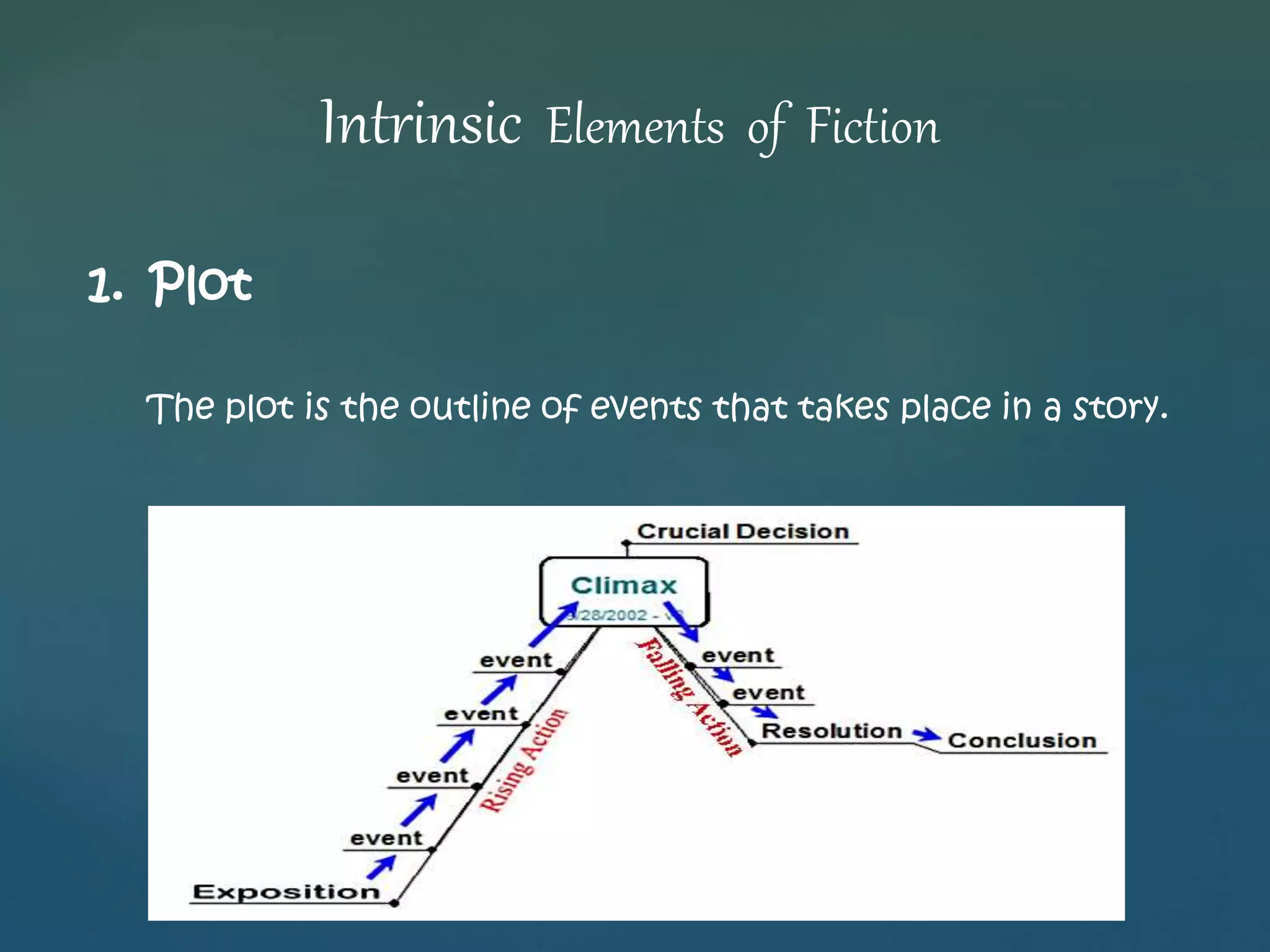
This document discusses the intrinsic elements of fiction, including plot, character, setting, theme, and point of view. It also describes different kinds of fiction such as short stories and novels. Finally, it explains that fiction theory involves questioning fundamental terms like text, narrative, and literature to understand how imaginary worlds in fiction relate to the real world.