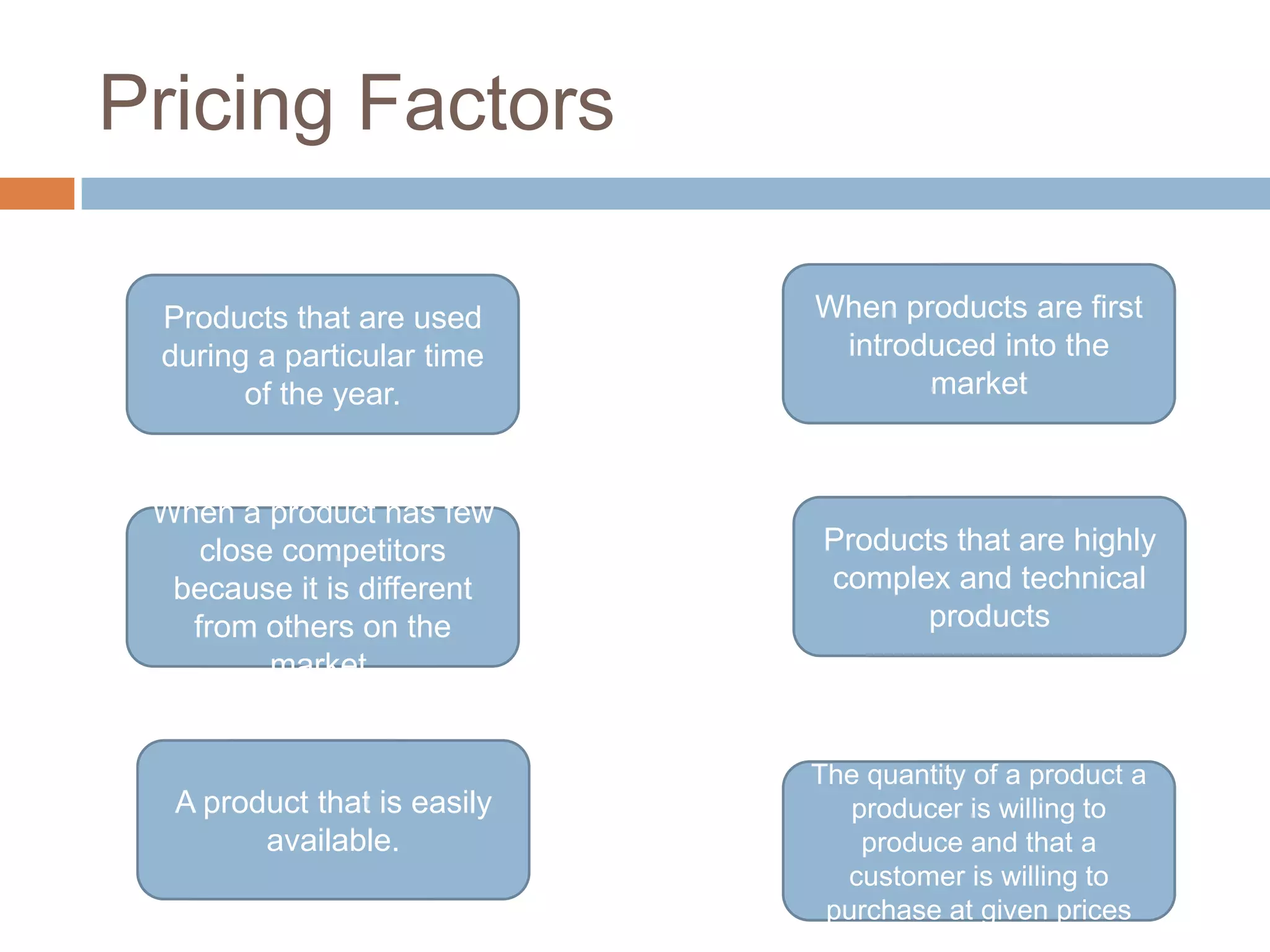
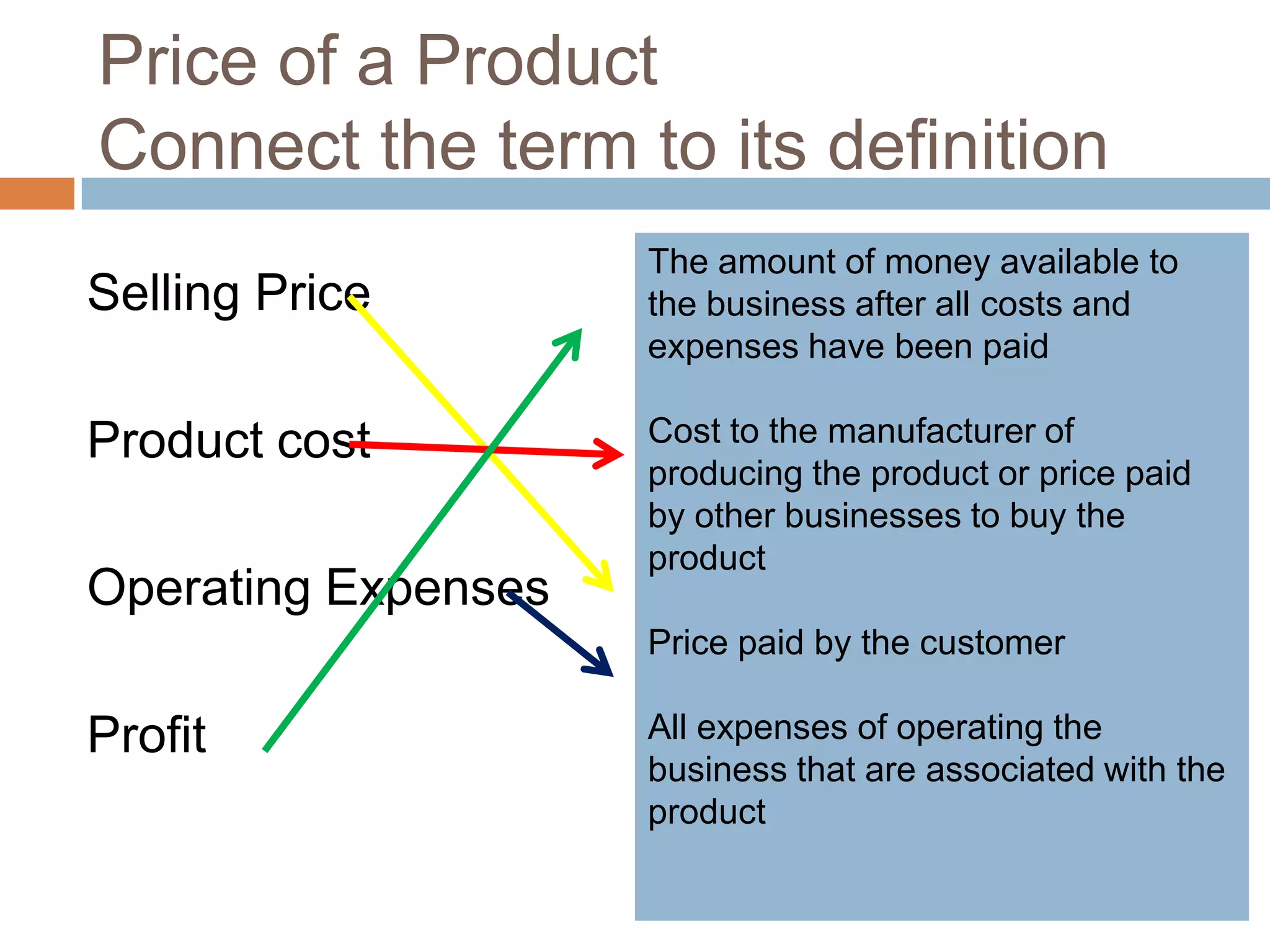
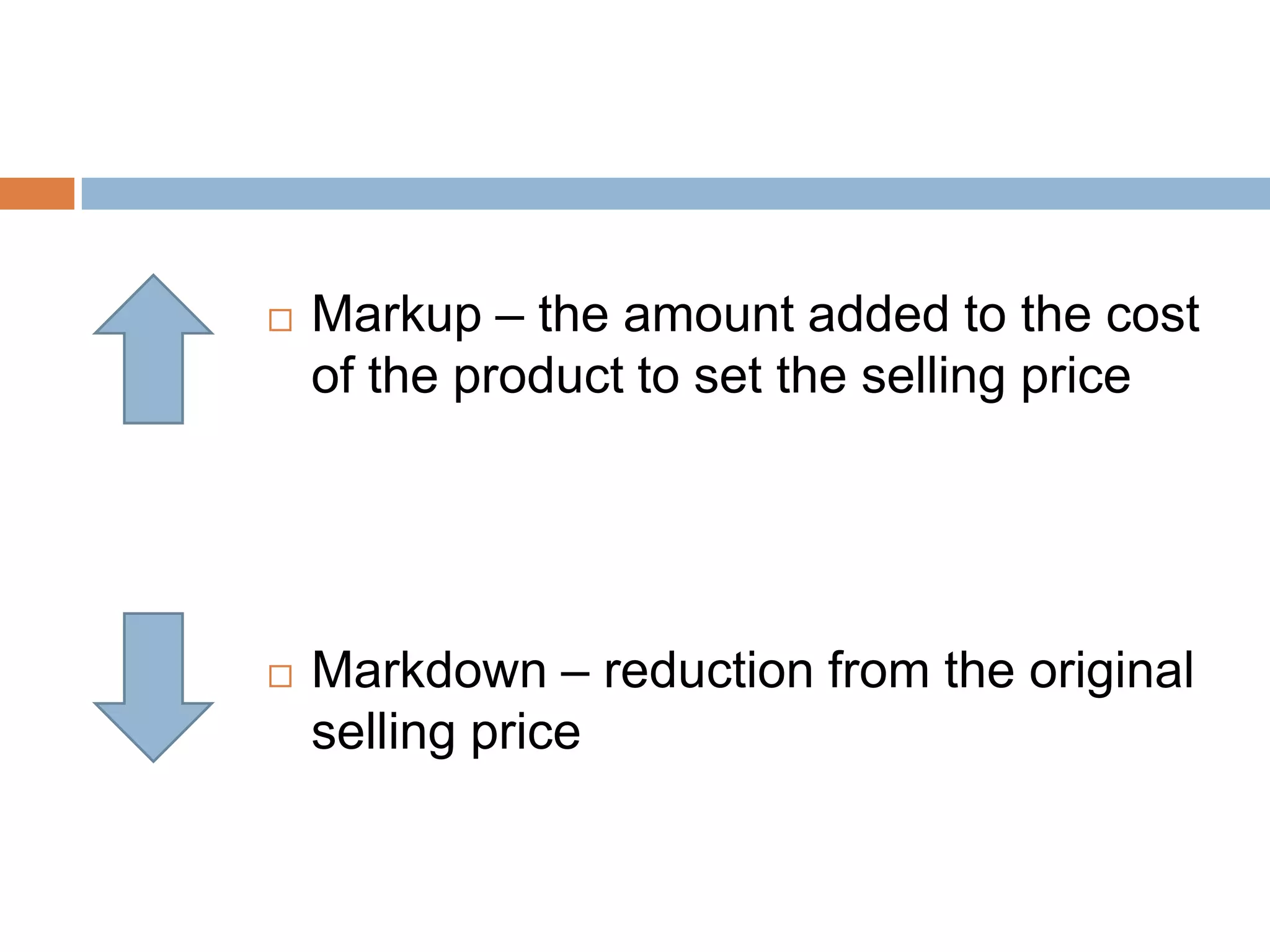
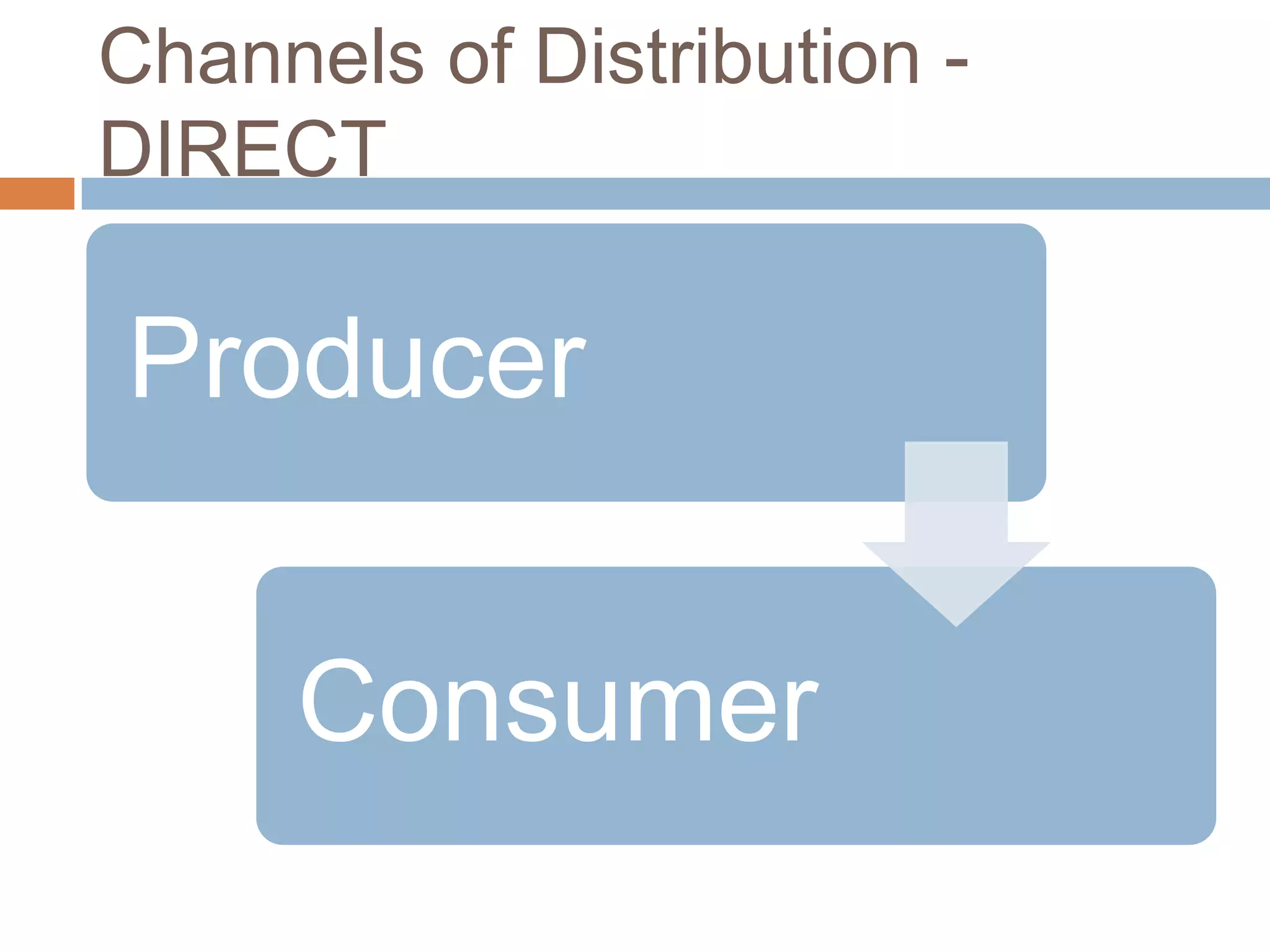
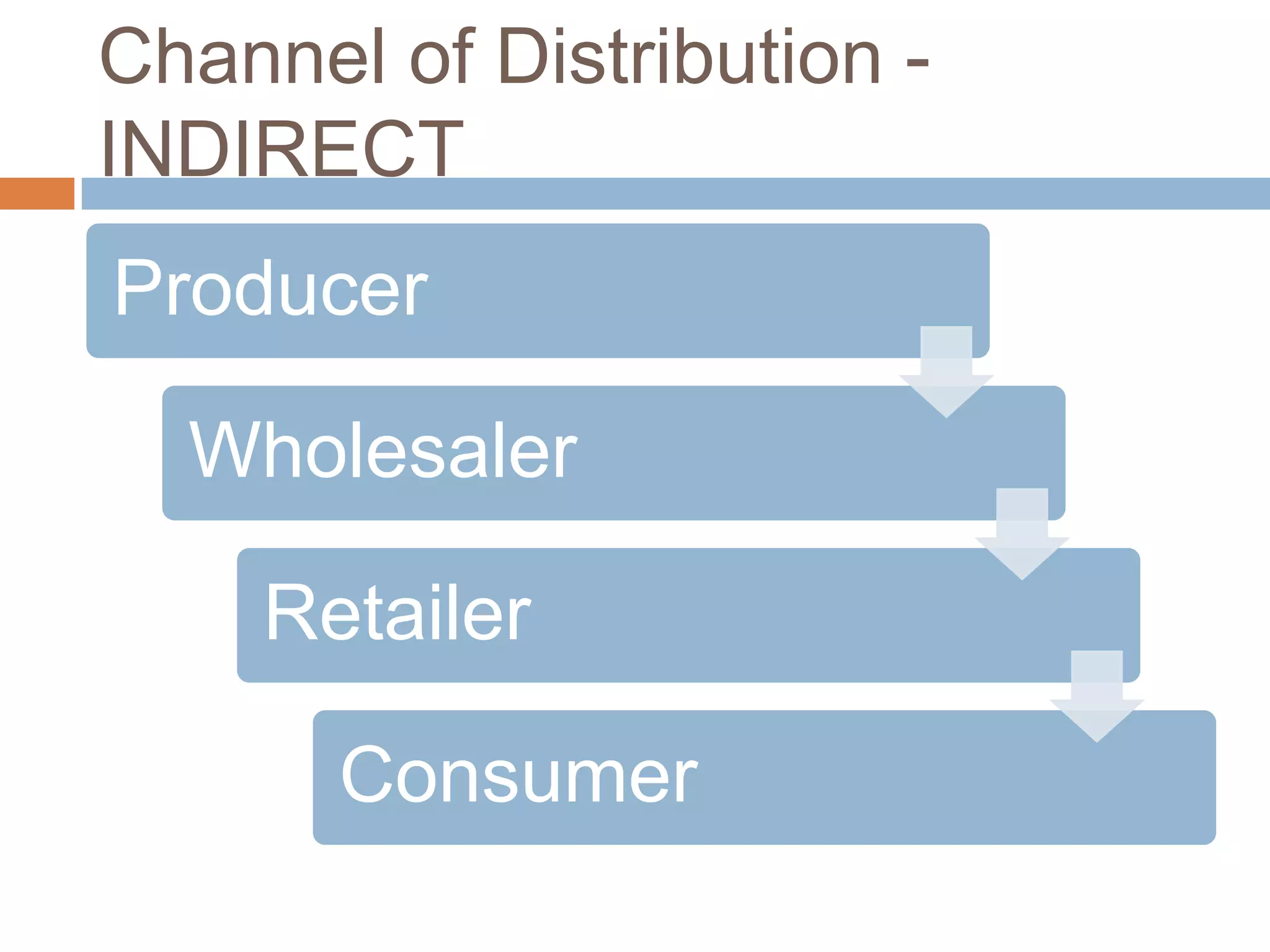
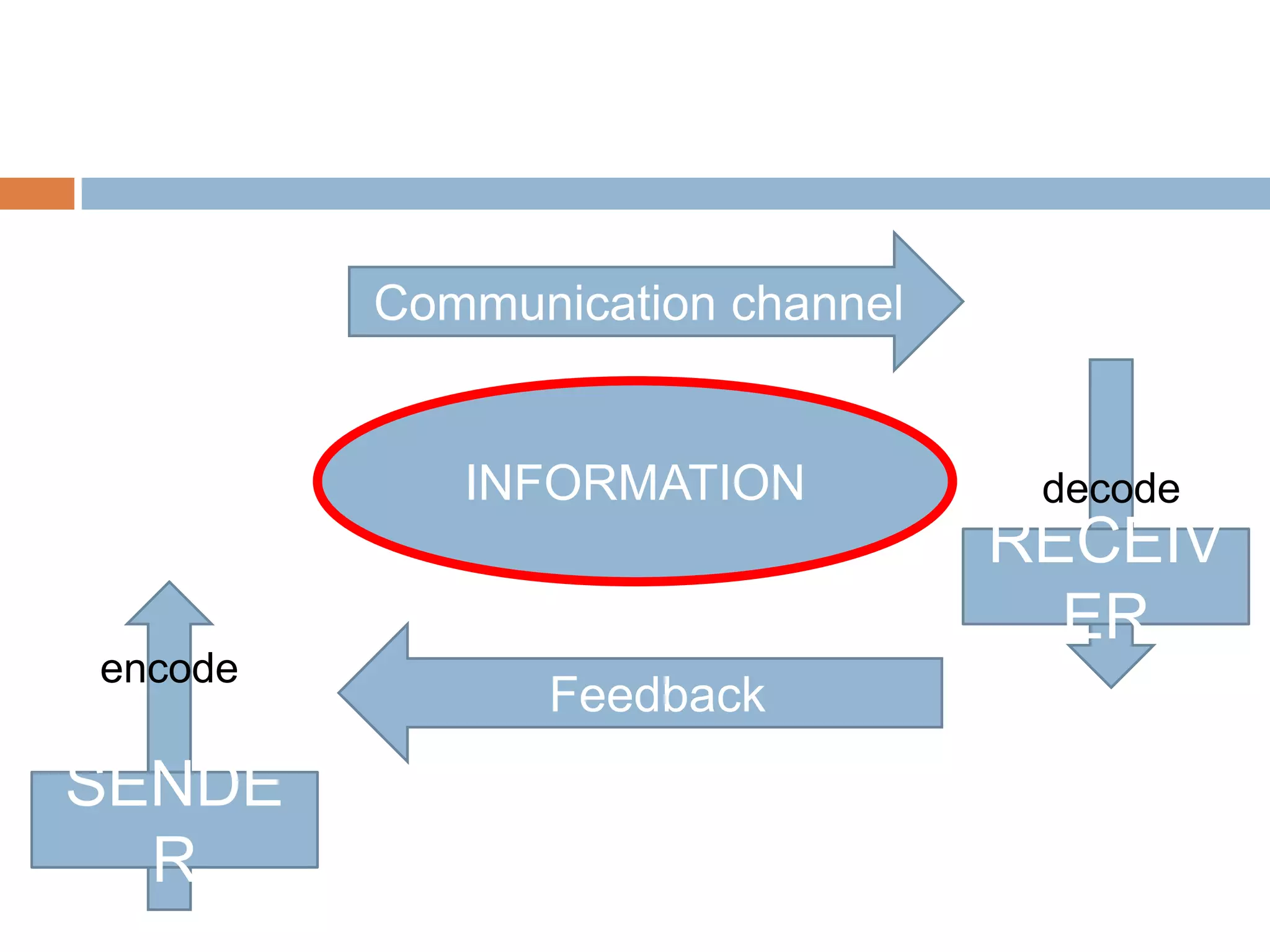
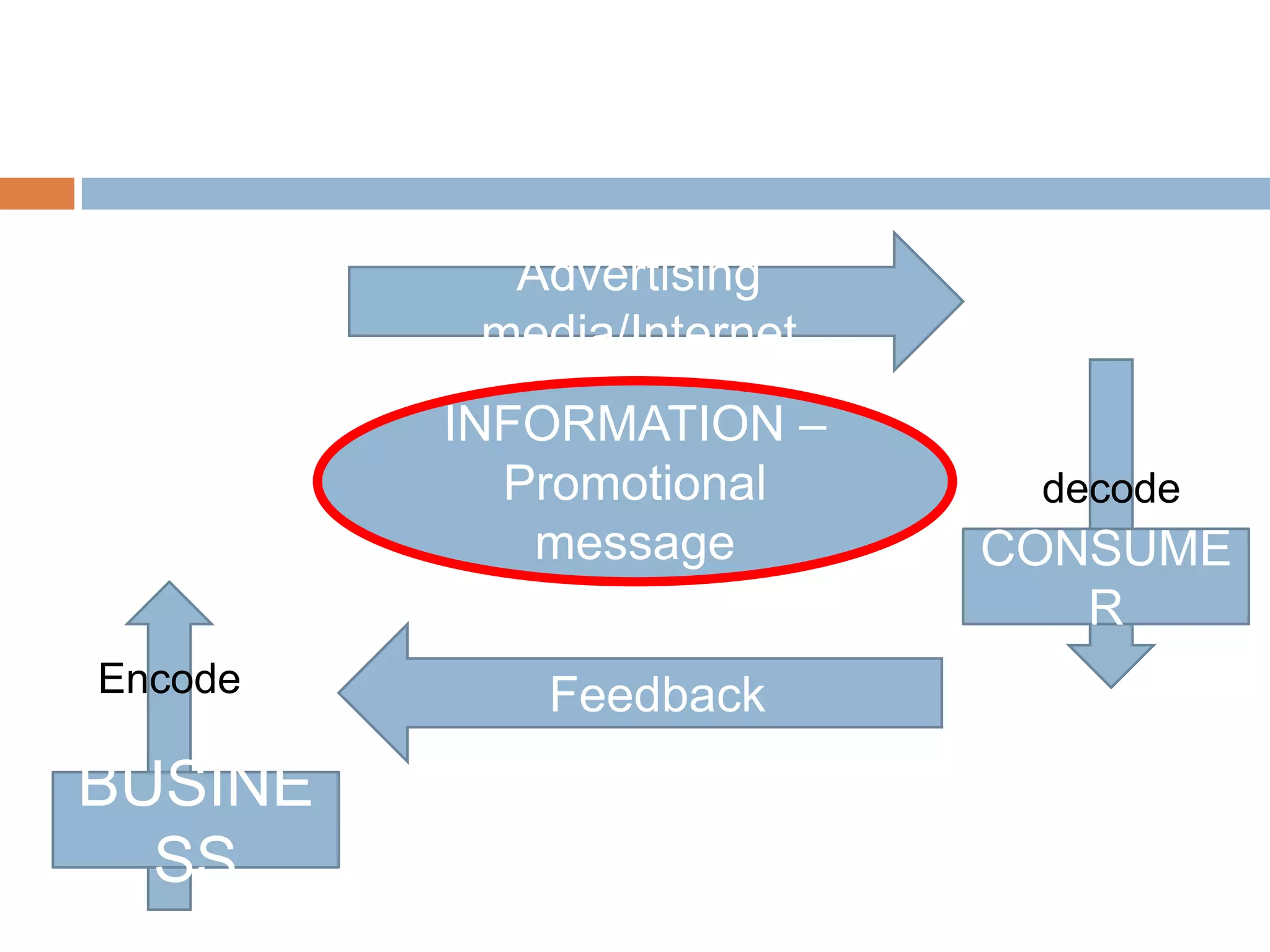
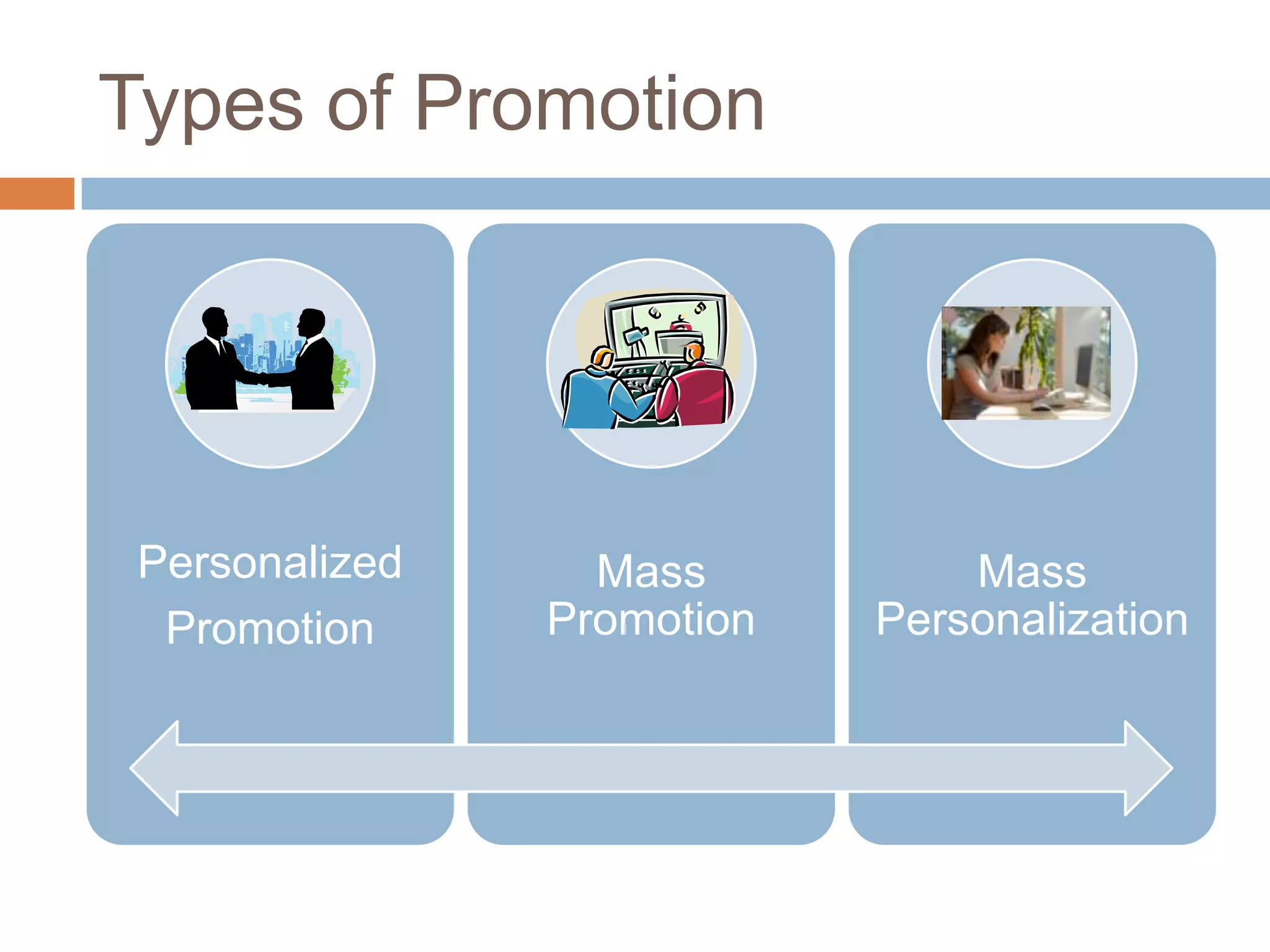
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to marketing research, product planning, pricing, distribution channels, and promotion. It discusses how businesses conduct marketing research to define problems and gather information to solve issues. It also outlines the typical parts of a product, different product planning procedures, and key characteristics of services. The document then explains various factors that influence pricing, how to calculate the price of a product, and different pricing strategies. It introduces distribution channels and reasons for using indirect or direct channels. Finally, it defines promotion and common promotional tools like advertising, and outlines the basic communication process.