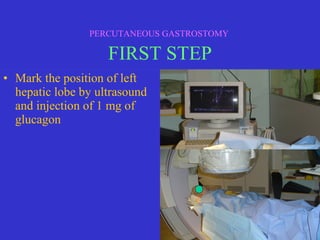
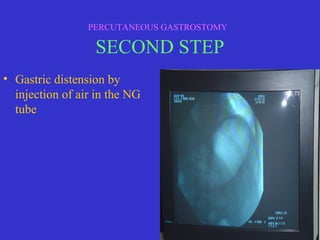
This document discusses percutaneous gastrostomy, a procedure to place a feeding tube directly into the stomach through the abdominal wall. It notes several conditions that may require long-term nutritional support via gastrostomy tube, including various cancers, neurological diseases, and swallowing disorders. The document outlines the indications, contraindications, and complications of the percutaneous gastrostomy procedure. It then describes the step-by-step process of performing the procedure, including patient preparation, ultrasound guidance, gastric distension, gastroplexy using T-fasteners, verification of tube placement, and securing the tube.