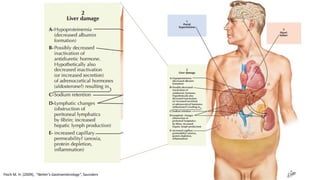
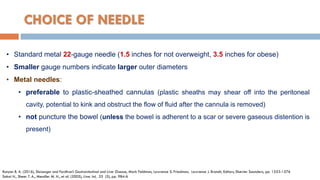
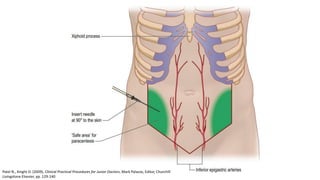
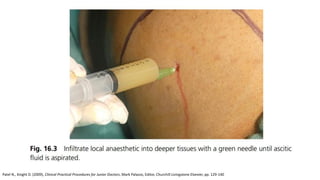
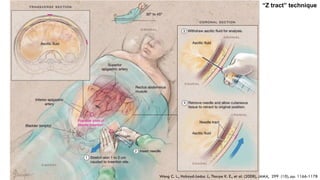
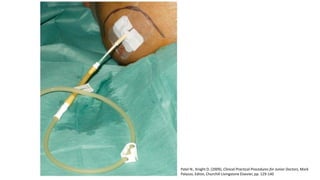
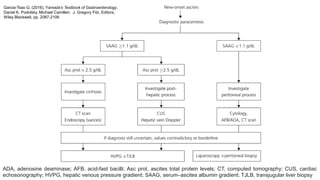
1. Abdominal paracentesis is used to diagnose the cause of ascites and detect ascitic fluid infection. It involves inserting a needle through the abdominal wall to drain fluid from the peritoneal cavity.
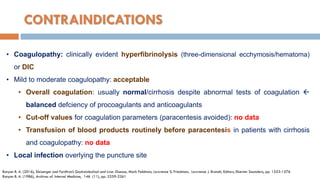
2. The document provides details on the indications, contraindications, complications, and techniques for performing diagnostic and therapeutic paracentesis. Precautions are taken to minimize risks such as abdominal wall hematoma or puncturing internal organs.
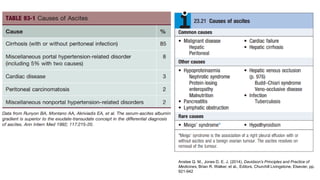
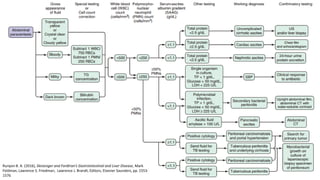
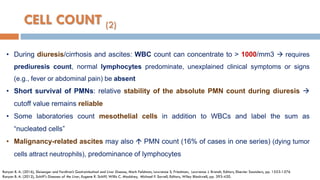
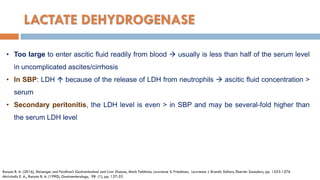
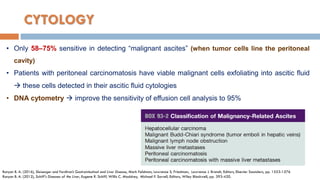
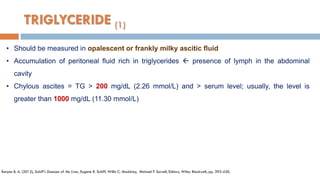
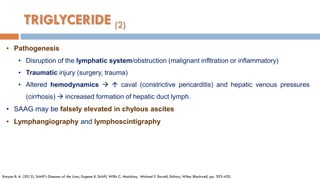
3. Analysis of the drained ascitic fluid can provide information on possible causes of ascites based on characteristics like appearance, cell count, protein level, and triglyceride content. A cloudy or bloody appearance may indicate infection or other conditions.














![Cesario K. B., Choure A., Carey W. D. Cirrhotic Ascites. 2013 [cited 2017 June]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abdominalparacentesis-200518100507/85/Abdominal-paracentesis-Ch-c-do-mang-b-ng-24-320.jpg)
![GROSS APPEARANCE (1)
• The opacity of many cloudy ascitic fluid specimens: neutrophils shimmering effect: glass
tube containing the fluid is rocked back and forth in front of a light
• Transparent and usually slightly yellow: Non-neutrocytic (i.e., ascitic fluid
polymorphonuclear neutrophil [PMN] count < 250/mm3)
• Nearly clear: absolute neutrophil count < 1000/mm3
• Quite cloudy: > 5000/mm3
• Frankly purulent: > 50000/mm3 (gross intraabdominal infection e.g secondary peritonitis or an
abscess) diferrential milky fluid! Lack of odor and TG >200 mg/dL: chylous ascites
• No pigment and look like water: very low protein concentration
Runyon B. A. (2016), Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, Mark Feldman, Lawrence S. Friedman, Lawrence J. Brandt, Editors, Elsevier Saunders, pp. 1553-1576
Garcia-Tsao G. (2016), Yamada’s Textbook of Gastroenterology, Daniel K. Podolsky, Michael Camilleri, J. Gregory Fitz, Editors, Wiley Blackwell, pp. 2087-2106](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abdominalparacentesis-200518100507/85/Abdominal-paracentesis-Ch-c-do-mang-b-ng-25-320.jpg)


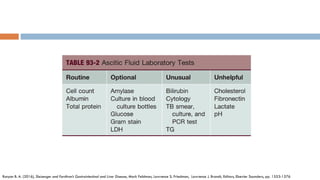

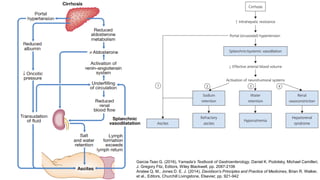
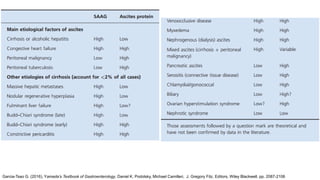
![SERUM-ASCITES ALBUMIN GRADIENT (SAAG) (1)
• Before the 1980s: total protein to classify ascites as either exudative or transudative (cut-off 2.5
g/dL [25 g/L]) not careful defined and validated.
• The serum-ascites albumin gradient (SAAG): proved to categorize ascites better, reflection
of hepatic sinusoidal pressure
• SAAG: not explain the pathogenesis of ascites formation, nor does it explain where the
albumin came from (liver or bowel)
• Oncotic-hydrostatic balance (Starling forces), difference between the serum and ascitic fluid
albumin concentrations correlates directly with portal pressure.
• The accuracy of the test is excellent (even with ascitic fluid infection, diuresis, therapeutic
paracentesis, IV infusions of albumin, and various causes of liver disease)
Runyon B. A. (2016), Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, Mark Feldman, Lawrence S. Friedman, Lawrence J. Brandt, Editors, Elsevier Saunders, pp. 1553-1576
Runyon B. A., Montano A. A., Akriviadis E. A., et al. (1992), Ann Intern Med, 117 (3), pp. 215-20.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abdominalparacentesis-200518100507/85/Abdominal-paracentesis-Ch-c-do-mang-b-ng-32-320.jpg)

![• SAAG = serum albumin - ascitic albumin
• ≥ 1.1 g/dL (11g/L) = high albumin gradient: portal hypertension
• < 1.1 g/dL (11g/L) = low albumin gradient: unlikely to have portal hypertension
• If the frst result is borderline (e.g., 1.0 or 1.1 g/dL [10 or 11 g/L]) repeating the
paracentesis and analysis usually provides a definitive result
• SAAG correlates very well with the hepatic venous pressure gradient (r = 0.72)
Runyon B. A. (2016), Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, Mark Feldman, Lawrence S. Friedman, Lawrence J. Brandt, Editors, Elsevier Saunders, pp. 1553-1576
Hoefs J. C. (1983), J Lab Clin Med, 102 (2), pp. 260-73
SERUM-ASCITES ALBUMIN GRADIENT (SAAG) (2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abdominalparacentesis-200518100507/85/Abdominal-paracentesis-Ch-c-do-mang-b-ng-34-320.jpg)
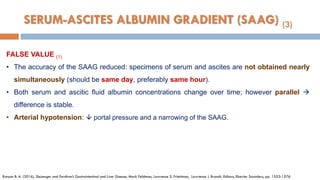
![FALSE VALUE (2)
• Lipid interferes with the assay for albumin, and chylous ascites may result in a falsely high
SAAG
• The accuracy of the albumin assay at low albumin concentrations (e.g., <1 g/dL [10 g/L])
should be confirmed (If serum albumin < 1.1 g/dL/ascitic cirrhosis, the SAAG will be falsely low)
• Serum hyperglobulinemia (serum globulin level > 5 g/dL [50 g/L]) high ascitic fluid globulin
concentration narrow the albumin gradient (contributing to the oncotic forces)
Runyon B. A. (2016), Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, Mark Feldman, Lawrence S. Friedman, Lawrence J. Brandt, Editors, Elsevier Saunders, pp. 1553-1576
Corrected SAAG = uncorrected SAAG x 0.16 x serum globulin (g/dL) + 2.5
SERUM-ASCITES ALBUMIN GRADIENT (SAAG) (4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abdominalparacentesis-200518100507/85/Abdominal-paracentesis-Ch-c-do-mang-b-ng-36-320.jpg)








![1. Akriviadis E. A., Runyon B. A. (1990), "Utility of an algorithm in differentiating spontaneous from secondary bacterial
peritonitis", Gastroenterology, 98 (1), pp. 127-33.
2. Anstee Q. M., Jones D. E. J. (2014), "Liver and biliary tract disease", Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicines, Brian R.
Walker, et al., Editors, Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier, pp. 921-942.
3. BA R. (2012), "Technique of diagnostic and therapeutic abdominal paracentesis", UpToDate.
4. Cesario K. B., Choure A., Carey W. D. Cirrhotic Ascites. 2013 [cited 2017 June].
5. De Gottardi A., Thévenot T., Spahr L., et al. (2009), "Risk of Complications After Abdominal Paracentesis in Cirrhotic Patients: A
Prospective Study", Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 7 (8), pp. 906-909.
6. EASL (2010), "EASL clinical practice guidelines on the management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatorenal
syndrome in cirrhosis", J Hepatol, 53 (3), pp. 397-417.
7. Garcia-Tsao G. (2016), "Ascites and its complications", Yamada’s Textbook of Gastroenterology, Daniel K. Podolsky, Michael
Camilleri, J. Gregory Fitz, Editors, Wiley Blackwell, pp. 2087-2106.
8. Grabau C. M., Crago S. F., Hoff L. K., et al. (2004), "Performance standards for therapeutic abdominal paracentesis",
Hepatology, 40 (2), pp. 484-488.
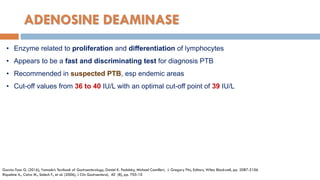
9. Hillebrand D. J., Runyon B. A., Yasmineh W. G., et al. (1996), "Ascitic fluid adenosine deaminase insensitivity in detecting
tuberculous peritonitis in the United States", Hepatology, 24 (6), pp. 1408-12.
10. Hoefs J. C. (1983), "Serum protein concentration and portal pressure determine the ascitic fluid protein concentration in patients
with chronic liver disease", J Lab Clin Med, 102 (2), pp. 260-73.
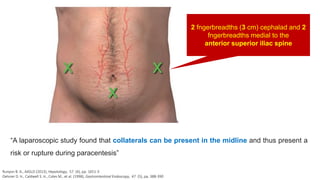
11. Oelsner D. H., Caldwell S. H., Coles M., et al. (1998), "Subumbilical midline vascularity of the abdominal wall in portal
hypertension observed at laparoscopy", Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 47 (5), pp. 388-390.
12. Patel N., Knight D. (2009), "Abdominal Paracentesis and Ascitic Drain Insertion", Clinical Practical Procedures for Junior Doctors,
Mark Palazzo, Editor, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, pp. 129-140.
REFERENCES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abdominalparacentesis-200518100507/85/Abdominal-paracentesis-Ch-c-do-mang-b-ng-54-320.jpg)
