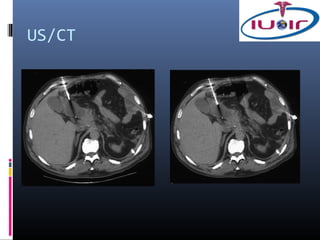
The document discusses biopsy and drainage procedures. It provides details on:
1) Biopsy results being positive 70-100% of the time, with the lowest success for lymphoma.
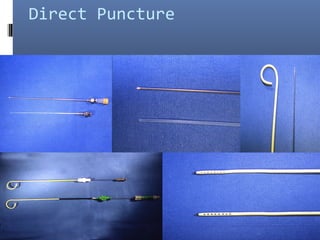
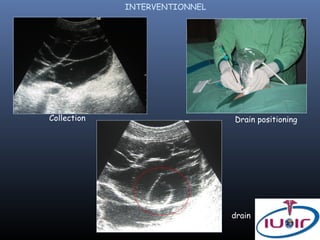
2) Techniques for abdominal drainage including direct puncture and the Seldinger technique using various sterile materials.
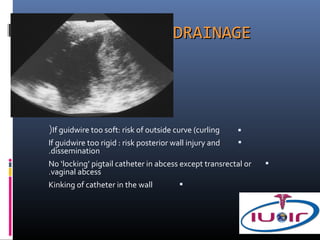
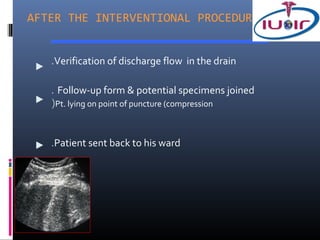
3) Precautions for drainage including using a fine needle to determine fluid characteristics and never fully emptying before draining.