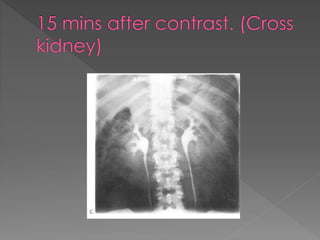
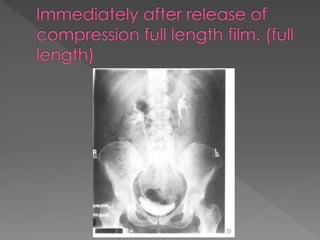
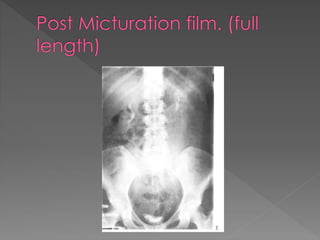
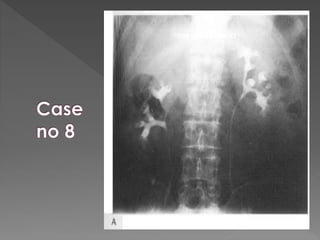
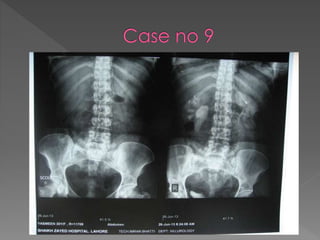
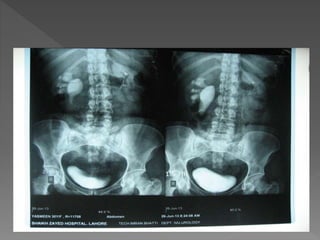
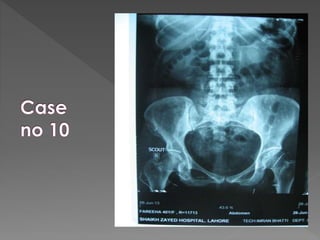
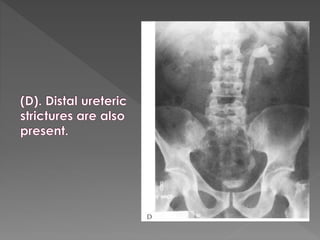
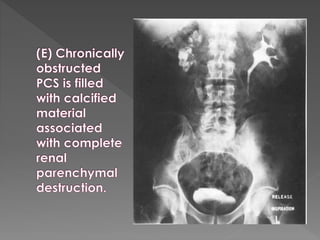
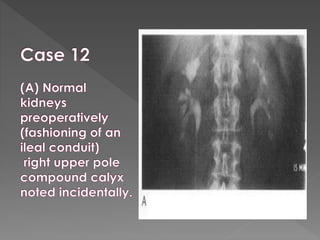
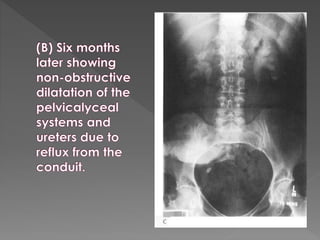
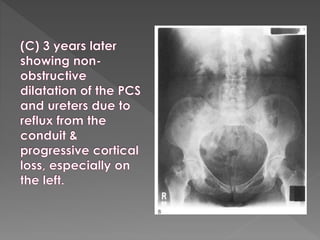
The document discusses the indications, technique, and findings of intravenous urography (IVU). It provides details on:
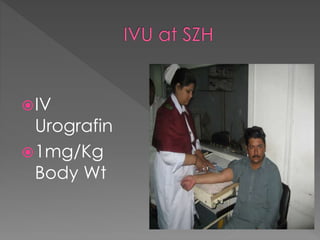
1) The traditional preparation of IVU including bowel preparation and fluid restriction to optimize contrast opacification of the urinary tract; however, recent recommendations state bowel preparation is unnecessary and fluid restriction should be avoided in high-risk patients.
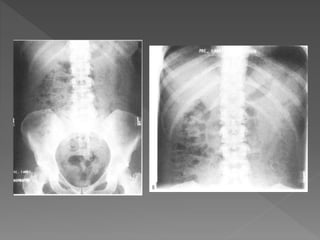
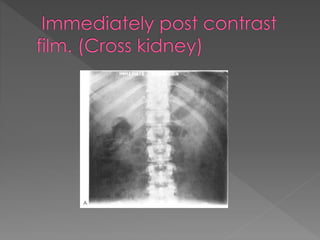
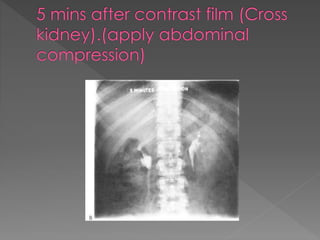
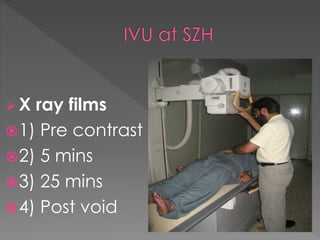
2) The standard technique involves a series of films before and after intravenous contrast administration, including compression of the abdomen to distend the collecting system, with modifications for different clinical situations.
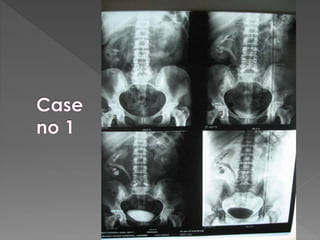
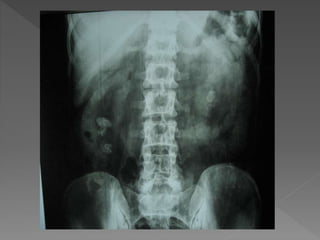
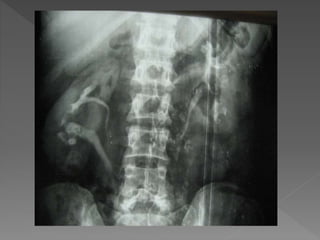
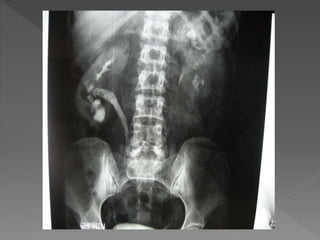
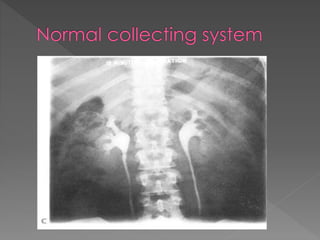
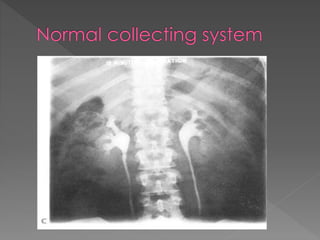
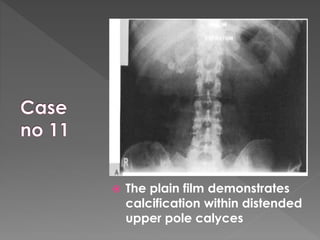
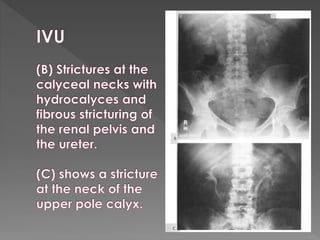
3) The expected timing of nephrogram, pyelogram, and other findings seen on IVU and their significance in evaluating the urinary tract anatomy and function.