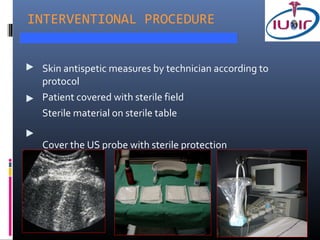
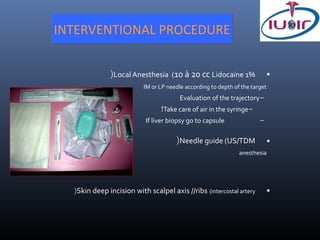
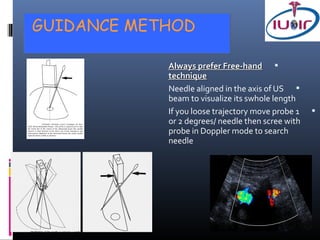
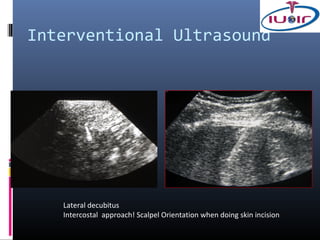
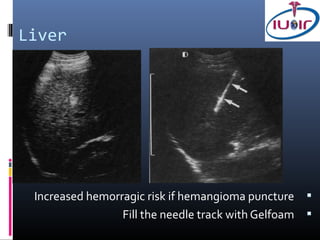
1) Ultrasound guidance allows real-time visualization of the needle and target, helping to determine the optimal access point and trajectory.
2) Proper technique includes using the shortest skin-target distance, avoiding large vessels and organs, and using Doppler to help guide needle placement.
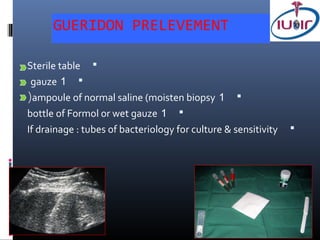
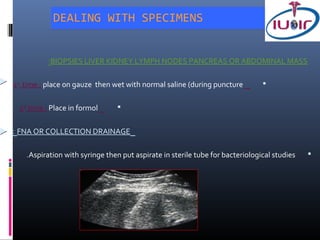
3) Specimen handling involves placing the first biopsy directly in saline and subsequent biopsies in formalin to preserve tissue integrity for analysis.