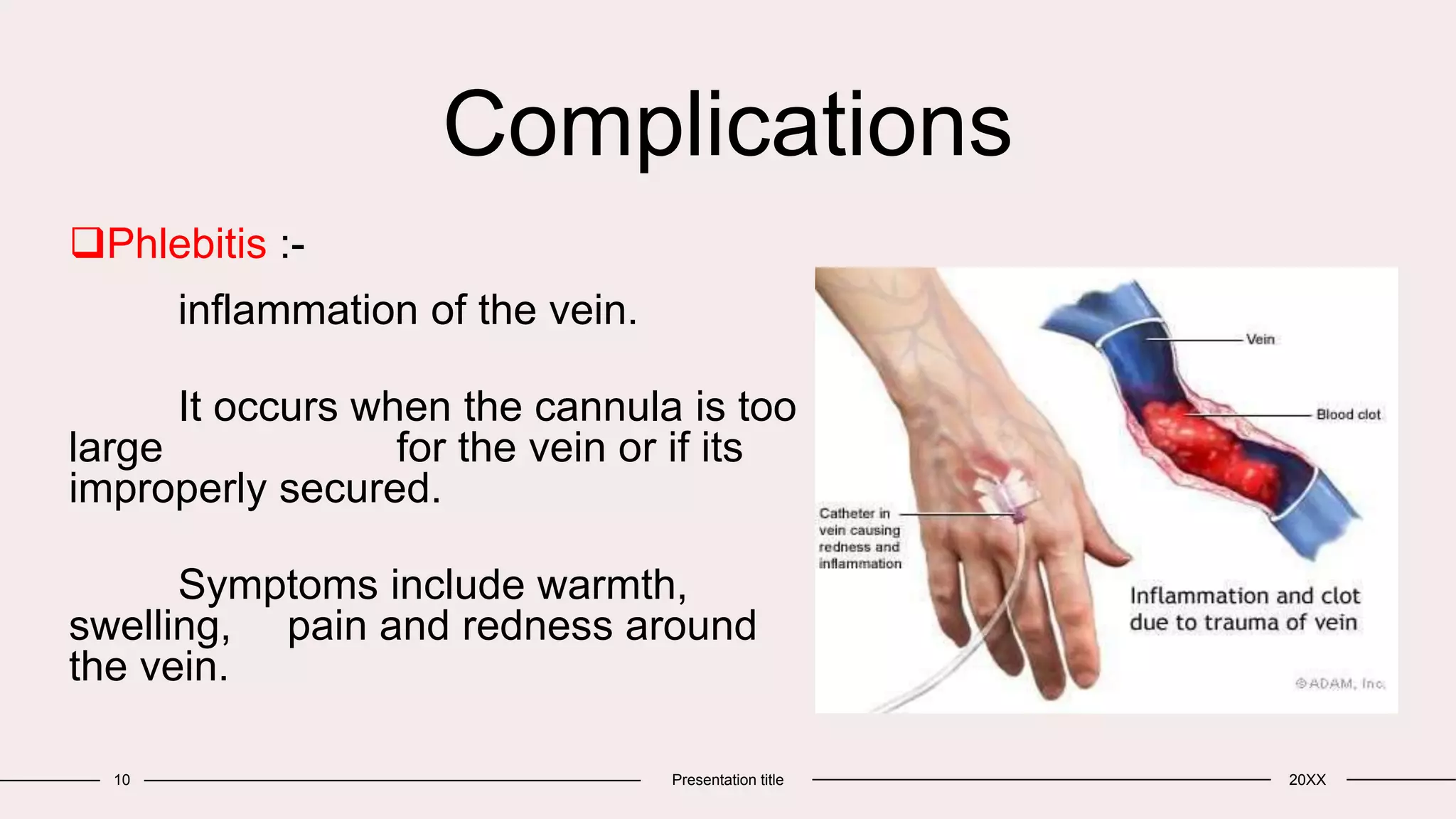
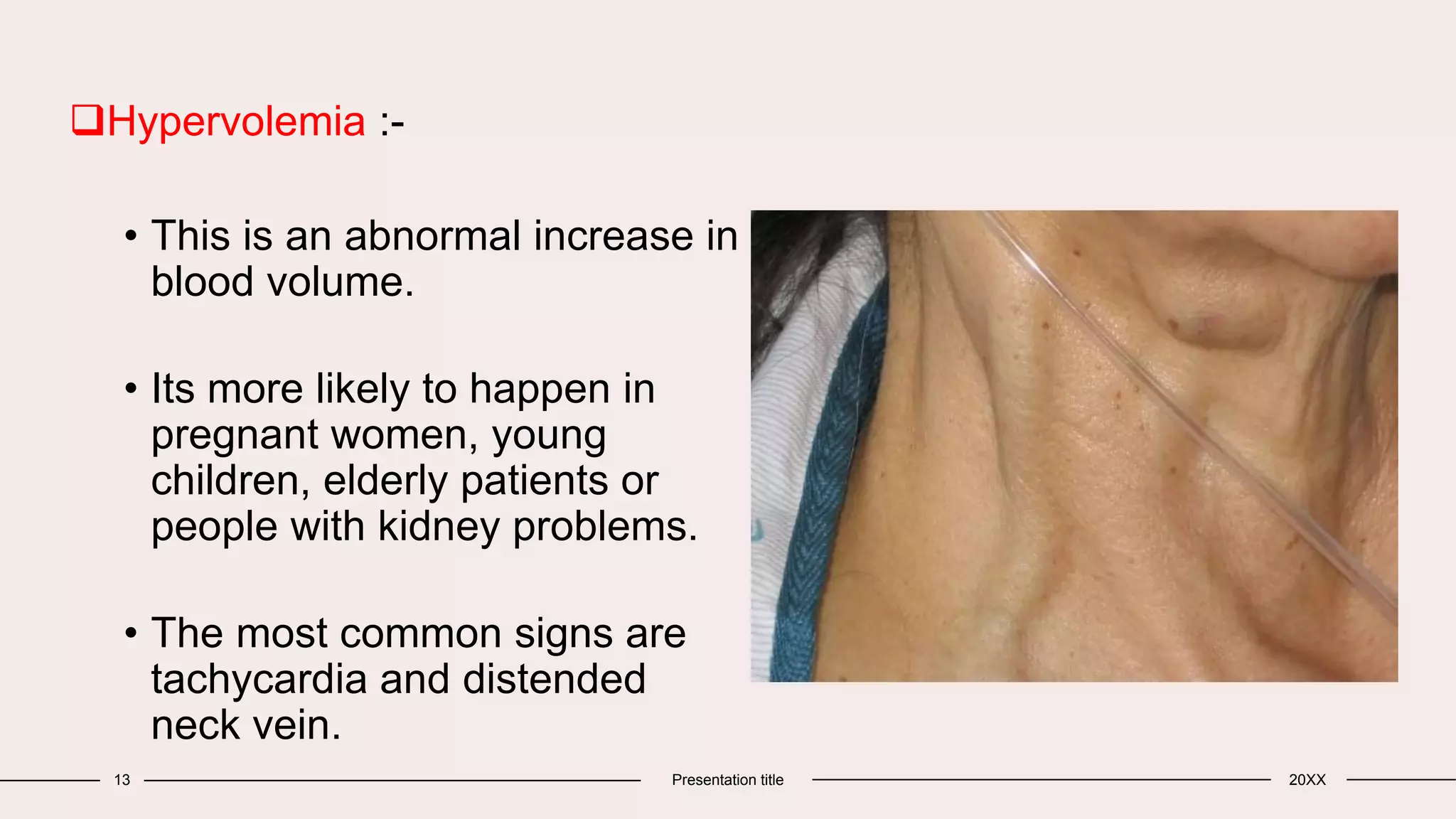
Intravenous therapy involves delivering liquid substances directly into a vein. It is the fastest way to administer medications and fluids throughout the body. IV therapy can be used for injections or infusions in both emergencies and for planned procedures like blood transfusions or anesthesia induction. Potential complications include phlebitis, extravasation, air embolism, and hypervolemia. Proper technique and site selection are important to minimize risks.