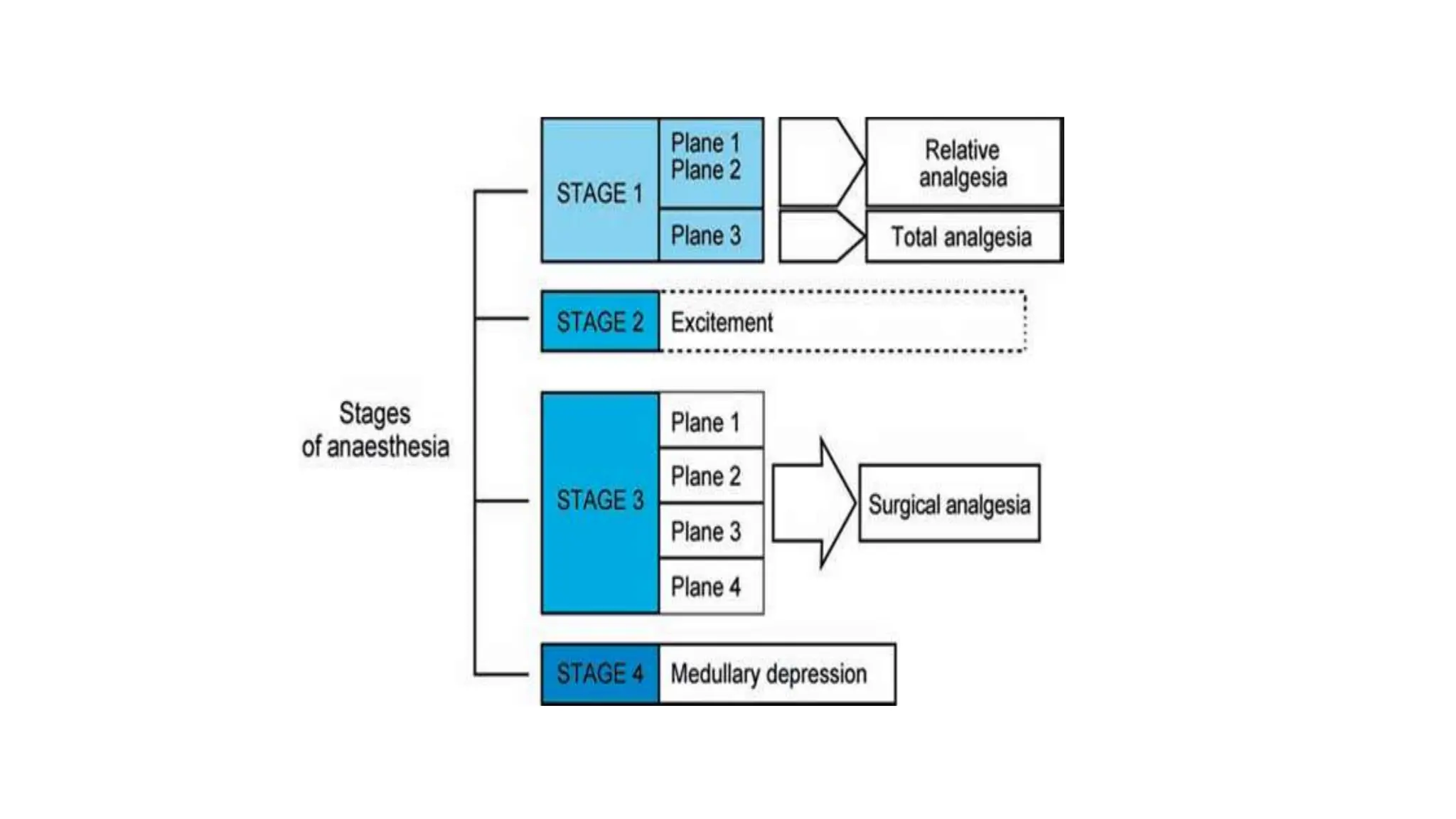
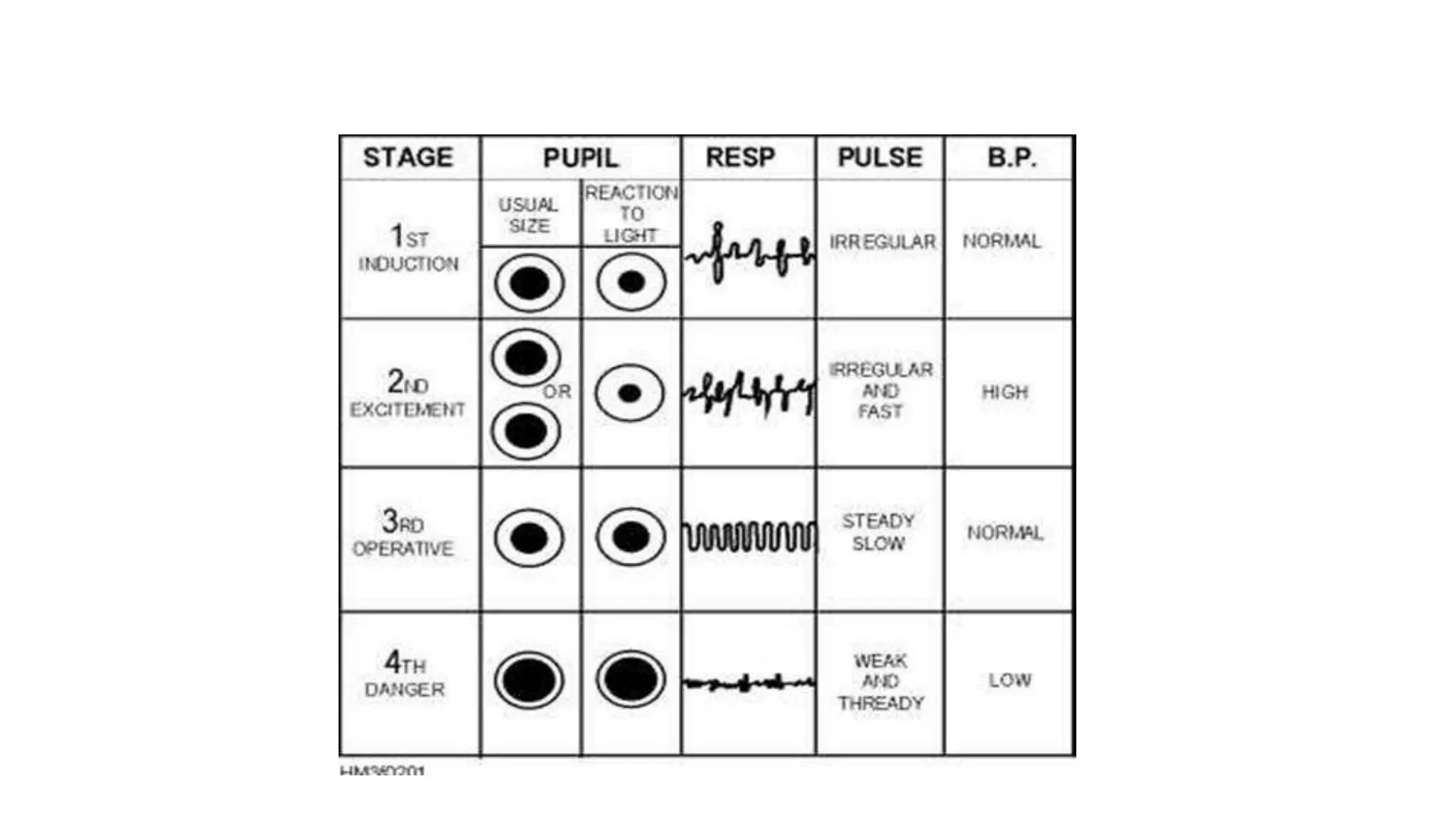
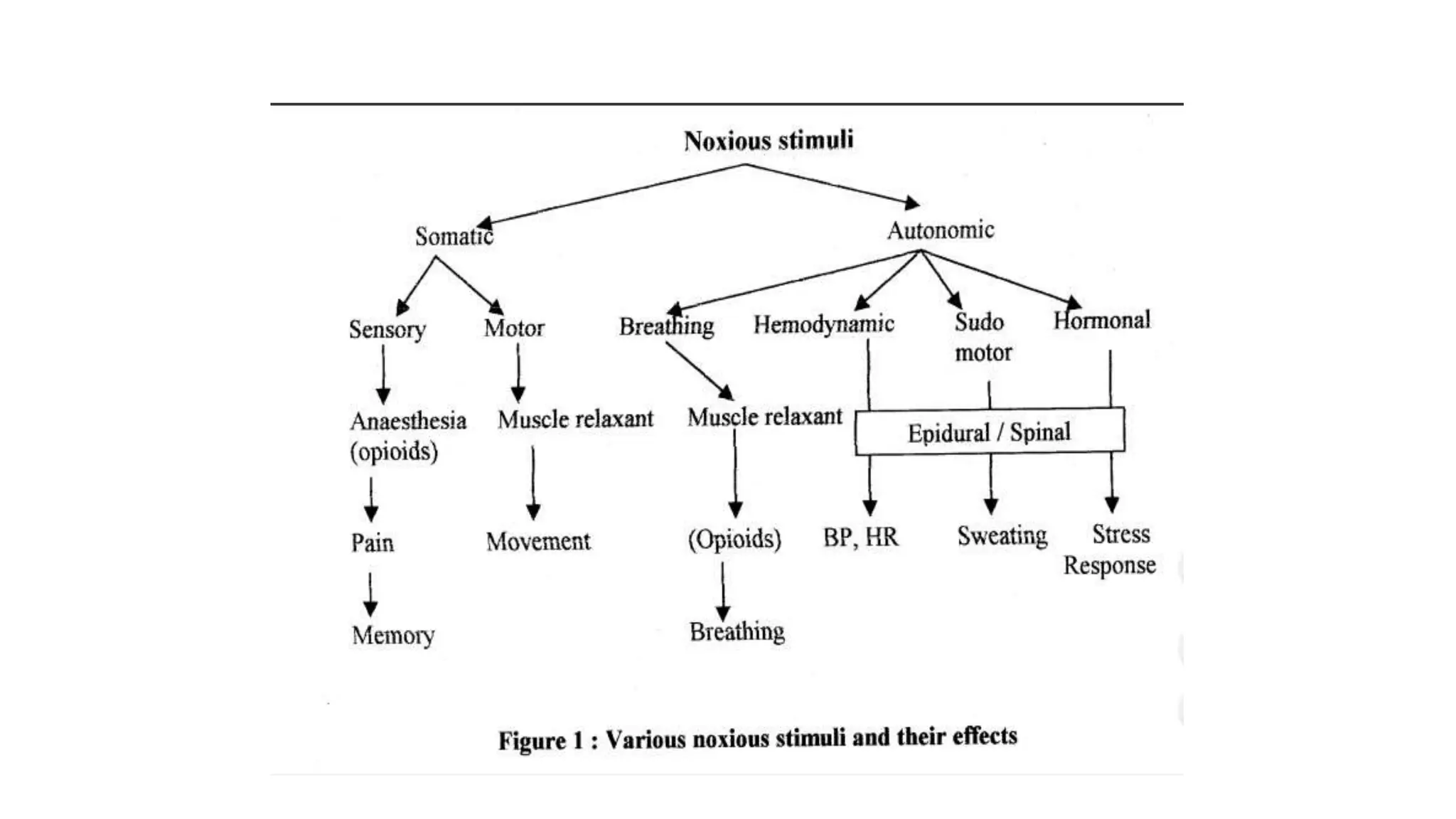
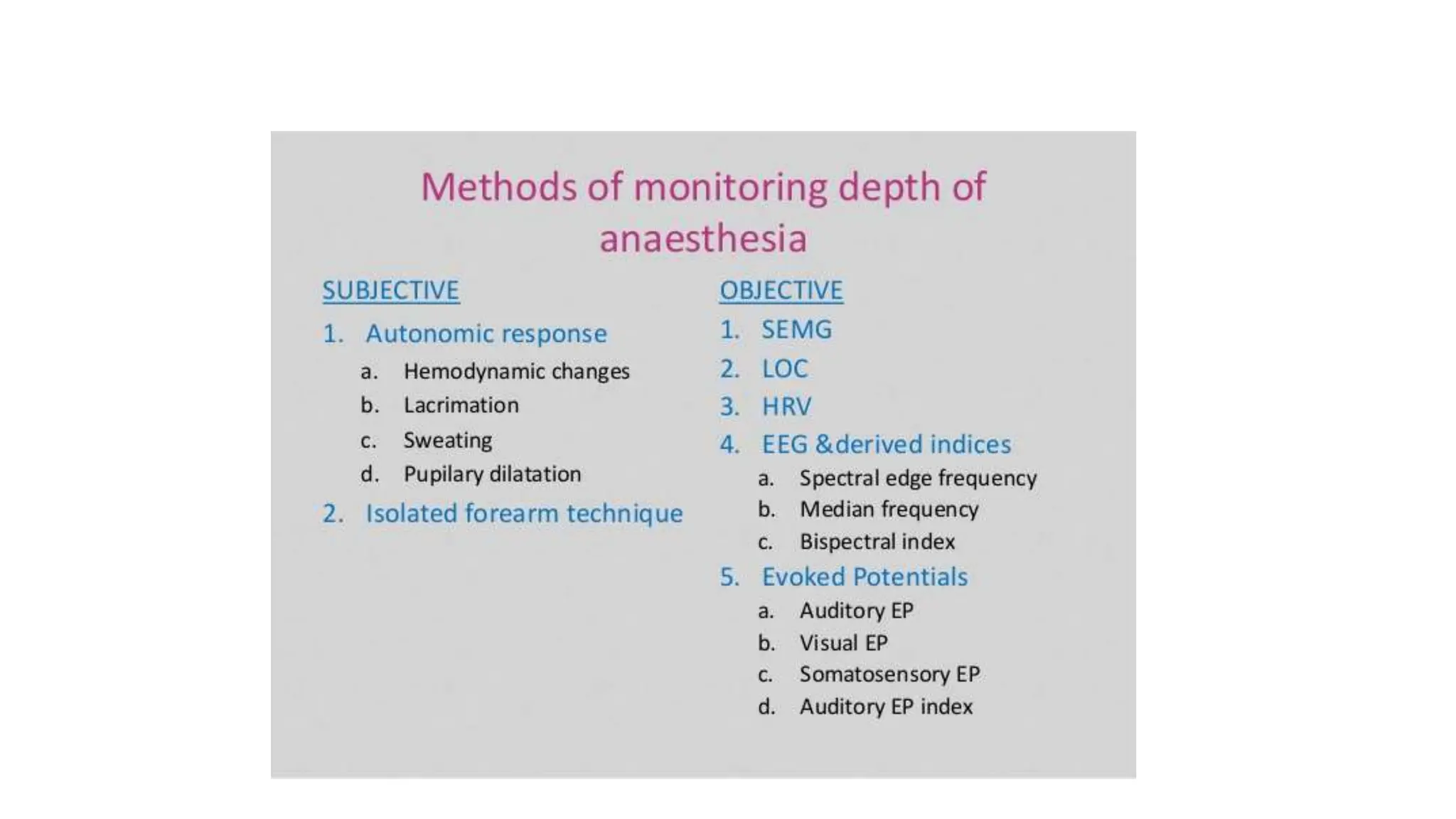
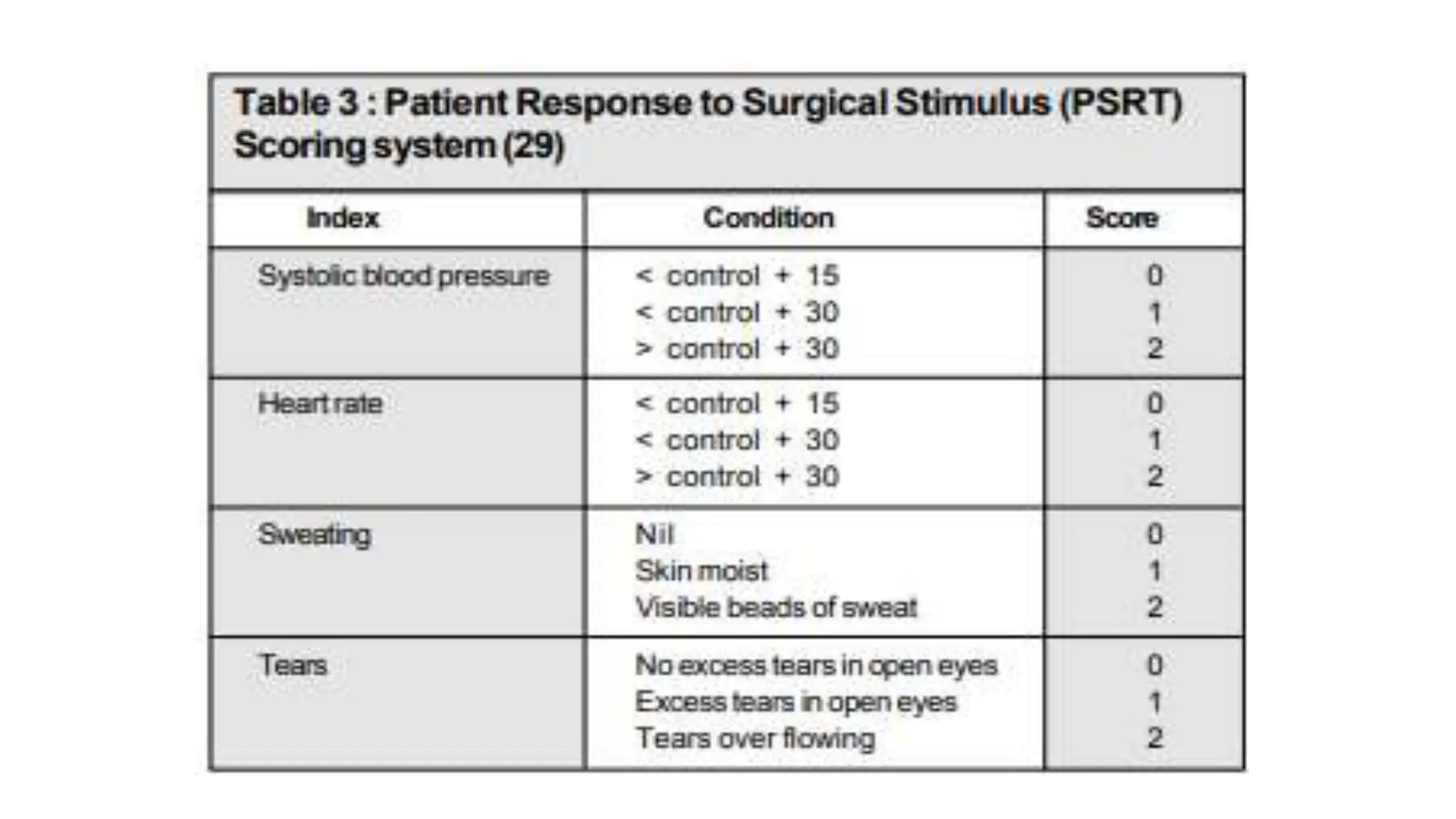
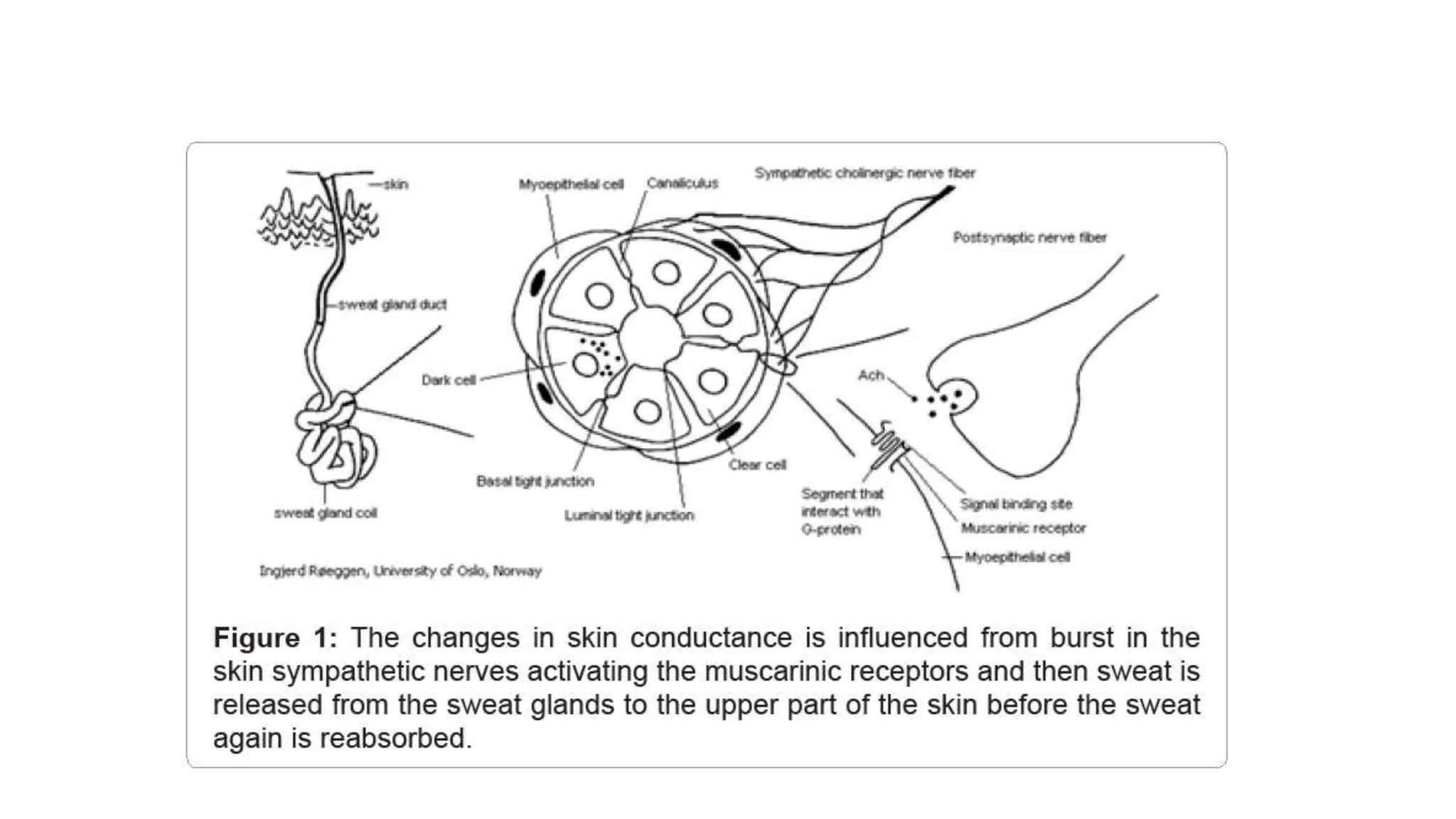
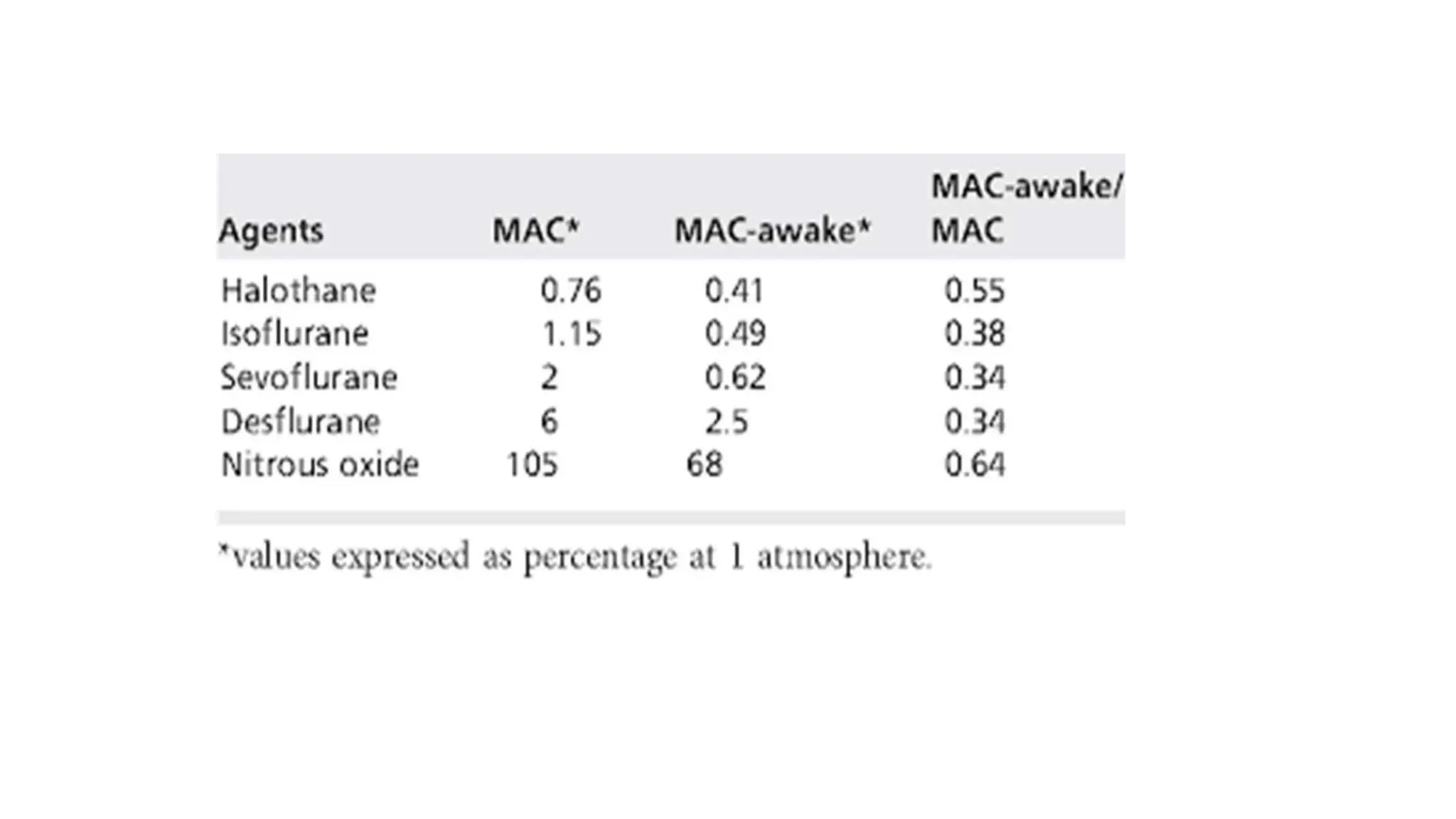
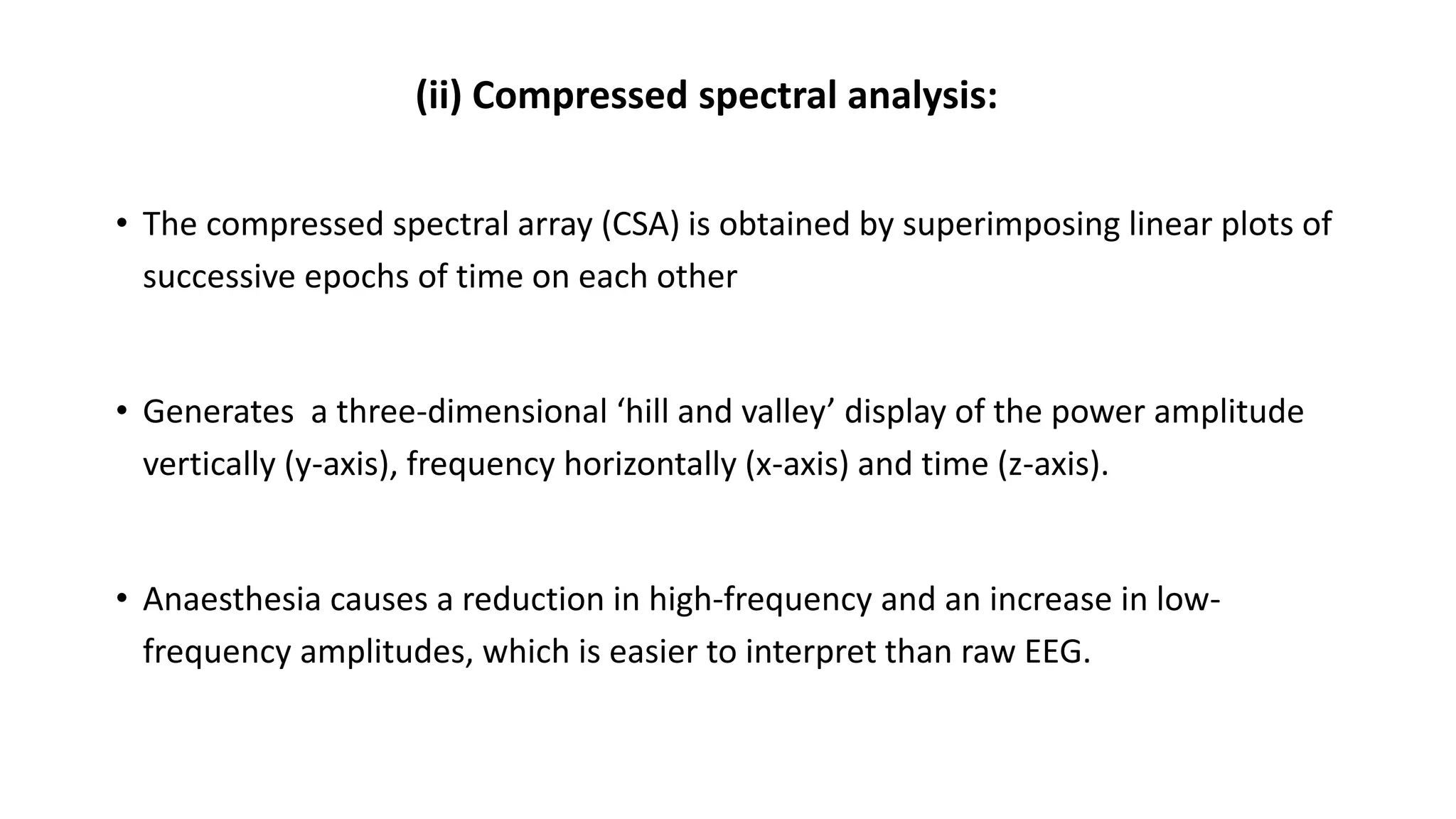
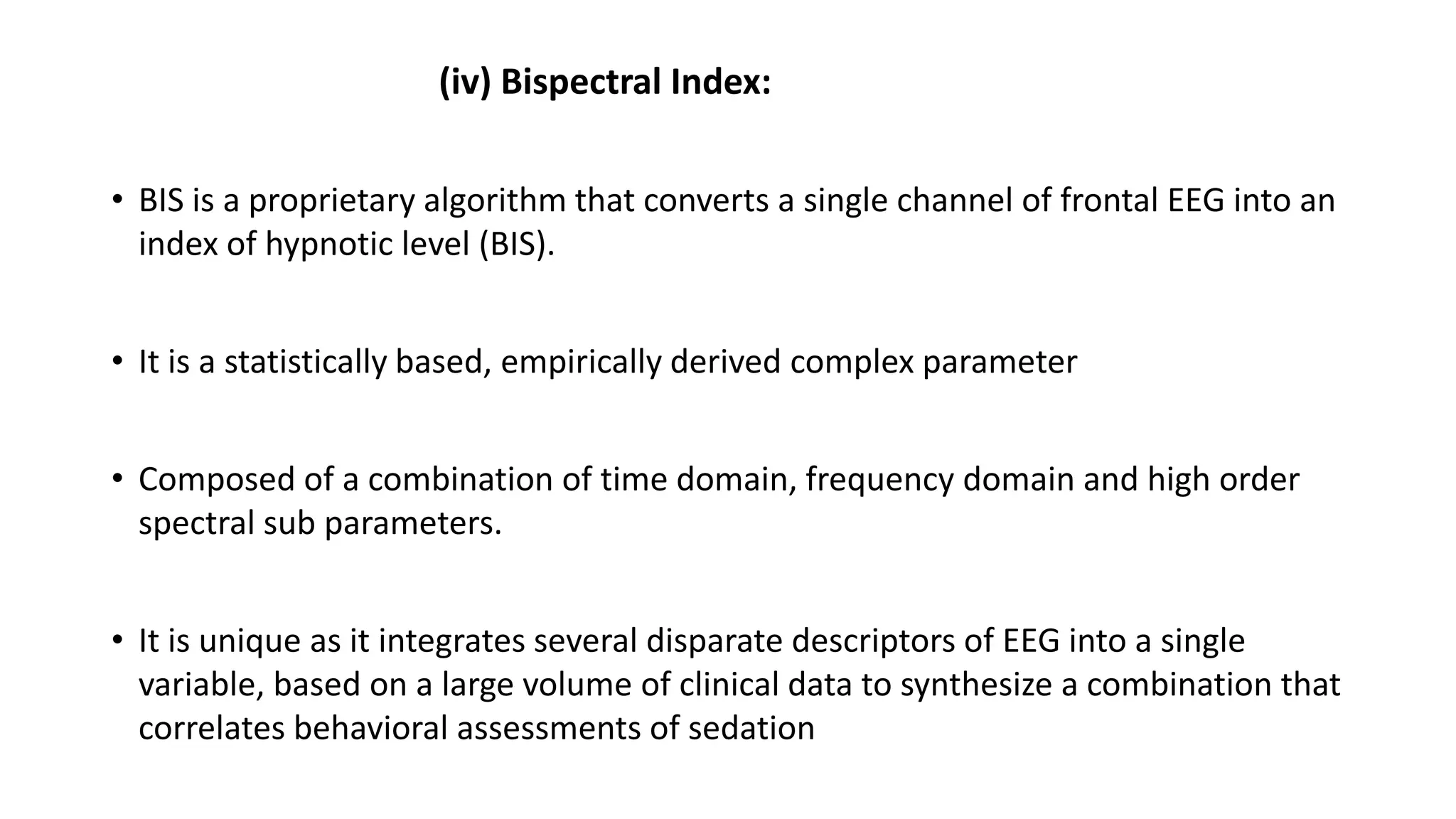
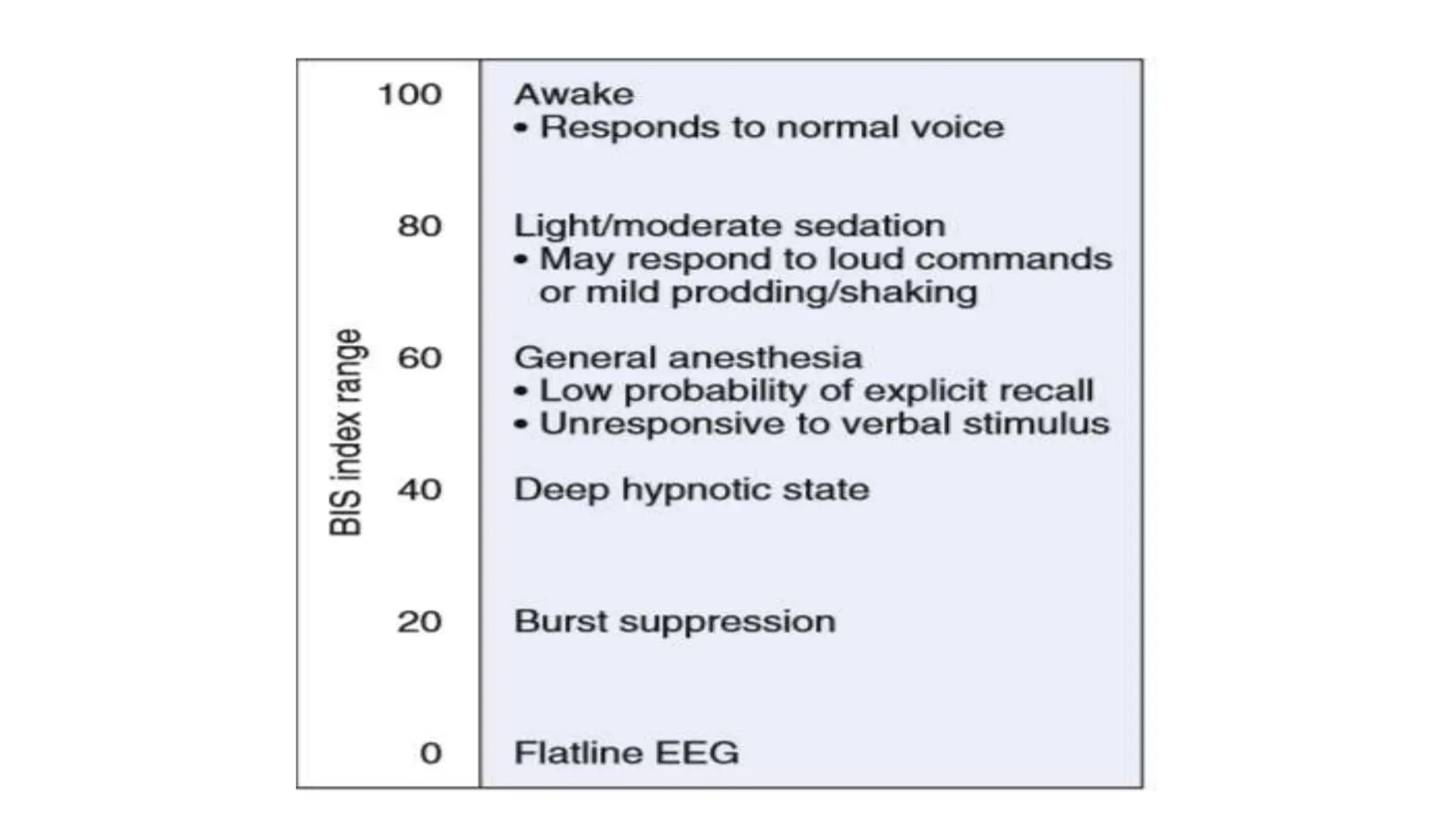
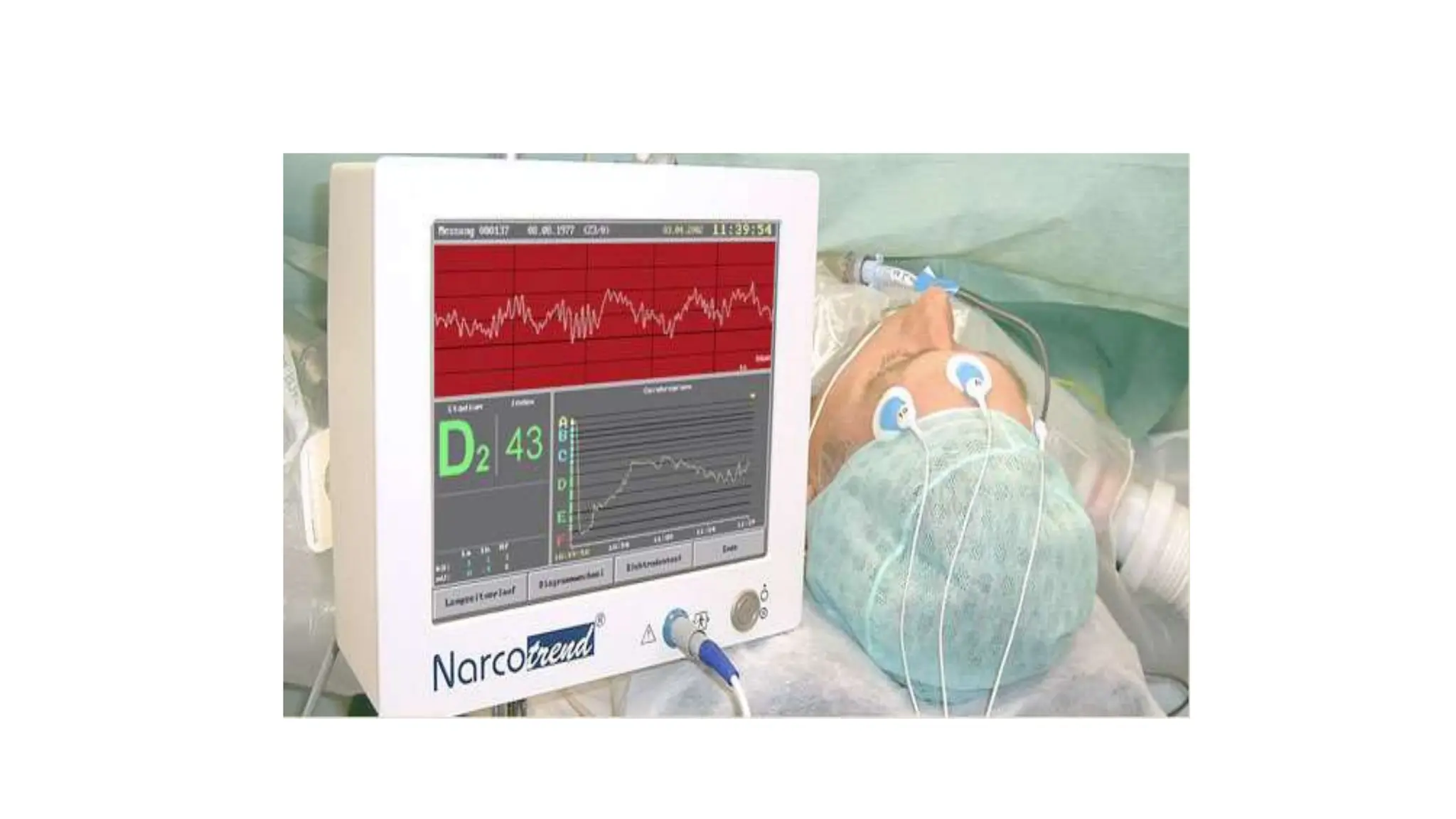
This document discusses various methods for monitoring the depth of anesthesia. It describes clinical techniques such as assessing autonomic responses and muscle movement. It also discusses pharmacological principles like minimum alveolar concentration for different anesthetic responses. Methods for monitoring brain electrical activity are outlined, including spontaneous EEG, compressed spectral analysis, bispectral index, and entropy monitors. Brain electrical activity monitors provide quantitative measures of anesthetic effect but can be influenced by other physiological factors. Overall depth of anesthesia monitoring aims to ensure patients do not experience awareness during surgery.