Cerebral aneurysms are abnormal bulges or sac-like outpouchings in the walls of arteries in the brain. When they rupture, they cause a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), which has devastating consequences - about 10-25% of people die within 24 hours and 40-65% die within 3 months of the SAH. Survivors often suffer permanent disabilities. Cerebral aneurysms are diagnosed using CT scans, MRI, angiography and other imaging tests and treatments involve surgical clipping or endovascular coiling to prevent further bleeding.


![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 3/29
eliminating any aneurysmal rests that may subsequently redevelop.
Endovascular treatment
Endovascular coiling of cerebral aneurysms has been found to yield a better clinical outcome than clipping does, with the benefit
greatest in patients with a good preoperative grade.[1, 2]
See Treatment and Medication for more detail.
Background
Cerebral aneurysms are pathologic focal dilatations of the cerebrovasculature that are prone to rupture. These vascular
abnormalities are classified by presumed pathogenesis. Saccular, berry, or congenital aneurysms constitute 90% of all cerebral
aneurysms and are located at the major branch points of large arteries. Dolichoectatic, fusiform, or arteriosclerotic aneurysms
are elongated outpouchings of proximal arteries that account for 7% of all cerebral aneurysms. Infectious or mycotic aneurysms
are situated peripherally and comprise 0.5% of all cerebral aneurysms. Other peripheral lesions include neoplastic aneurysms,
rare sequelae of embolized tumor fragments, and traumatic aneurysms. Traumatic injury also may result in dissecting
aneurysms in proximal vessels. Microaneurysms of small perforating vessels may result from hypertension.
Saccular aneurysms are situated in the anterior circulation in 85-95% of cases, whereas dolichoectatic aneurysms affect
predominantly the vertebrobasilar system. The location of saccular aneurysms at specific arterial segments varies in frequency
because of differences in reported study populations. Multiple saccular aneurysms are noted in 20-30% of patients with cerebral
aneurysms.
Saccular aneurysms frequently rupture into the subarachnoid space, accounting for 70-80% of spontaneous subarachnoid
hemorrhages (SAH). Aneurysmal rupture also may result in intraparenchymal, intraventricular, or subdural hemorrhage. Giant
saccular aneurysms, defined as greater than 25 mm in diameter, represent 3-5% of all intracranial aneurysms. Although giant
aneurysms may cause SAH, these lesions frequently produce mass effects and result in distal thromboembolism.
Aneurysmal SAH is a catastrophic condition, affecting 30,000 individuals in the United States every year. Most of these
individuals (60%) either die or suffer permanent disability; 50% of survivors with favorable outcomes experience considerable
neuropsychological dysfunction. Cerebral vasospasm (ie, narrowing of proximal arterial segments) complicates 20-50% of cases
and is the major cause of death and disability associated with aneurysmal SAH.
Pathophysiology
The pathogenesis of cerebral aneurysms is related inherently to structural aberrations of the cerebrovasculature, although the
etiology of these abnormalities may be diverse. The integrity of the internal elastic lamina is compromised, with associated
elastic defects in the adjacent layers of the tunica media and adventitia. Muscular defects of the tunica media and minimal
support of adjacent brain parenchyma augment the pathologic potential of chronic hemodynamic stress on the arterial wall.
Focal turbulence and discontinuity of the normal architecture at vessel bifurcations may account for the propensity of saccular
aneurysm formation at these locations. Distal aneurysms may be smaller compared with proximal sites, yet the risk of rupture
may be dissimilar due to the relatively thinner parent artery wall thickness.
The development of cerebral aneurysms remains a controversial topic. A multifactorial etiology is most likely, reflecting the
interaction of environmental factors, such as atherosclerosis or hypertension, and a congenital predisposition associated with
various vascular abnormalities. Abnormalities of the internal elastic lamina may be congenital or degenerative. Multiple
conditions have been associated with cerebral aneurysms; they include the following:
Autosomal dominant inherited polycystic kidney disease
Fibromuscular dysplasia
Arteriovenous malformations
Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome
Coarctation of the aorta
Other vascular anomalies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-3-320.jpg)

![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 5/29
the incidence of ruptured aneurysms is approximately 12 per 100,000 individuals or 30,000 annual cases of aneurysmal SAH.
The frequency of cerebral aneurysms has not declined in recent years.
International
Incidence of aneurysmal SAH varies widely depending on geographic location, ranging from 3.9-19.4 per 100,000 individuals,
with the highest reported rates in Finland and Japan. Overall, the incidence has been estimated at 10.5 per 100,000 individuals.
Mortality/Morbidity
Aneurysmal SAH has devastating consequences. About 10% of individuals with aneurysmal SAH die before reaching medical
attention, 25% die within 24 hours, and 40-49% die within 3 months. Mortality rate has been estimated to be as high as 65%,
with most deaths occurring early in the clinical course.
Early surgical treatment is associated with higher operative morbidity and mortality rates; however, overall morbidity and
mortality rates are lower in patients who undergo surgery. Intraoperative aneurysmal rupture has a combined morbidity and
mortality rate of 30-35%.
Aneurysmal SAH during pregnancy has a mortality rate of 35%, accounting for one of the leading causes of maternal mortality
during pregnancy.
In one study of 102 pediatric patients with cerebral aneurysm followed for a mean of 26.8 years, researchers found long-term
excess mortality after successful treatment of ruptured aneurysms, especially among males; this excess mortality was largely
aneurysm-related.[3]
Race
The racial predilection of cerebral aneurysms is largely unknown, although a higher incidence has been noted in African
Americans, with an odds ratio of 2:1.
Sex
Cerebral aneurysms affect equal numbers of women and men younger than 40 years, although women are affected more
frequently in older age groups. Overall, the female-to-male ratio has been estimated at 1.6:1.
Saccular aneurysms are most common in the anterior communicating artery (ACoA) or anterior cerebral artery (ACA) in
men, whereas the junction of the ICA with the posterior communicating artery (PCoA) is the most common site for
saccular aneurysms in women.
Giant aneurysms are 3 times more common in women than men.
The prognosis of aneurysmal SAH is worse for women than men.
Age
See the list below:
Cerebral aneurysms are rarely apparent in infants and children. Clinical manifestations increase with age, reaching a
peak in people aged 55-60 years.
Carotid artery is affected most commonly in individuals younger than 18 years.
The prognosis of aneurysmal SAH worsens with increasing age.
Presentation
History](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-5-320.jpg)
![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 6/29
The clinical presentation of cerebral aneurysms includes symptoms associated with major aneurysmal rupture (eg, SAH), minor
aneurysmal hemorrhage (eg, warning leak or sentinel bleed), nonhemorrhagic manifestations (eg, mass effects or cerebral
ischemia), and asymptomatic scenarios (eg, incidental aneurysm detection or identification through screening[4] ).
Although aneurysmal SAH has characteristic historical features, the constellation of symptoms may vary with location, size,
shape, and direction of the aneurysm.
Aneurysmal rupture also may present with intraparenchymal hemorrhage (more common with distal aneurysms), intraventricular
hemorrhage (13-28%), or subdural hematoma (2-5%).
Minor aneurysmal hemorrhage may precede rupture with a wide variation in latency, although these warning leaks also may be
clinically silent.
Giant aneurysms may compress brain parenchyma, resulting in focal neurological complaints.
Aneurysmal expansion may produce pain or herald new neurological manifestations.
Traumatic aneurysms may have a delayed presentation, with intracranial hemorrhage or recurrent epistaxis.
Symptoms associated with cerebral aneurysms and SAH are as follows:
Headache: This is characterized by the acute onset of severe pain, which patients often describe as "the worst headache
of my life." Aneurysmal expansion, thrombosis, or intramural hemorrhage may cause a subacute, unilateral, periorbital
headache. Headache does not always accompany aneurysmal SAH.
Facial pain: Cavernous-carotid aneurysms may produce facial pain.
Alterations in consciousness: The sudden elevation of intracranial pressure associated with aneurysmal rupture may lead
to a precipitous decline in cerebral perfusion pressure, causing syncope (50% of cases). Confusion or mild impairment in
alertness also may be noted.
Seizures: Focal or generalized seizures are present in 25% of aneurysmal SAH cases, with most events occurring within
24 hours of onset.
Manifestations of meningeal irritation: Neck pain or stiffness, photophobia, sonophobia, or other hyperesthesia may be
noted with SAH.
Autonomic disturbances: Subarachnoid accumulation of products of blood degradation may elicit fever. Nausea or
vomiting, sweating, chills, and cardiac arrhythmias also may be present.
Focal neurological complaints: Hemorrhage or ischemia may manifest with focal deficits including weakness,
hemisensory loss, language disturbances, neglect, memory loss, or olfactory disturbances. Focal symptoms are more
common with giant aneurysms.
Visual symptoms: Blurring of vision, diplopia, or visual field defects may be present.
Respiratory dysfunction or cardiovascular instability: These are ominous signs of brainstem compression.
Hormonal dysfunction: Intrasellar aneurysms may interfere with pituitary function.
Epistaxis: This is noted occasionally with traumatic aneurysms.
Physical
The general examination occasionally reveals manifestations of associated conditions such as subacute bacterial endocarditis,
trauma, or collagen-vascular disease.
Specific physical examination findings may include prominent scalp veins, signs of congestive heart failure (eg, vein of Galen
aneurysms), or orbital bruits (eg, cavernous carotid aneurysms).
Neurologic findings exhibit considerable variability, depending on aneurysm characteristics.
Aneurysmal SAH may be accompanied by nuchal rigidity, decreased level of consciousness, subhyaloid hemorrhages,
pupillary abnormalities (ie, typically dilated), ophthalmoplegia, cranial neuropathies, and other focal deficits.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-6-320.jpg)

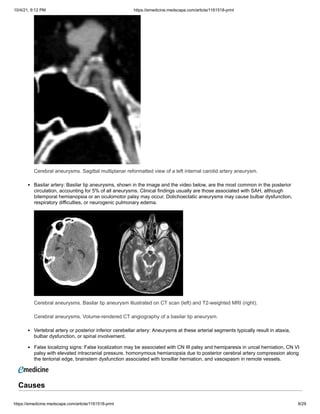
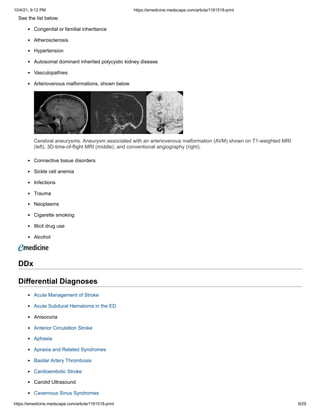
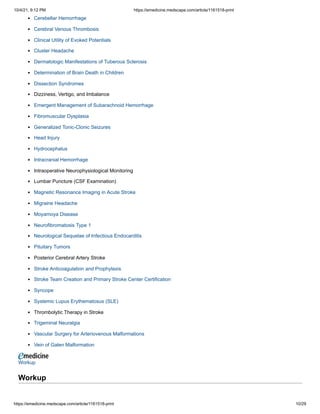
![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 11/29
Laboratory Studies
Lab studies that may be helpful for diagnosis include the following:
CBC with platelets: Monitor for infection, evaluate anemia, and identify bleeding risk.
Prothrombin time (PT)/activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT): Identify a coagulopathy that increases bleeding risk.
Serum chemistries, including electrolytes and osmolarity: Obtain baseline studies to monitor hyponatremia, address
arrhythmogenic abnormalities, assess blood glucose, and monitor hyperosmolar therapy for elevated intracranial
pressure.
Liver function tests: Identify hepatic dysfunction that may complicate clinical course.
Arterial blood gases: Assess blood oxygenation.
Imaging Studies
Advances in neuroimaging techniques have altered the diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms dramatically. Noninvasive angiographic
methods, such as computed tomographic angiography (CTA) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), allow for detection
and characterization of aneurysms, further enhanced by postprocessing techniques that enable 3-dimensional evaluation of
aneurysm morphology. Contemporaneous parenchymal imaging with CT scan or MRI yields a wealth of information that may
assist surgical planning. However, minor aneurysmal hemorrhage may not be detected with noninvasive methods.
A study of 20 years of screening results of individuals with a positive family history of SAH found that the yield of long-term
screening is substantial even after more than 10 years of follow-up and two initial negative screens. These data suggest that
repeated screening should be considered in individuals with 2 or more first-degree relatives who had SAH or unruptured
intracranial aneurysms.[5, 6]
CT scan
Aneurysmal SAH may be detected in 90-95% of cases. If CT scan result is negative and SAH is suspected, perform lumbar
puncture (LP).
Noncontrast CT scan should be performed, as contrast may obscure detection of SAH.
Curvilinear calcification, aneurysmal thrombosis, or bone erosion may be characterized; however, bone structures also may
produce artifacts.
Surrounding edema and an inflammatory reaction may be appreciated with contrast administration following the noncontrast
study.
CTA may detect aneurysms greater than 3 mm, providing detailed evaluation of morphology such as relationship to the parent
vessel and neck width.
CTA can detect more than 95% of aneurysms identified on conventional angiography. CTA may be superior to MRA because of
shorter acquisition times, diminished motion artifacts, and detailed demonstration of other landmarks. However, bone and
venous structures may complicate analysis.
Increasing use of CT perfusion in combination with CTA allows for reconstruction of multiphase CT angiographic images,
potentially providing greater definition beyond standard CTA.[7]
MRI
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences are very sensitive for SAH, although the comparison of CT scan and
MRI in detection of SAH is controversial.
MRI may be impractical for patients in unstable condition. Flow voids may be seen extending from the parent vessel into the
aneurysm.
Heterogeneous signal intensity adjacent to the aneurysm wall may be seen with thrombus of varying ages, although MRI is
relatively insensitive to the presence of calcium.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-11-320.jpg)
![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 12/29
Dolichoectatic and giant aneurysms are identified readily with MRI. Pulsation artifacts and the presence of turbulence may help
to differentiate these aneurysms from other mass lesions, but slow and turbulent flow may preclude visualization on MRA.
MRA may reliably provide 3-dimensional imaging of aneurysms 4 mm or larger.
Phase-contrast techniques may facilitate detection of flow patterns and slow flow. Although phase-contrast MRA is preferable for
large aneurysms, 3-dimensional time-of-flight techniques are preferable for small aneurysms. Source images should be
inspected routinely in conjunction with the reconstructed views.
Angiography
Conventional angiography is the definitive procedure for the detection and characterization of cerebral aneurysms. Aneurysm
location, size, and morphology may be evaluated in the acute or chronic setting with this modality.
Digital subtraction angiography with biplanar magnification views provides details that may be helpful in identifying an acutely
ruptured aneurysm.
Aneurysmal irregularity, the presence of a daughter loculus, or focal spasm may be noted with acute rupture. Vasospasm may
be depicted reliably and the collateral circulation may be demonstrated.
Perform 4-vessel angiography to identify remote vasospasm and the presence of multiple aneurysms. Acute angiography
occasionally yields negative results (eg, due to thrombosis or vasospasm), in which case angiography should be repeated 1-3
weeks later. However, the risk and expense of this procedure may not be appropriate for screening of high-risk individuals.
A junctional dilatation of the terminal carotid artery at the origin of the PCoA may be noted in about 5-10% of patients. These
infundibula or conical enlargements of less than 3 mm are unlikely to enlarge or rupture. However, overt aneurysms at the
juncture of the terminal carotid artery with a persistent PCoA configuration may be more prone to rupture.
Further refinements in the characterization of cerebral aneurysms are expected following the recent introduction of 3-
dimensional rotational angiography. Recent work has demonstrated that this technique may offer superior resolution and
increased sensitivity for detection of small aneurysms.[8]
Other imaging studies
Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography: TCD facilitates the diagnosis of vasospasm and serial monitoring of cerebral blood flow
at the bedside. TCD has exhibited close correlation with angiography in the setting of vasospasm, typically manifesting 3-21
days following aneurysmal SAH.
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), xenon-CT (XeCT): With these
techniques, cerebral blood flow studies may depict ischemia associated with vasospasm, although these modalities are not
employed routinely.
Cervical spine imaging: Radiographic assessment of the cervical spine should be performed in all comatose patients with an
unwitnessed loss of consciousness.
Other Tests
Other tests that may be helpful for diagnosis include the following:
ECG: Cardiac arrhythmias and myocardial ischemia may be evident. Aneurysmal SAH may be associated with several
ECG changes, including peaked P waves, prolonged QT interval, and tall T waves.
Echocardiography: Cardiac sources of embolism, including endocarditis and myxomas, may be visualized in cases of
infectious or neoplastic aneurysms.
Evoked potentials and EEG: These functional neurophysiologic studies may be used to monitor cerebral aneurysm
surgery or patients critically ill with aneurysmal SAH.
Procedures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-12-320.jpg)


![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 15/29
Treatment
Medical Care
Prehospital care should include assessment of vital signs and neurological status. Airway, breathing, and circulation should be
addressed with endotracheal intubation, if necessary, and establishment of intravenous access.
Medical therapy of cerebral aneurysms involves general supportive measures and prevention of complications for individuals
who are in the periprocedural period or are poor surgical candidates. Treatment decisions should be based on the clinical status
of the patient, vascular anatomy of the aneurysm, and surgical or endovascular considerations.
Medical management of aneurysmal SAH is orchestrated in the ICU, with cardiac monitoring and placement of an arterial line.
Prior to definitive aneurysm treatment, medical approaches involve control of hypertension, administration of calcium channel
blockers, and prevention of seizures.
Following surgical or endovascular aneurysm treatment, blood pressure is maintained at higher levels to diminish complications
associated with vasospasm. Vasospasm usually occurs between days 3 and 21, presenting with headache, decreased level of
consciousness, and variable neurological deficits. Serial TCD may be employed to detect trends in cerebral blood flow during
this period.
Induced hypertension, hypervolemia, and hemodilution (ie, "triple-H therapy") aimed to maintain adequate cerebral perfusion
pressure in the setting of impaired cerebrovascular autoregulation. However, guidelines have moved toward maintenance of
euvolemia and induced hypertension based on recent literature.[9]
Intraarterial papaverine or endovascular balloon angioplasty may be used to treat vasospasm in select patients.
Infectious aneurysms are friable, with an increased propensity for hemorrhage. Anticoagulation is avoided in this setting. As
these lesions resolve with antibiotic therapy, surgical approaches usually are deferred. Regression or evolution of these
aneurysms is monitored with serial angiography.
Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms
The management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms is highly controversial. The International Study of Unruptured
Intracranial Aneurysms (ISUIA) indicated a relatively low risk of rupture in small aneurysms without history of SAH. Aneurysms
less than 10 mm in size had an annual rupture rate of approximately 0.05%. For posterior communicating,
vertebrobasilar/posterior cerebral, or basilar tip aneurysms less than 10 mm, the risk of rupture over 7.5 years approximated
2%, with all other locations harboring a risk of almost 0%. Recent guidelines and an evidence-based systematic review of the
literature have formulated recommendations for the care of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms, principally based on
age, history, and aneurysm size.
The anatomical characterization and morphology of unruptured aneurysms are not readily standardized, however. Some
investigators have advocated endovascular or surgical treatment of all aneurysms less than 10 mm if age is less than 50 years,
in the absence of contraindications. The presence of cigarette smoking, family history of aneurysms, polycystic kidney disease,
or systemic lupus erythematosus may elevate the risk of rupture and should be considered. Asymptomatic aneurysms greater
than 10 mm should also be considered for treatment, accounting for age, coexisting medical conditions, and relative risks for
treatment.
Considerable surgical mortality and morbidity rates at 1 year (as high as 3.8% and 15.7%, respectively) have been
demonstrated in preventive treatment of unruptured aneurysms. The surgeon's experience may be a significant and highly
variable factor in operative morbidity rate and functional outcome. More recently, application of diffusion-weighted MRI has
demonstrated silent thromboembolic events associated with endovascular treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Quality-
of-life issues, including the psychological morbidity of living with an unruptured intracranial aneurysm, also must be addressed.
Therapeutic decision making must balance endovascular or surgical morbidity and mortality rates with the risk of hemorrhage
and other considerations on an individual basis. Future studies in the management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms may
systematically account for the evolving technology of advanced endovascular approaches, detailed aneurysm morphology, novel
neuroimaging correlates, ethnic and geographical variation, neurocognitive impairment following endovascular or surgical
treatment, and quality-of-life issues.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-15-320.jpg)
![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 16/29
Surgical Therapy
Microsurgical techniques focus on excluding the aneurysm from the cerebral circulation and reducing mass effects on adjacent
structures. Various approaches have been developed and tailored to the anatomy and location of the aneurysm. A surgical clip
usually is placed across the aneurysm neck with preservation of the parent vessel, eliminating any aneurysmal rests that may
redevelop subsequently. Alternative techniques involve proximal or Hunterian ligation, wrapping the aneurysm, and trapping (ie,
combined proximal and distal vessel occlusion).
Adjunctive measures have been developed to reduce operative morbidity and to provide cerebral protection. Aneurysmal
rupture, the principal surgical complication, may be avoided with induced hypotension, CSF drainage, diuretics, hyperventilation,
and use of minimal brain retraction. Hypothermia, with or without circulatory arrest, and systemic hypotension are used
commonly. A large study of mild intraoperative hypothermia, however, failed to demonstrate benefit of this adjunctive technique.
Lumbar spinal drainage allows relaxation of brain parenchyma and provides a clean surgical field. Postoperative angiography is
performed routinely to check for major vessel occlusion or persistence of an aneurysmal rest. Operative morbidity rate increases
with aneurysm size (2.3% for < 5 mm; 6.8% for 6-15 mm, 14% for 16-25 mm) and varies by location.
Optimal timing of aneurysm surgery depends on the clinical status of the patient and associated factors. Early surgery (ie, < 48-
96 hours after SAH) is favored for candidates in good condition or those with unstable blood pressure, seizures, mass effect
from thrombus, large amounts of blood, or evidence of aneurysm growth or rebleeding. Early surgery carries an increased
operative morbidity, although the risks of vasospasm and rebleeding are reduced considerably.
Delayed surgery (ie, 10-14 d after SAH) may be considered for large aneurysms in difficult locations or for candidates in poor
clinical condition. Surgery is indicated for ruptured or symptomatic aneurysms in patients without extenuating contraindications
or considerably advanced age. Surgery generally is precluded if the clinical status is poor, corresponding to Hunt and Hess
grade 4 or 5.
Endovascular Techniques
Advances in endovascular techniques have provided therapeutic alternatives that may be employed even in the setting of acute
aneurysmal SAH. These techniques allow parent vessel preservation and may be combined with surgical approaches.
Electrolytically detachable platinum coils (eg, Guglielmi detachable coils [GDC]) may be deployed strategically within the
aneurysm, promoting thrombosis and eventual obliteration. Wide-neck aneurysms may be more difficult to occlude with these
devices. Other materials, such as balloons or glue, also may be used. Complications include vessel perforation, hemorrhage, or
distal thromboembolism.
Endovascular therapy or coiling of cerebral aneurysms has proliferated during the past of particular cerebral aneurysms are
likely influenced by numerous factors. The International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) demonstrated the superiority of
coiling with improved clinical outcomes. Seizures were also less common in patients with endovascular treatment, yet late
rebleeding was also more common. Selection bias may also have influenced ISAT and, therefore, treatment for a given
individual must still be tailored to each case.
A meta-analysis of relevant studies (including ISAT) found that endovascular coiling of cerebral aneurysms yields a better
clinical outcome than clipping does, with the benefit greatest in patients with a good preoperative grade.[1, 2] The analysis also
confirmed, however, that there is a greater risk of rebleeding with coiling, particularly for patients with a poor preoperative grade.
Patient mortality at 1 year with coiling was not significantly different from 1-year mortality with clipping.[1, 2]
Progressive refinement in endovascular techniques and devices tailored for the cerebrovasculature have expanded therapeutic
options available for definitive treatment of cerebral aneurysms. More pliable, low-profile stents may be used for stent-assisted
coiling for obliteration of wide-necked aneurysms.
Self-expanding or balloon-expandable covered stents may be used for treatment of selected carotid or vertebral artery
pseudoaneurysms.[10] The Silk flow-diverter stent allows complete occlusion in most cases after 1 year of treatment, with 7.8%
permanent morbidity and 3% mortality.[11]
Large or giant intracranial aneurysms may be treated with a combination of devices, such as stent-assisted coil placement.[12]
However, the requirement of dual antiplatelet therapy in stent-assisted coiling may increase the risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
[13]
Refinement of endovascular techniques for very small intracranial aneurysms has expanded treatment options, yet
complications may also increase in this particular subset.[14]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-16-320.jpg)
![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 17/29
Although endovascular coiling is a feasible, effective treatment for many elderly patients with ruptured and unruptured
intracranial aneurysms, careful patient selection is crucial in view of the risks of the procedure, which may outweigh the risk of
rupture in some patients with unruptured aneurysms, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis that included 21
studies of 1511 patients aged 65 years or older.[15, 16]
In this study, long-term occlusion was achieved in 79% of patients.[16] The rate of perioperative stroke (4%) was similar for
patients with unruptured and ruptured aneurysms. Intraprocedural rupture occurred in 1% of patients with unruptured aneurysms
and in 4% of patients with ruptured aneurysms. Perioperative mortality was 23% for patients with ruptured aneurysms and 1%
for those with unruptured aneurysms. At 1-year follow-up, 93% of patients with unruptured aneurysms and 66% of patients with
ruptured aneurysms had good outcomes.
Consultations
A multidisciplinary approach to the treatment of cerebral aneurysms is recommended. The following specialists should be a part
of the multidisciplinary team:
Neurosurgeon
Interventional neuroradiologist
Neurologist
Rehabilitation specialist
Diet
Restrict possible surgical candidates to taking nothing by mouth (NPO).
Employ nasogastric feedings for individuals with a decreased level of consciousness.
Recommend a soft, high-fiber diet to alert patients; patients should avoid caffeine.
Activity
Advise bed rest in a quiet dark environment during the initial week following aneurysmal SAH.
Perform passive range of motion exercises and frequent turning.
Assist patients with self-care activities, followed by slow advancement in activity as tolerated.
Medication
Medication Summary
Nimodipine has been demonstrated to improve outcome and decrease the incidence of delayed neurological deficits when
administered for the first 21 days after aneurysmal SAH. Although the prophylactic role of antiepileptic medications in
aneurysmal SAH is controversial, seizures may be treated with these medications. Antihypertensive medications may be
needed to control blood pressure. After aneurysmal occlusion, these medications are held typically for 2 weeks. Sedatives and
pain control may be needed for aneurysmal SAH. Antiemetics, antacids, and stool softeners also are used routinely.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-17-320.jpg)


![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 20/29
These agents help in softening stools and minimizing straining.
Docusate sodium (Colace, Dialox, Surfak, Regulax, Sulfalax)
For patients who should avoid straining during defecation; allows incorporation of water and fat into stool, causing stool to
soften.
Follow-up
Further Outpatient Care
See the list below:
After hospital discharge, continue physical, occupational, and speech therapy.
Administer medications for vasospasm and to prevent complications such as seizures, urinary tract infections, or venous
thromboses.
Following definitive treatment of a cerebral aneurysm with either endovascular or surgical obliteration, serial imaging
studies should be obtained as an outpatient. Various imaging modalities, including CTA, 1.5 or 3T MRA, and conventional
angiography may be used. The use of noninvasive angiographic techniques for serial evaluation has grown in recent
years.[17]
Further Inpatient Care
Following neurosurgical or endovascular intervention, continued care in the ICU generally includes the following:
Serial neurologic examinations
Avoidance of hypotension or hypertension (mean arterial pressure [MAP] should be in the range of 70-130 mm Hg)
Use of isotonic solutions, such as normal saline, to minimize cerebral edema
Treatment or prophylaxis of seizures
Treatment of urinary tract infections
Prevention of venous thrombosis
Prophylaxis for gastric ulcers
Physical, occupational, and speech therapy
Repeat CT scan in case of clinical deterioration
Inpatient & Outpatient Medications
See the list below:
Nimodipine for vasospasm
Phenytoin for prevention or treatment of seizures
Transfer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-20-320.jpg)




![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 26/29
References
1. Brooks M. Does Coiling Beat Clipping for Ruptured Aneurysms? Medscape Medical News. Dec 31 2012. Available at
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/776939. Accessed: Jan 16, 2013.
2. Li H, Pan R, Wang H, Rong X, Yin Z, Milgrom DP, et al. Clipping versus coiling for ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a systematic
review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013 Jan. 44(1):29-37. [Medline].
3. Koroknay-Pál P, Laakso A, Lehto H, Seppä K, Kivisaari R, Hernesniemi J, et al. Long-term Excess Mortality in Pediatric Patients
With Cerebral Aneurysms. Stroke. 2012 Aug. 43(8):2091-6. [Medline].
4. Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, Vincent AJ, Hofman A, Krestin GP, et al. Incidental findings on brain MRI in the general
population. N Engl J Med. 2007 Nov 1. 357(18):1821-8. [Medline].
5. Brooks M. Serial Screening for Cerebral Aneurysm Fruitful. Medscape Medical News. Available at
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/824618. Accessed: May 14, 2014.
6. Bor AS, Rinkel GJ, van Norden J, Wermer MJ. Long-term, serial screening for intracranial aneurysms in individuals with a family
history of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: a cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2014 Apr. 13(4):385-92. [Medline].
7. Yang CY, Chen YF, Lee CW, Huang A, Shen Y, Wei C, et al. Multiphase CT angiography versus single-phase CT angiography:
comparison of image quality and radiation dose. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 Aug. 29(7):1288-95. [Medline].
8. van Rooij WJ, Sprengers ME, de Gast AN, Peluso JP, Sluzewski M. 3D rotational angiography: the new gold standard in the
detection of additional intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 May. 29(5):976-9. [Medline].
9. [Guideline] Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, Derdeyn CP, Dion J, et al. Guidelines for the management of
aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american
Stroke Association. Stroke. 2012 Jun. 43 (6):1711-37. [Medline].
10. Yi AC, Palmer E, Luh GY, Jacobson JP, Smith DC. Endovascular treatment of carotid and vertebral pseudoaneurysms with covered
stents. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 May. 29(5):983-7. [Medline].
11. Berge J, Biondi A, Machi P, Brunel H, Pierot L, Gabrillargues J, et al. Flow-Diverter Silk Stent for the Treatment of Intracranial
Aneurysms: 1-year Follow-Up in a Multicenter Study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012 Feb 2. [Medline].
12. Yang X, Wu Z, Mu S, Li Y, Lv M. Endovascular treatment of giant and large intracranial aneurysms using the neuroform stent-
assisted coil placement. Neurol Res. 2008 Jul. 30(6):598-602. [Medline].
13. Tumialán LM, Zhang YJ, Cawley CM, Dion JE, Tong FC, Barrow DL. Intracranial hemorrhage associated with stent-assisted coil
embolization of cerebral aneurysms: a cautionary report. J Neurosurg. 2008 Jun. 108(6):1122-9. [Medline].
14. Nguyen TN, Raymond J, Guilbert F, Roy D, Bérubé MD, Mahmoud M, et al. Association of endovascular therapy of very small
ruptured aneurysms with higher rates of procedure-related rupture. J Neurosurg. 2008 Jun. 108(6):1088-92. [Medline].
15. Harding A. Careful selection key to coiling in elderly aneurysm patients. Medscape Medical News. May 23, 2013. [Full Text].
16. Sturiale CL, Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Lanzino G. Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms in Elderly Patients: A Systematic
Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke. 2013 May 16. [Medline].
17. Anzalone N, Scomazzoni F, Cirillo M, Righi C, Simionato F, Cadioli M, et al. Follow-up of coiled cerebral aneurysms at 3T:
comparison of 3D time-of-flight MR angiography and contrast-enhanced MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 Sep.
29(8):1530-6. [Medline].
18. Adams WM, Laitt RD, Jackson A. The role of MR angiography in the pretreatment assessment of intracranial aneurysms: a
comparative study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000 Oct. 21(9):1618-28. [Medline].
Board for Coherex Medical; National Leader and Steering Committee Clinical Trial, Bristol Myers Squibb; Abbott Laboratories,
advisory group.
Additional Contributors
Draga Jichici, MD, FRCPC, FAHA Associate Clinical Professor, Division of Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and
Neurology, Co-Director, Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit, Co-Director, Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound, Hamilton Health
Sciences, McMaster University School of Medicine, Canada
Draga Jichici, MD, FRCPC, FAHA is a member of the following medical societies: American Academy of Neurology, Canadian
Critical Care Society, Canadian Medical Protective Association, Canadian Neurocritical Care Society, Canadian Neurological
Sciences Federation, Neurocritical Care Society, Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada
Disclosure: Nothing to disclose.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-26-320.jpg)
![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 27/29
19. Alg VS, Sofat R, Houlden H, Werring DJ. Genetic risk factors for intracranial aneurysms: A meta-analysis in more than 116,000
individuals. Neurology. 2013 Jun 4. 80(23):2154-65. [Medline].
20. Andaluz N, Zuccarello M. Recent trends in the treatment of cerebral aneurysms: analysis of a nationwide inpatient database. J
Neurosurg. 2008 Jun. 108(6):1163-9. [Medline].
21. Anson JA, Lawton MT, Spetzler RF. Characteristics and surgical treatment of dolichoectatic and fusiform aneurysms. J Neurosurg.
1996 Feb. 84(2):185-93. [Medline].
22. Aoki N, Beck JR, Kitahara T. Reanalysis of unruptured intracranial aneurysm management: effect of a new international study on the
threshold probabilities. Med Decis Making. 2001 Mar-Apr. 21(2):87-96. [Medline].
23. Becker KJ. Epidemiology and clinical presentation of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1998 Jul.
9(3):435-44. [Medline].
24. Bederson JB, Awad IA, Wiebers DO. Recommendations for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: A
Statement for healthcare professionals from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association. Stroke. 2000 Nov. 31(11):2742-
50. [Medline].
25. Benndorf G, Klucznik RP, Meyer D. "Cross-over" technique for horizontal stenting of an internal carotid bifurcation aneurysm using a
new self-expandable stent: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2006 Feb. 58(1 Suppl):ONS-E172. [Medline].
26. Brennan JW, Schwartz ML. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: appraisal of the literature and suggested recommendations for
surgery, using evidence-based medicine criteria. Neurosurgery. 2000 Dec. 47(6):1359-71; discussion 1371-2. [Medline].
27. Brilstra EH, Rinkel GJ, van der Graaf Y. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by embolization with coils: a systematic review. Stroke.
1999 Feb. 30(2):470-6. [Medline].
28. Broderick JP. Coiling, clipping, or medical management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: time to randomize?. Ann Neurol. 2000
Jul. 48(1):5-6. [Medline].
29. Campi A, Ramzi N, Molyneux AJ, Summers PE, Kerr RS, Sneade M, et al. Retreatment of ruptured cerebral aneurysms in patients
randomized by coiling or clipping in the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT). Stroke. 2007 May. 38(5):1538-44.
[Medline].
30. Carter BS, Sheth S, Chang E. Epidemiology of the size distribution of intracranial bifurcation aneurysms: smaller size of distal
aneurysms and increasing size of unruptured aneurysms with age. Neurosurgery. 2006 Feb. 58(2):217-23; discussion 217-23.
[Medline].
31. Chyatte D, Fode NC, Sundt TM. Early versus late intracranial aneurysm surgery in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1988
Sep. 69(3):326-31. [Medline].
32. Chyatte D, Porterfield R. Functional outcome after repair of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2001 Mar. 94(3):417-
21. [Medline].
33. Connolly ES, Mohr JP, Solomon RA. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 1999 May 6. 340(18):1440-1; discussion
1441-2. [Medline].
34. de Oliveira JG, Beck J, Ulrich C, Rathert J, Raabe A, Seifert V. Comparison between clipping and coiling on the incidence of cerebral
vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev. 2007 Jan.
30(1):22-30; discussion 30-1. [Medline].
35. Donnan GA, Davis SM. Patients with small, asymptomatic, unruptured intracranial aneurysms and no history of subarachnoid
hemorrhage should be treated conservatively. Stroke. 2005 Feb. 36(2):407. [Medline].
36. Gonzalez N, Murayama Y, Nien YL. Treatment of unruptured aneurysms with GDCs: clinical experience with 247 aneurysms. AJNR
Am J Neuroradiol. 2004 Apr. 25(4):577-83. [Medline].
37. Haley EC, Kassell NF, Torner JC. The International Cooperative Study on the Timing of Aneurysm Surgery. The North American
experience. Stroke. 1992 Feb. 23(2):205-14. [Medline].
38. Hashimoto H, Iida J, Hironaka Y. Use of spiral computerized tomography angiography in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage in
whom subtraction angiography did not reveal cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2000 Feb. 92(2):278-83. [Medline].
39. Johnston SC, Dowd CF, Higashida RT, Lawton MT, Duckwiler GR, Gress DR. Predictors of rehemorrhage after treatment of ruptured
intracranial aneurysms: the Cerebral Aneurysm Rerupture After Treatment (CARAT) study. Stroke. 2008 Jan. 39(1):120-5. [Medline].
40. Johnston SC, Wilson CB, Halbach VV. Endovascular and surgical treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms: comparison of risks.
Ann Neurol. 2000 Jul. 48(1):11-9. [Medline].
41. Johnston SC, Zhao S, Dudley RA. Treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in California. Stroke. 2001 Mar. 32(3):597-605.
[Medline].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-27-320.jpg)
![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 28/29
42. Juvela S. Recommendations for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Stroke. 2001 Mar. 32(3):815-6.
[Medline].
43. Juvela S, Poussa K, Porras M. Factors affecting formation and growth of intracranial aneurysms: a long-term follow-up study. Stroke.
2001 Feb. 32(2):485-91. [Medline].
44. Karmonik C, Strother CM, Chen X. Stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms aided by virtual parent artery reconstruction.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005 Oct. 26(9):2368-70. [Medline].
45. Kim DH, Haney CL, Van Ginhoven G. Utility of outcome measures after treatment for intracranial aneurysms: a prospective trial
involving 520 patients. Stroke. 2005 Apr. 36(4):792-6. [Medline].
46. Kurre W, Berkefeld J. Materials and techniques for coiling of cerebral aneurysms: how much scientific evidence do we have?.
Neuroradiology. 2008 Nov. 50(11):909-27. [Medline].
47. Lavine SD, Meyers PM. Application of new techniques and technologies: stenting for cerebral aneurysm. Clin Neurosurg. 2007.
54:64-9. [Medline].
48. Le Roux PD, Winn HR. Management of the ruptured aneurysm. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1998 Jul. 9(3):525-40. [Medline].
49. Lylyk P, Ferrario A, Pasbon B. Buenos Aires experience with the Neuroform self-expanding stent for the treatment of intracranial
aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2005 Feb. 102(2):235-41. [Medline].
50. Mayberg MR. Cerebral vasospasm. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1998 Jul. 9(3):615-27. [Medline].
51. McKinney AM, Palmer CS, Truwit CL, Karagulle A, Teksam M. Detection of aneurysms by 64-section multidetector CT angiography
in patients acutely suspected of having an intracranial aneurysm and comparison with digital subtraction and 3D rotational
angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 Mar. 29(3):594-602. [Medline].
52. Mitchell P, Kerr R, Mendelow AD, Molyneux A. Could late rebleeding overturn the superiority of cranial aneurysm coil embolization
over clip ligation seen in the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial?. J Neurosurg. 2008 Mar. 108(3):437-42. [Medline].
53. Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular
coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2002 Oct 26. 360(9342):1267-74. [Medline].
54. Molyneux AJ, Cekirge S, Saatci I. Cerebral Aneurysm Multicenter European Onyx (CAMEO) trial: results of a prospective
observational study in 20 European centers. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004 Jan. 25(1):39-51. [Medline].
55. Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular
coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures,
rebleeding, subgroups, a. Lancet. 2005 Sep 3-9. 366(9488):809-17. [Medline].
56. Niimi Y, Song J, Madrid M. Endosaccular treatment of intracranial aneurysms using matrix coils: early experience and midterm
follow-up. Stroke. 2006 Apr. 37(4):1028-32. [Medline].
57. Parra A, Kreiter KT, Williams S. Effect of prior statin use on functional outcome and delayed vasospasm after acute aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage: a matched controlled cohort study. Neurosurgery. 2005 Mar. 56(3):476-84; discussion 476-84. [Medline].
58. Pierot L, Spelle L, Vitry F. Immediate clinical outcome of patients harboring unruptured intracranial aneurysms treated by
endovascular approach: results of the ATENA study. Stroke. 2008 Sep. 39(9):2497-504. [Medline].
59. Pluta RM, Dejam A, Grimes G. Nitrite infusions to prevent delayed cerebral vasospasm in a primate model of subarachnoid
hemorrhage. JAMA. 2005 Mar 23. 293(12):1477-84. [Medline].
60. Qureshi AI, Mohammad Y, Yahia AM. Ischemic events associated with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: multicenter clinical study
and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2000 Feb. 46(2):282-9; discussion 289-90. [Medline].
61. Raaymakers TW, Buys PC, Verbeeten B. MR angiography as a screening tool for intracranial aneurysms: feasibility, test
characteristics, and interobserver agreement. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999 Dec. 173(6):1469-75. [Medline].
62. Reeves BC, Langham J, Lindsay KW, Molyneux AJ, Browne JP, Copley L, et al. Findings of the International Subarachnoid
Aneurysm Trial and the National Study of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage in context. Br J Neurosurg. 2007 Aug. 21(4):318-23;
discussion 323-7. [Medline].
63. Rinkel GJ. Medical management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Int J Stroke. 2008 Aug. 3(3):193-204.
[Medline].
64. Rordorf G, Bellon RJ, Budzik RE Jr. Silent thromboembolic events associated with the treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms
by use of Guglielmi detachable coils: prospective study applying diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001 Jan.
22(1):5-10. [Medline].
65. Rosen DS, Macdonald RL. Subarachnoid hemorrhage grading scales: a systematic review. Neurocrit Care. 2005. 2(2):110-8.
[Medline].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-28-320.jpg)
![10/4/21, 9:12 PM https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1161518-print 29/29
66. Ryttlefors M, Enblad P, Kerr RS, Molyneux AJ. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial of neurosurgical clipping versus
endovascular coiling: subgroup analysis of 278 elderly patients. Stroke. 2008 Oct. 39(10):2720-6. [Medline].
67. Salary M, Quigley MR, Wilberger JE Jr. Relation among aneurysm size, amount of subarachnoid blood, and clinical outcome. J
Neurosurg. 2007 Jul. 107(1):13-7. [Medline].
68. Sanai N, Tarapore P, Lee AC, Lawton MT. The current role of microsurgery for posterior circulation aneurysms: a selective approach
in the endovascular era. Neurosurgery. 2008 Jun. 62(6):1236-49; discussion 1249-53. [Medline].
69. Schievink WI. Genetics and aneurysm formation. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1998 Jul. 9(3):485-95. [Medline].
70. Schmid-Elsaesser R, Kunz M, Zausinger S, Prueckner S, Briegel J, Steiger HJ. Intravenous magnesium versus nimodipine in the
treatment of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a randomized study. Neurosurgery. 2006 Jun. 58(6):1054-65;
discussion 1054-65. [Medline].
71. Sherlock M, O'sullivan E, Agha A. The incidence and pathophysiology of hyponatraemia after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Clin
Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006 Mar. 64(3):250-4. [Medline].
72. Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ. Early rebleeding after coiling of ruptured cerebral aneurysms: incidence, morbidity, and risk factors.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005 Aug. 26(7):1739-43. [Medline].
73. Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Beute GN. Late rebleeding of ruptured intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 2005 Nov-Dec. 26(10):2542-9. [Medline].
74. Solenski NJ, Haley EC, Kassell NF. Medical complications of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a report of the multicenter,
cooperative aneurysm study. Participants of the Multicenter Cooperative Aneurysm Study. Crit Care Med. 1995 Jun. 23(6):1007-17.
[Medline].
75. Solomon RA, Fink ME, Pile-Spellman J. Surgical management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1994 Mar.
80(3):440-6. [Medline].
76. Standhardt H, Boecher-Schwarz H, Gruber A, Benesch T, Knosp E, Bavinzski G. Endovascular treatment of unruptured intracranial
aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils: short- and long-term results of a single-centre series. Stroke. 2008 Mar. 39(3):899-904.
[Medline].
77. Todd MM, Hindman BJ, Clarke WR. Mild intraoperative hypothermia during surgery for intracranial aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 2005
Jan 13. 352(2):135-45. [Medline].
78. van den Bergh WM, Algra A, van Kooten F. Magnesium sulfate in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a randomized controlled
trial. Stroke. 2005 May. 36(5):1011-5. [Medline].
79. Velthuis BK, Van Leeuwen MS, Witkamp TD. Computerized tomography angiography in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage:
from aneurysm detection to treatment without conventional angiography. J Neurosurg. 1999 Nov. 91(5):761-7. [Medline].
80. Vespa PM, Gobin YP. Endovascular treatment and neurointensive care of ruptured aneurysms. Crit Care Clin. 1999 Oct. 15(4):667-
84. [Medline].
81. Vinuela F, Murayama Y, Duckwiler GR. Present and future technical developments on aneurysm embolization. Impact on indications
and anatomic results. Clin Neurosurg. 2000. 47:221-41. [Medline].
82. Viñuela F, Duckwiler G, Mawad M. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: perioperative anatomical
and clinical outcome in 403 patients. 1997. J Neurosurg. 2008 Apr. 108(4):832-9. [Medline].
83. Wermer MJ, van der Schaaf IC, Velthuis BK. Follow-up screening after subarachnoid haemorrhage: frequency and determinants of
new aneurysms and enlargement of existing aneurysms. Brain. 2005 Oct. 128(Pt 10):2421-9. [Medline].
84. White PM, Wardlaw JM, Easton V. Can noninvasive imaging accurately depict intracranial aneurysms? A systematic review.
Radiology. 2000 Nov. 217(2):361-70. [Medline].
85. Wiebers DO, Torres VE. Screening for unruptured intracranial aneurysms in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J
Med. 1992 Sep 24. 327(13):953-5. [Medline].
86. Yuki I, Murayama Y, Vinuela F. Development of medical devices for neuro-interventional procedures: special focus on aneurysm
treatment. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2005 Sep. 2(5):539-46. [Medline].
87. Zada G, Breault J, Liu CY, Khalessi AA, Larsen DW, Teitelbaum GP, et al. Internal carotid artery aneurysms occurring at the origin of
fetal variant posterior cerebral arteries: surgical and endovascular experience. Neurosurgery. 2008 Jul. 63(1 Suppl 1):ONS55-61;
discussion ONS61-2. [Medline].
88. Zaidat OO, Ionita CC, Hussain SI, Alexander MJ, Friedman AH, Graffagnino C. Impact of Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm Coiling and
Clipping on the Incidence of Cerebral Vasospasm and Clinical Outcome. J Neuroimaging. 2008 Aug 4. [Medline].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aneurysm-211007094255/85/Aneurysm-29-320.jpg)