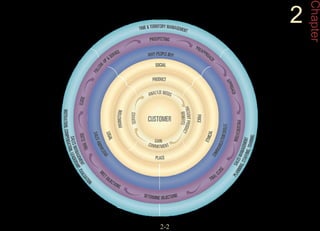
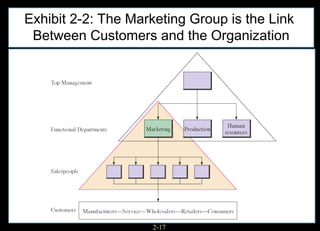
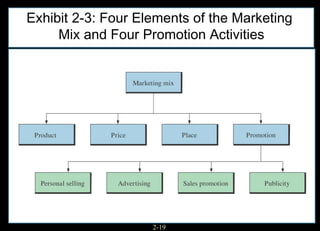
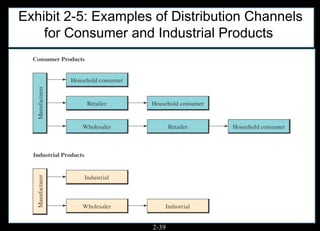
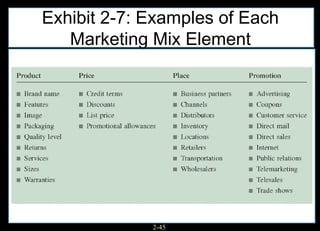
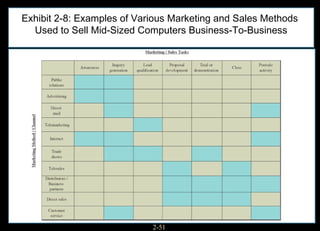
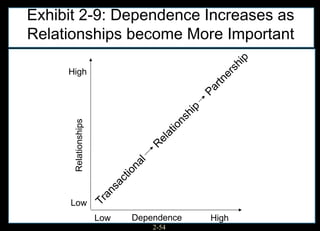
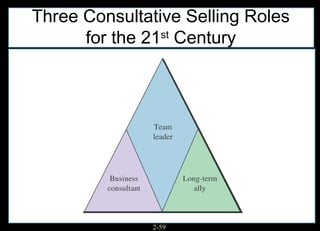
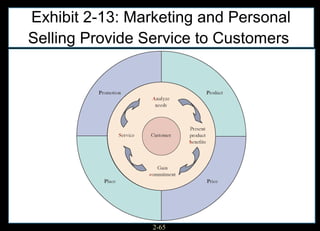
This chapter discusses relationship marketing and how personal selling fits within it. Relationship marketing aims to create customer loyalty through long-term collaborative relationships. The sales force plays a key role in implementing relationship marketing by building relationships with customers. There are three levels of relationship marketing: transactional selling, relationship selling, and partnering. Partnering involves both companies working together towards shared objectives. Consultative selling also builds strong customer relationships through helping clients achieve their strategic goals.