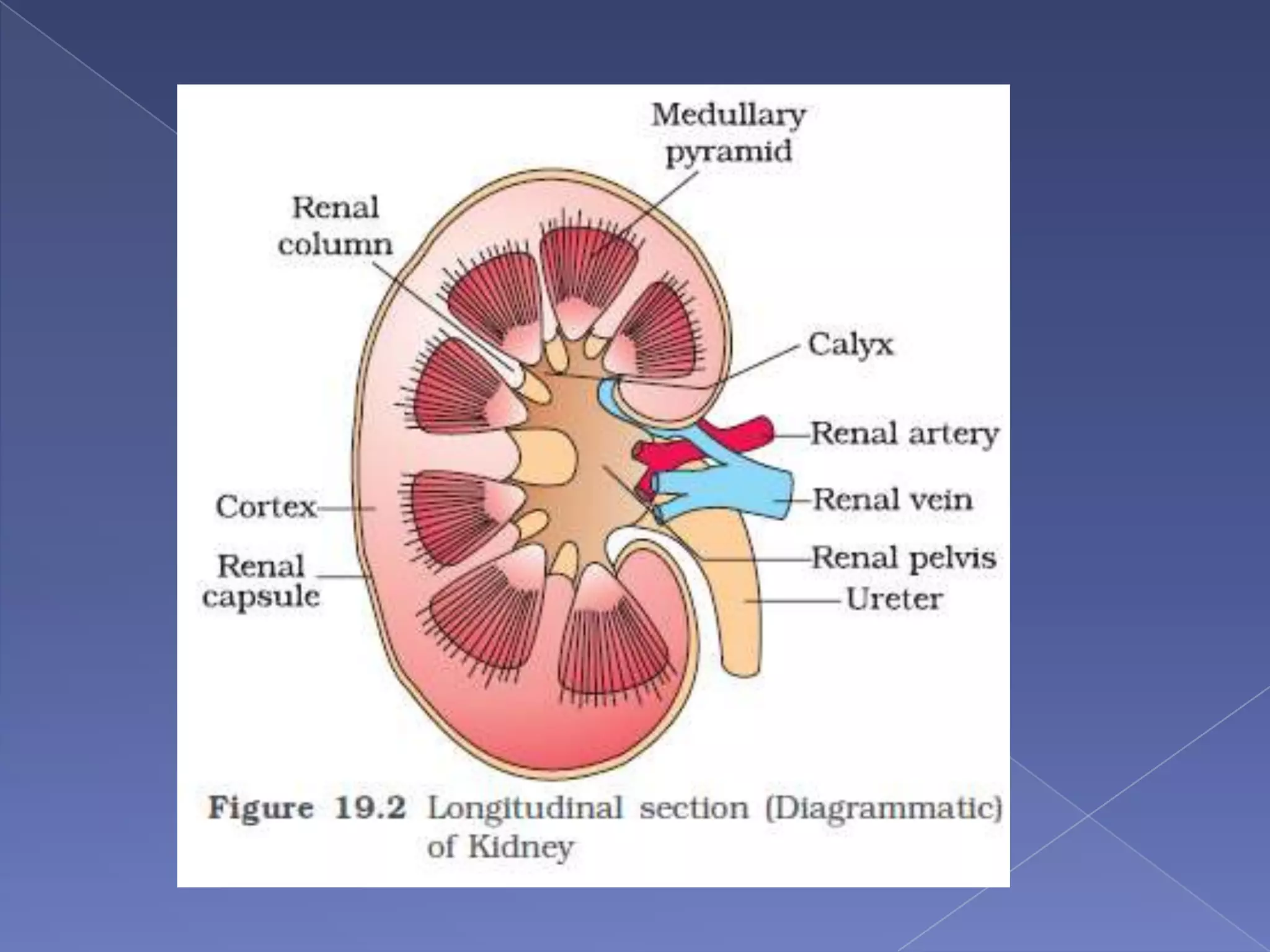
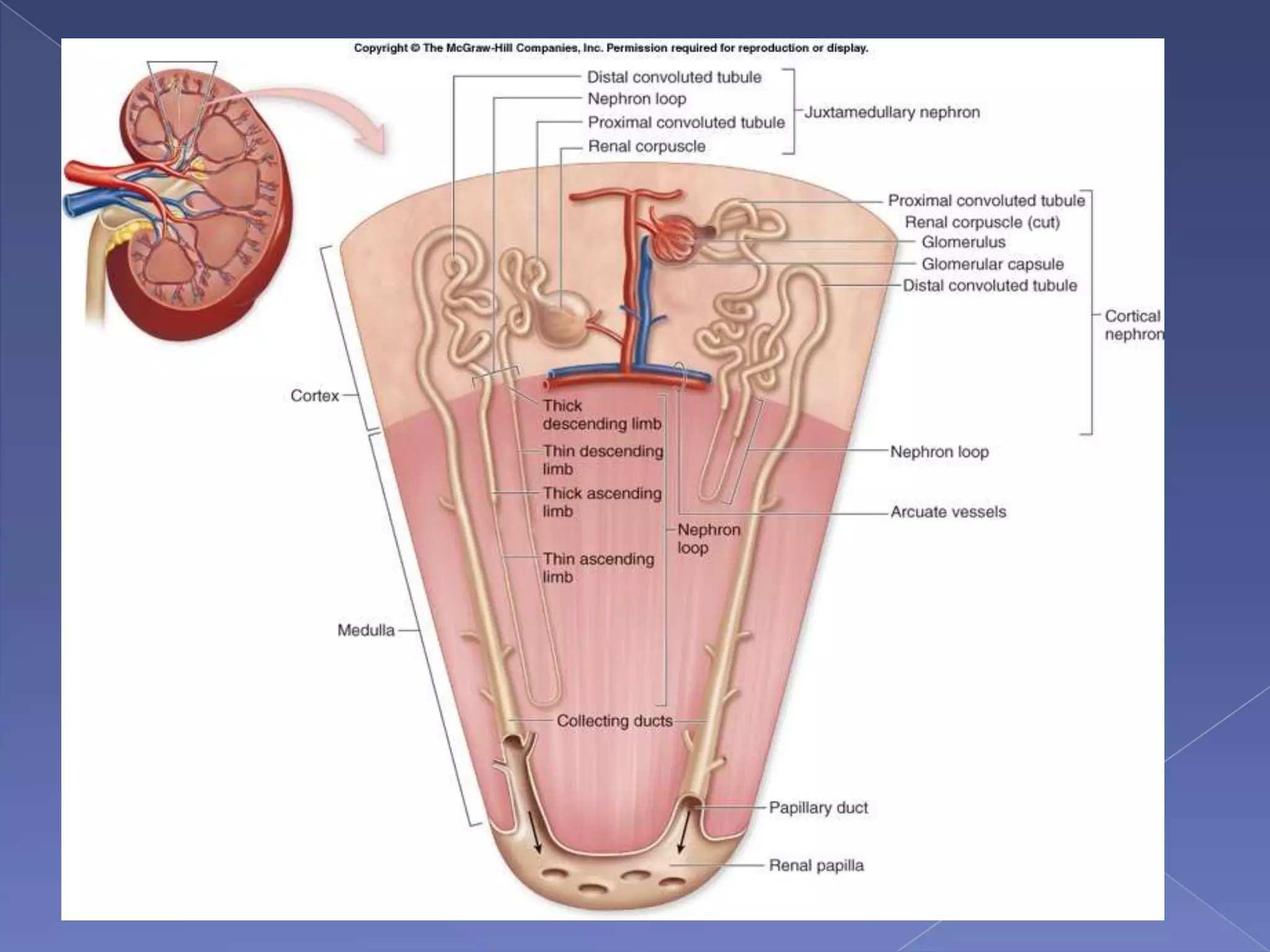
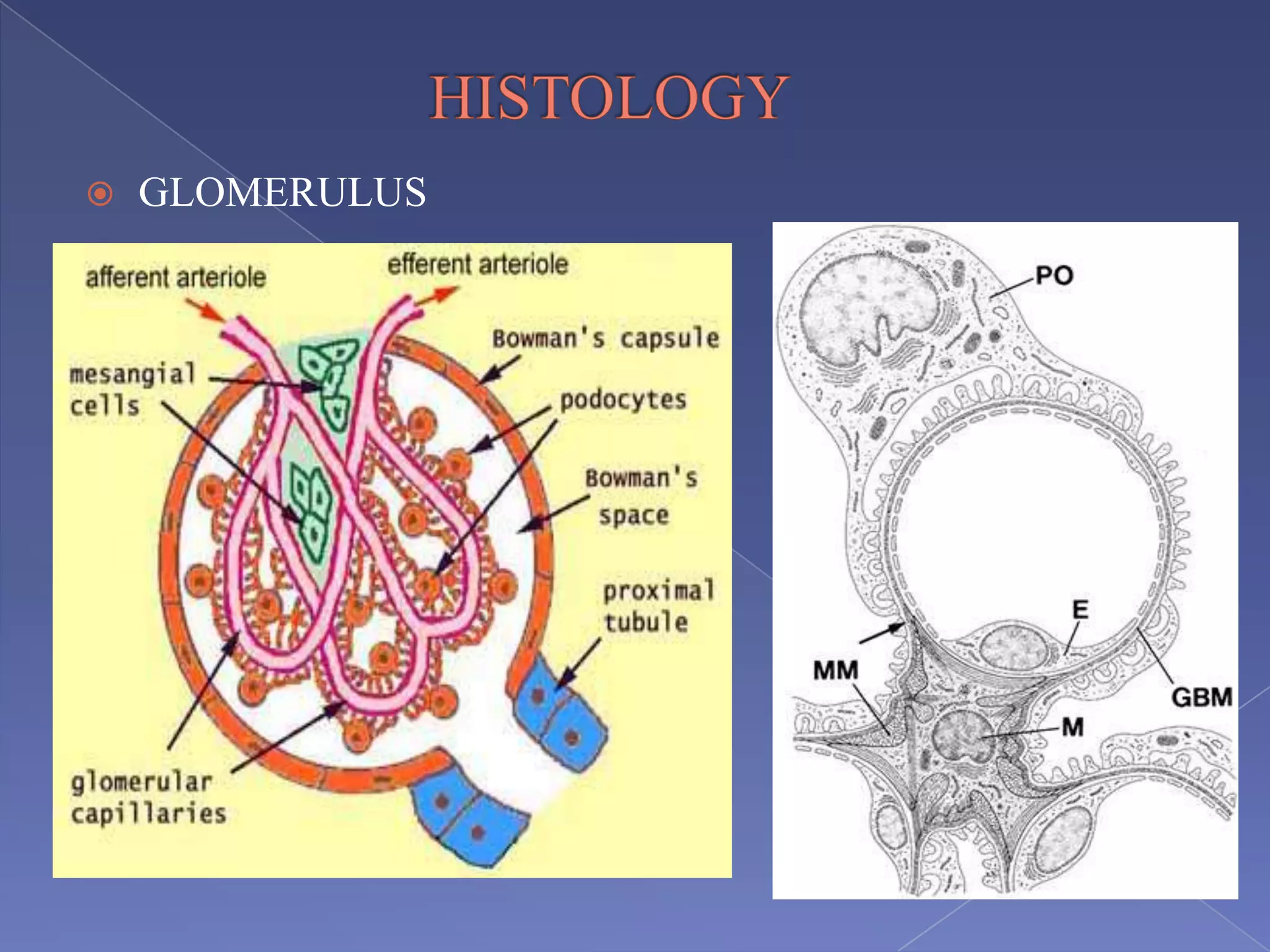
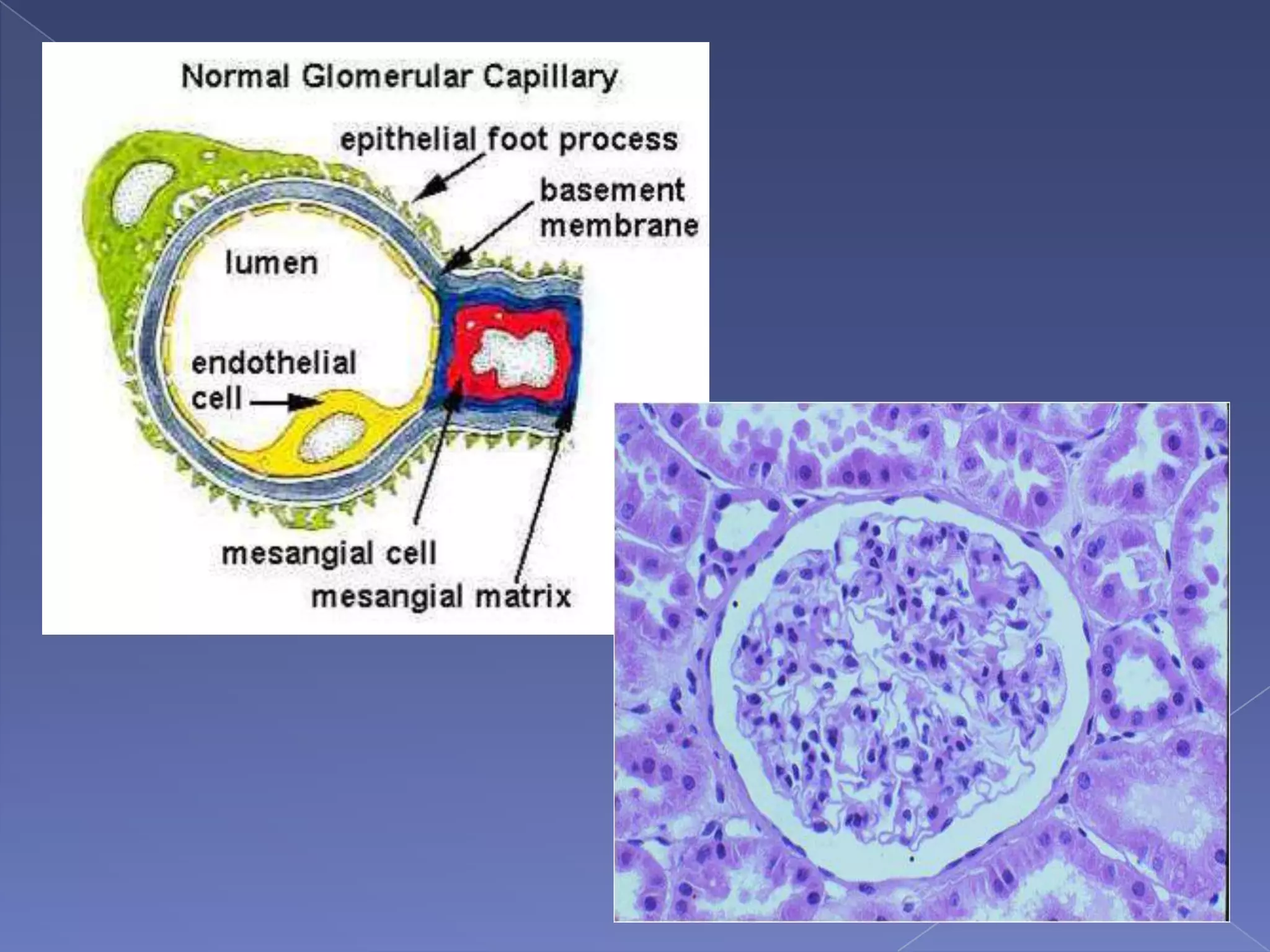
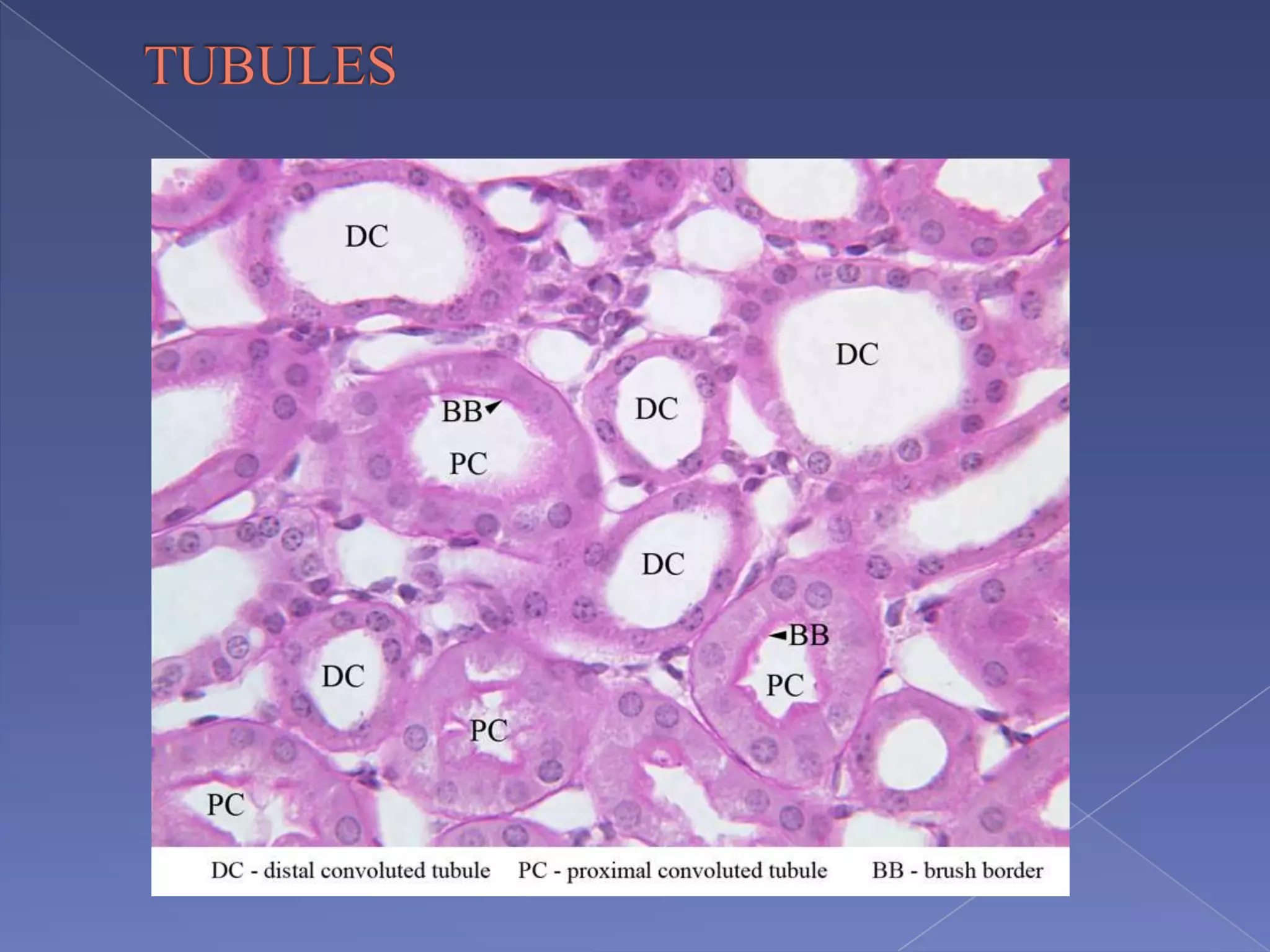
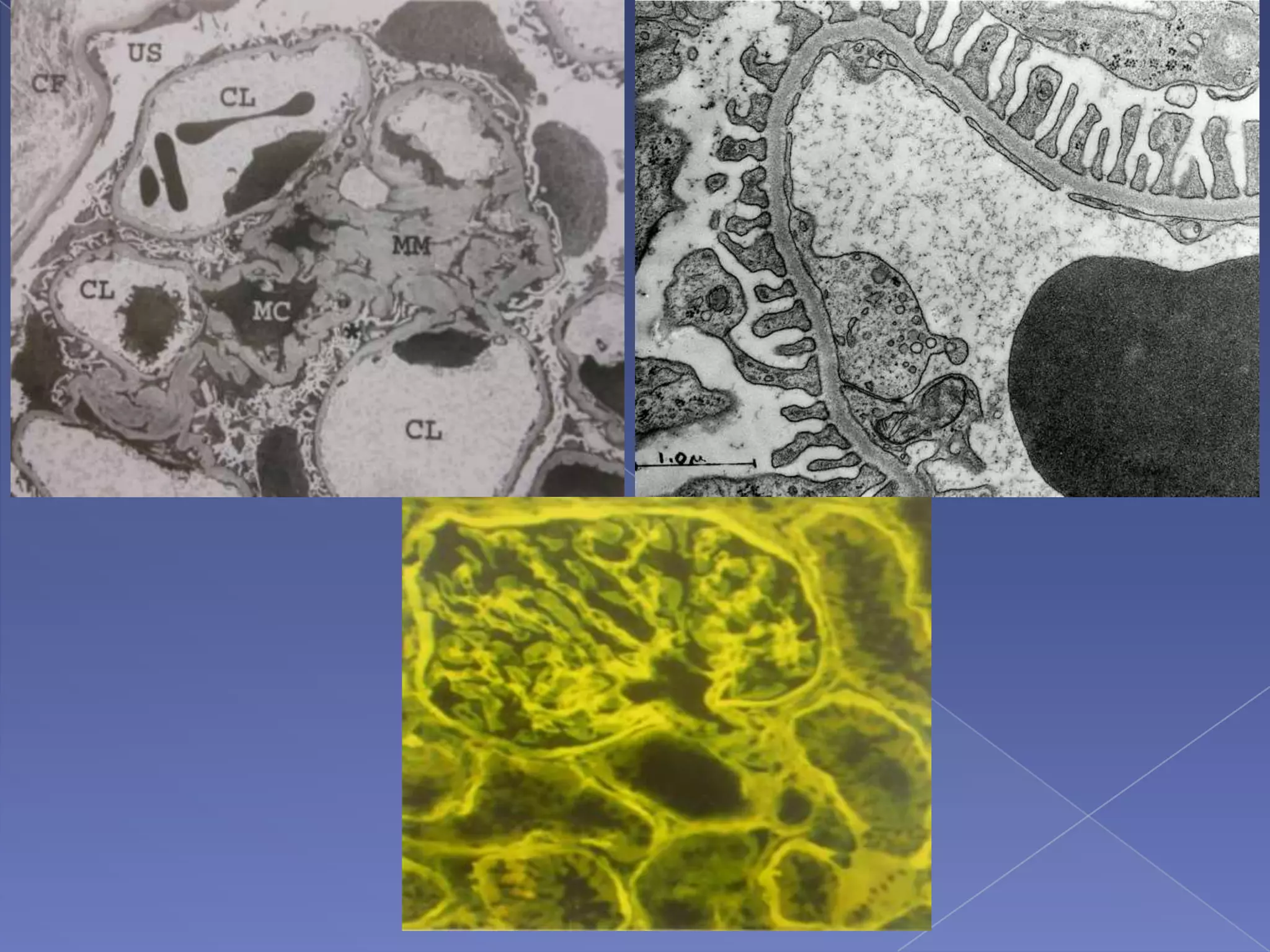
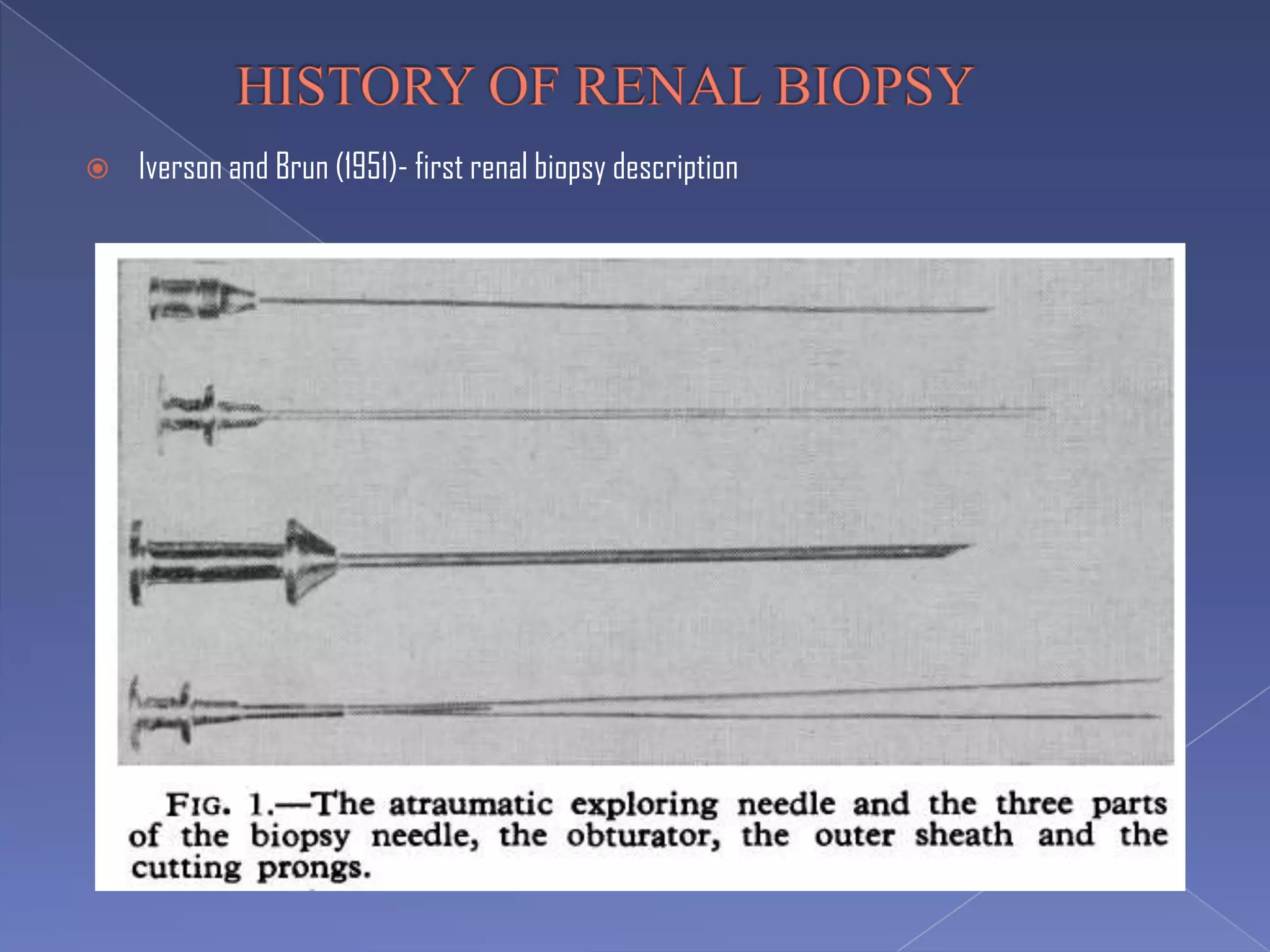
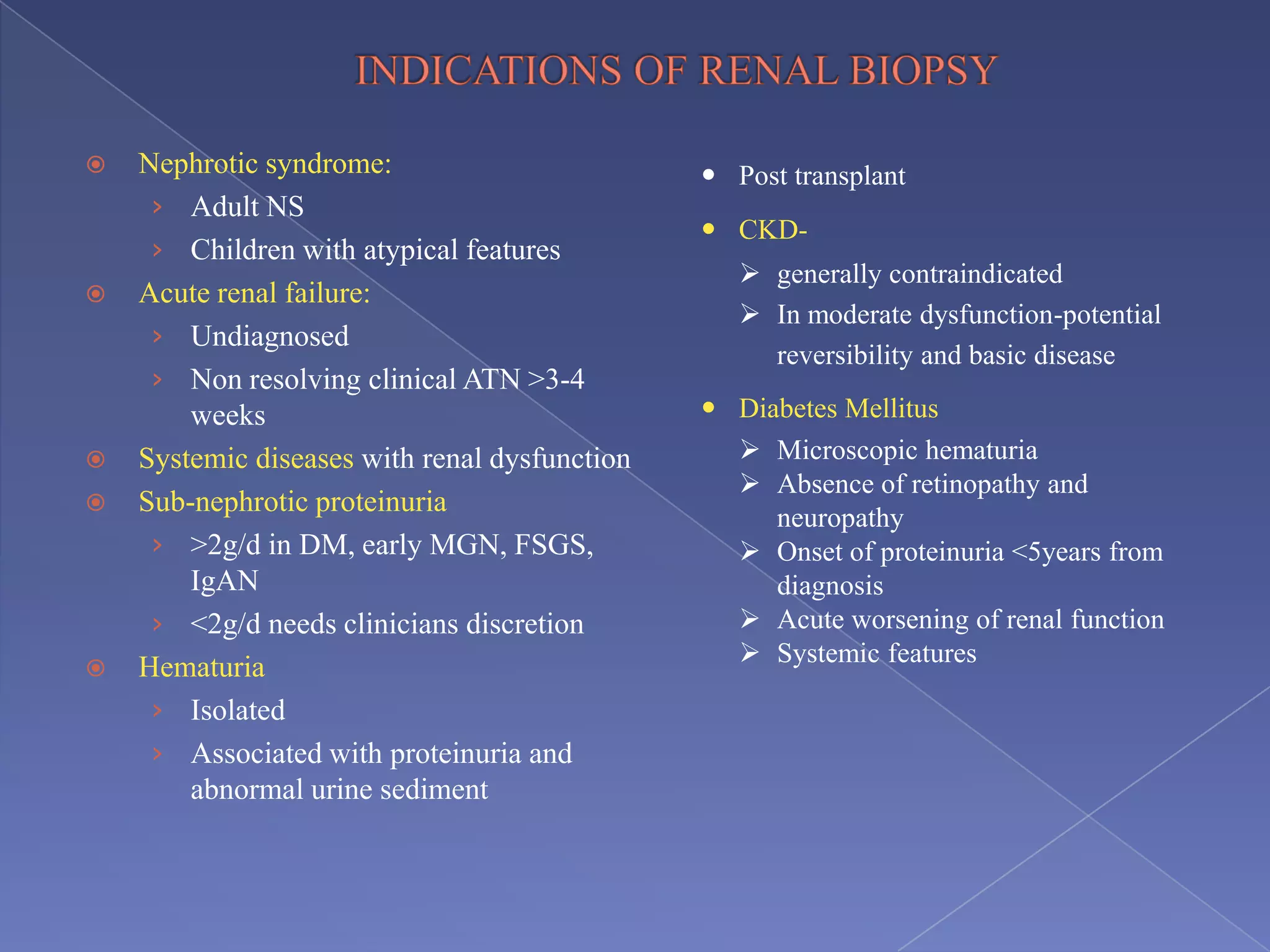
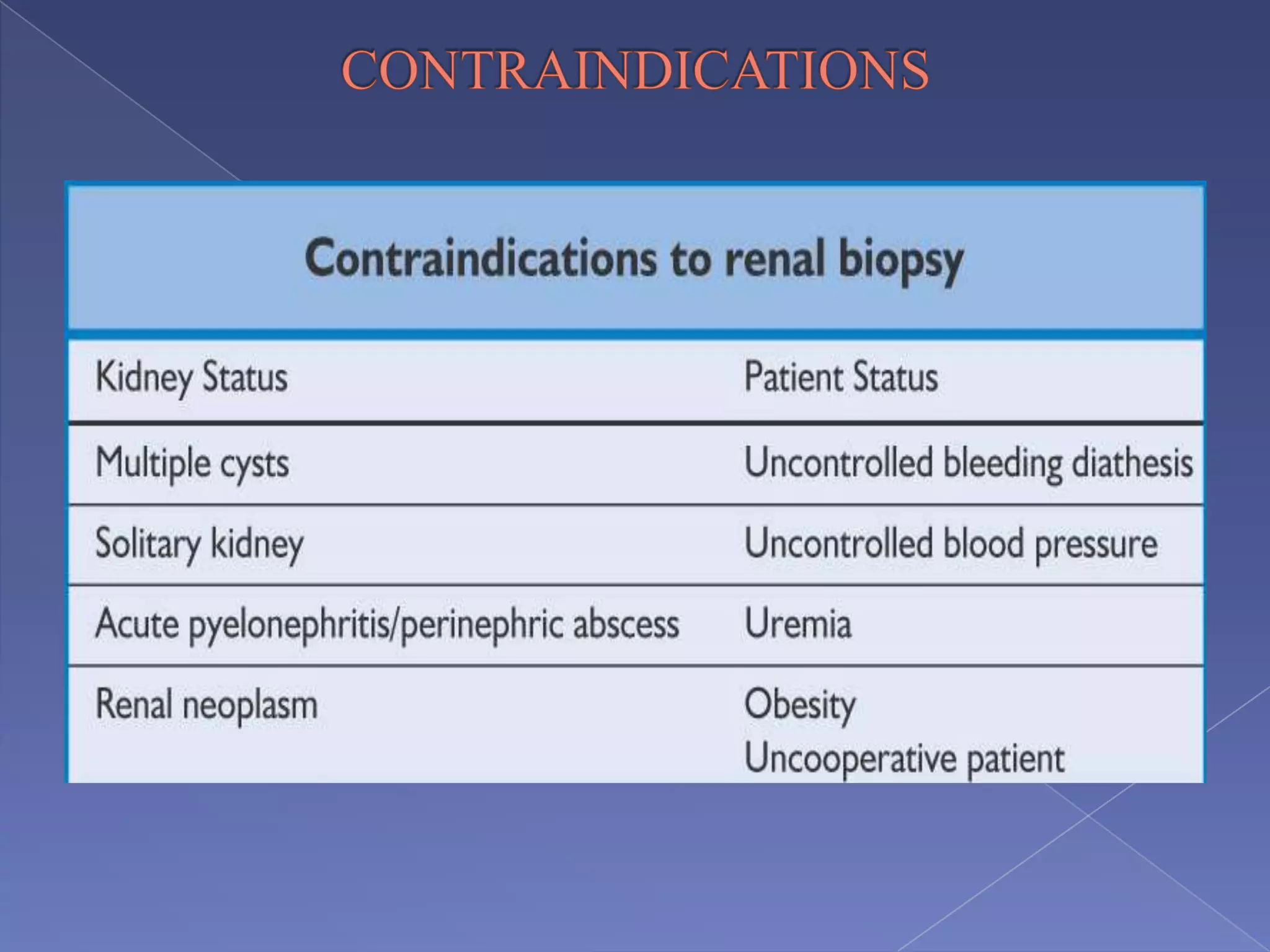
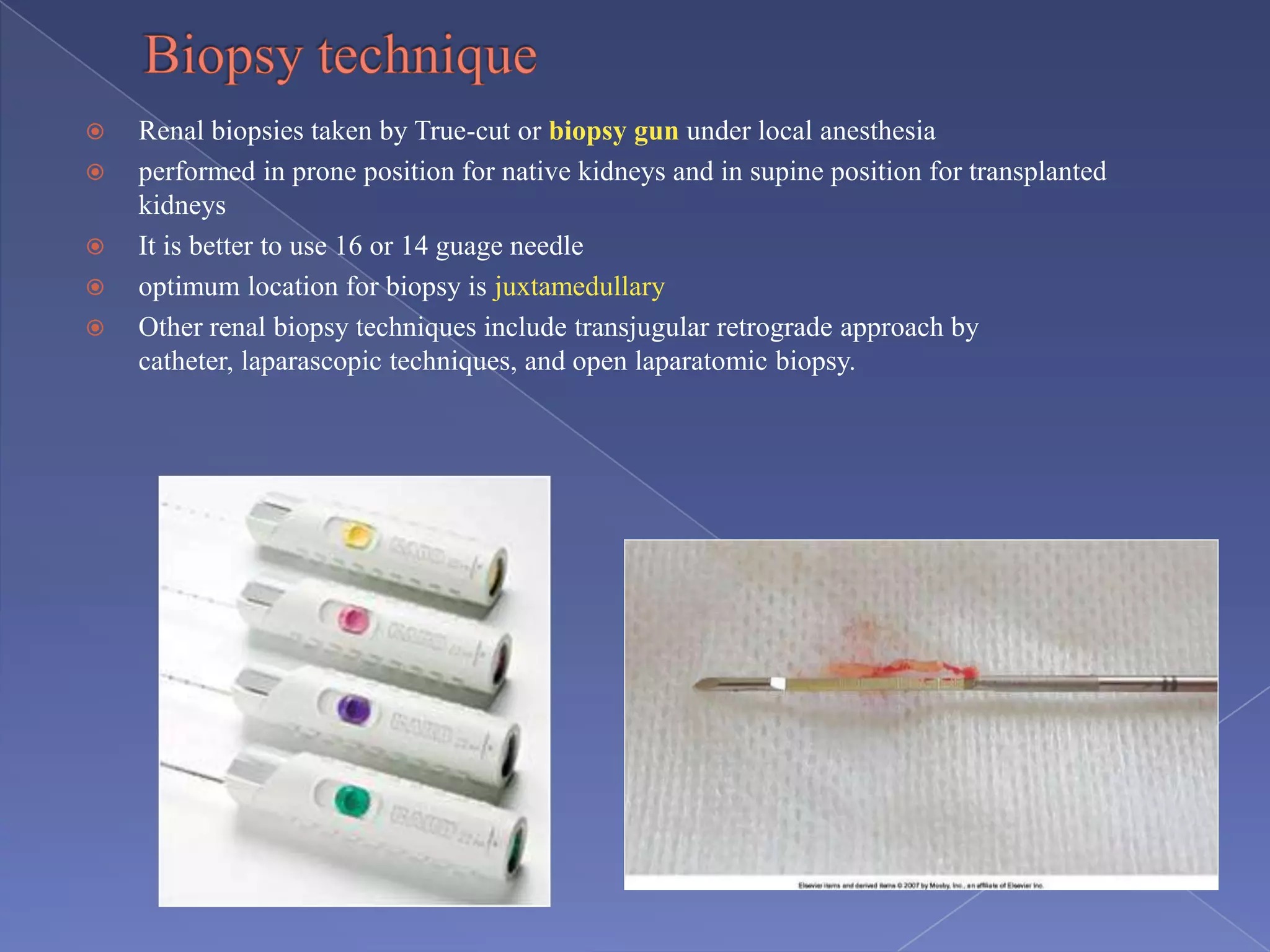
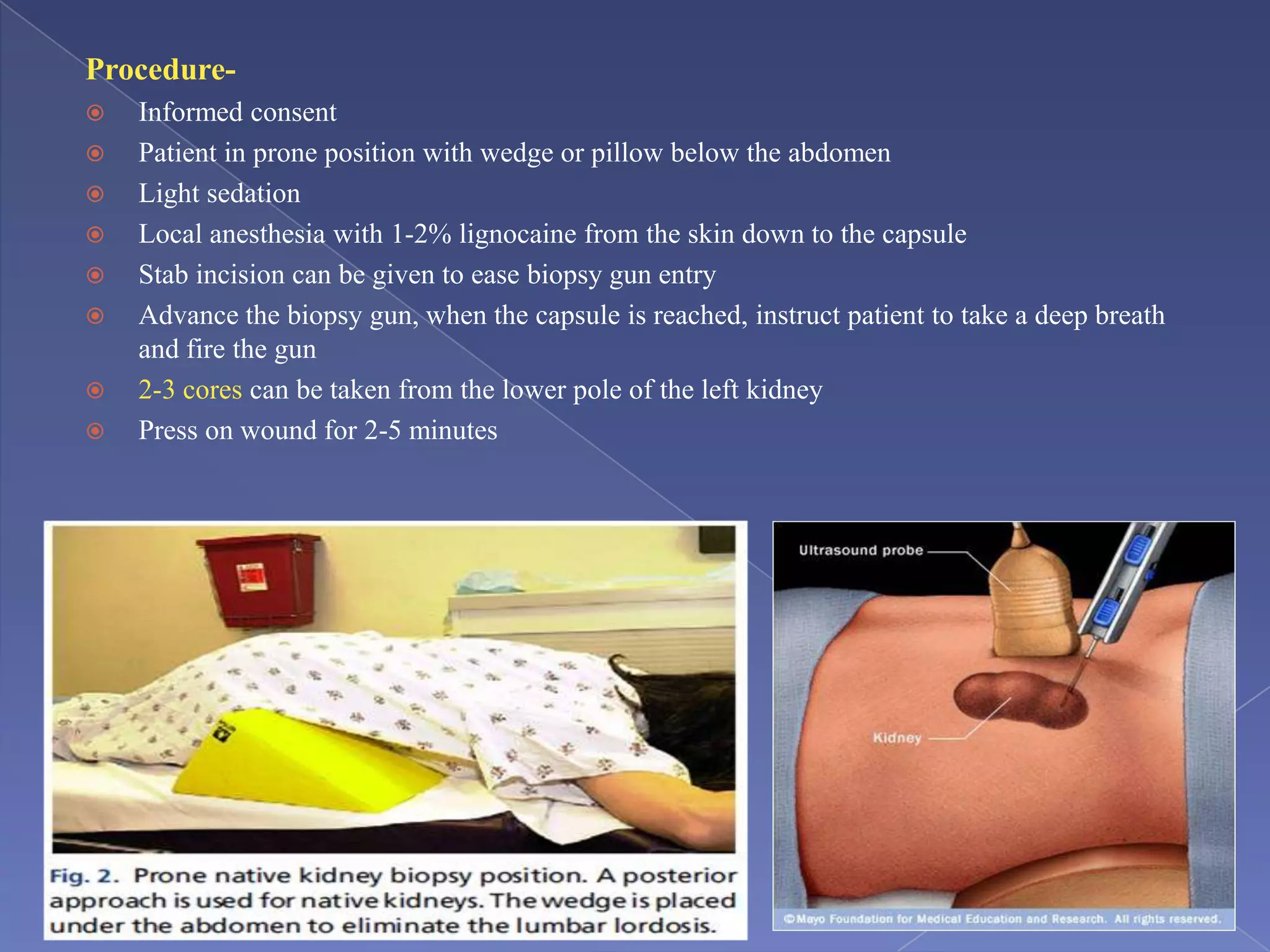
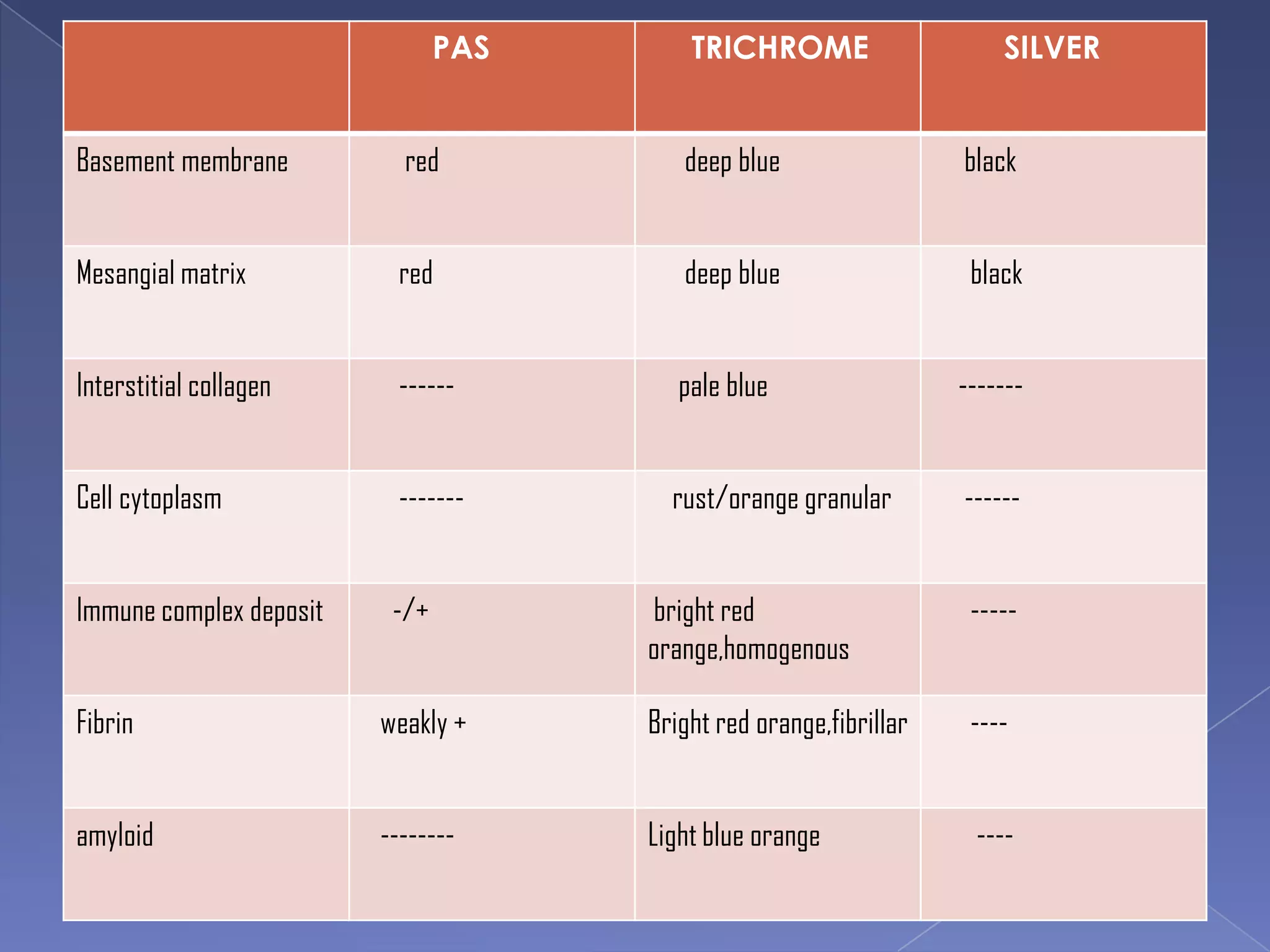
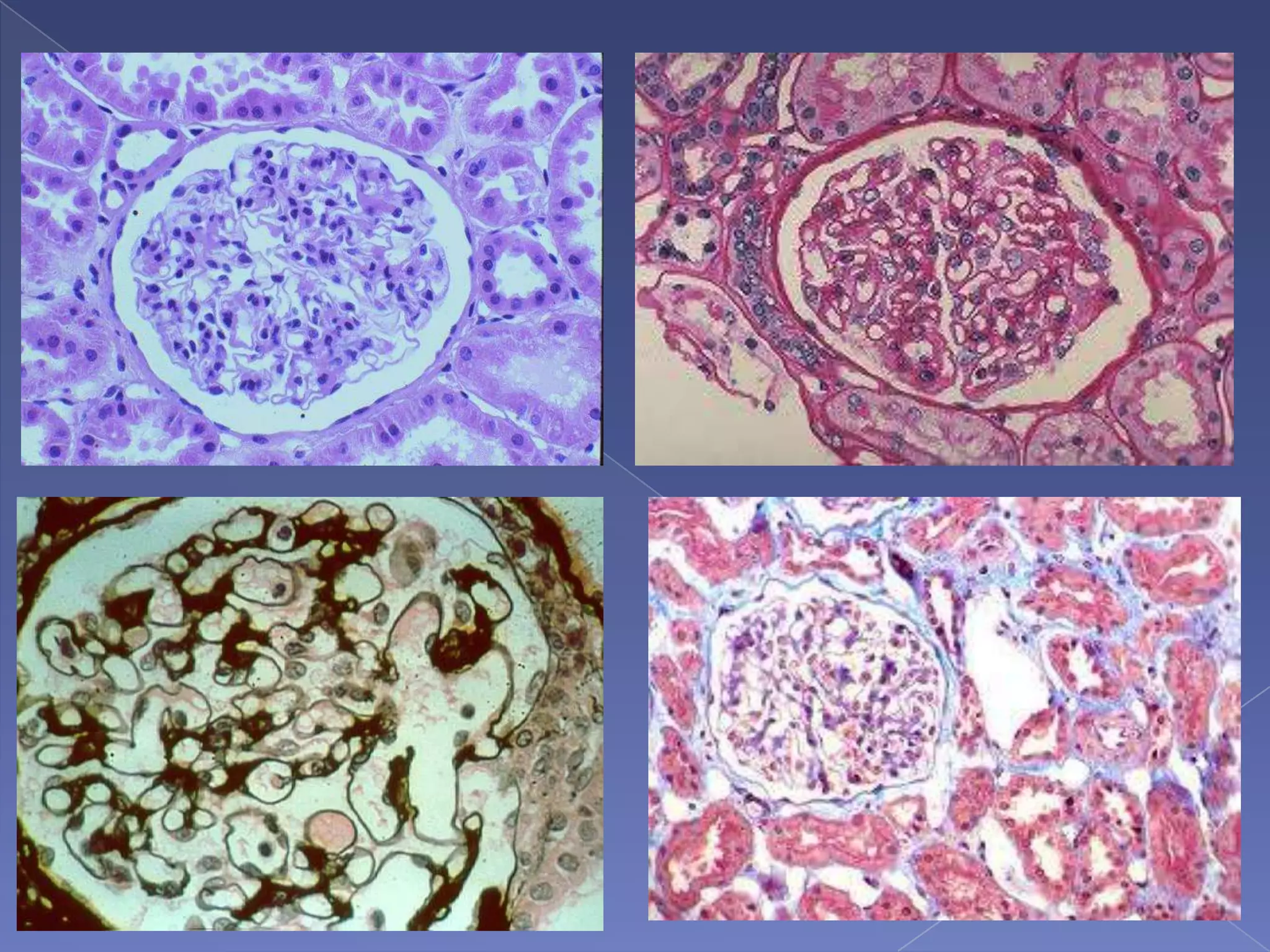
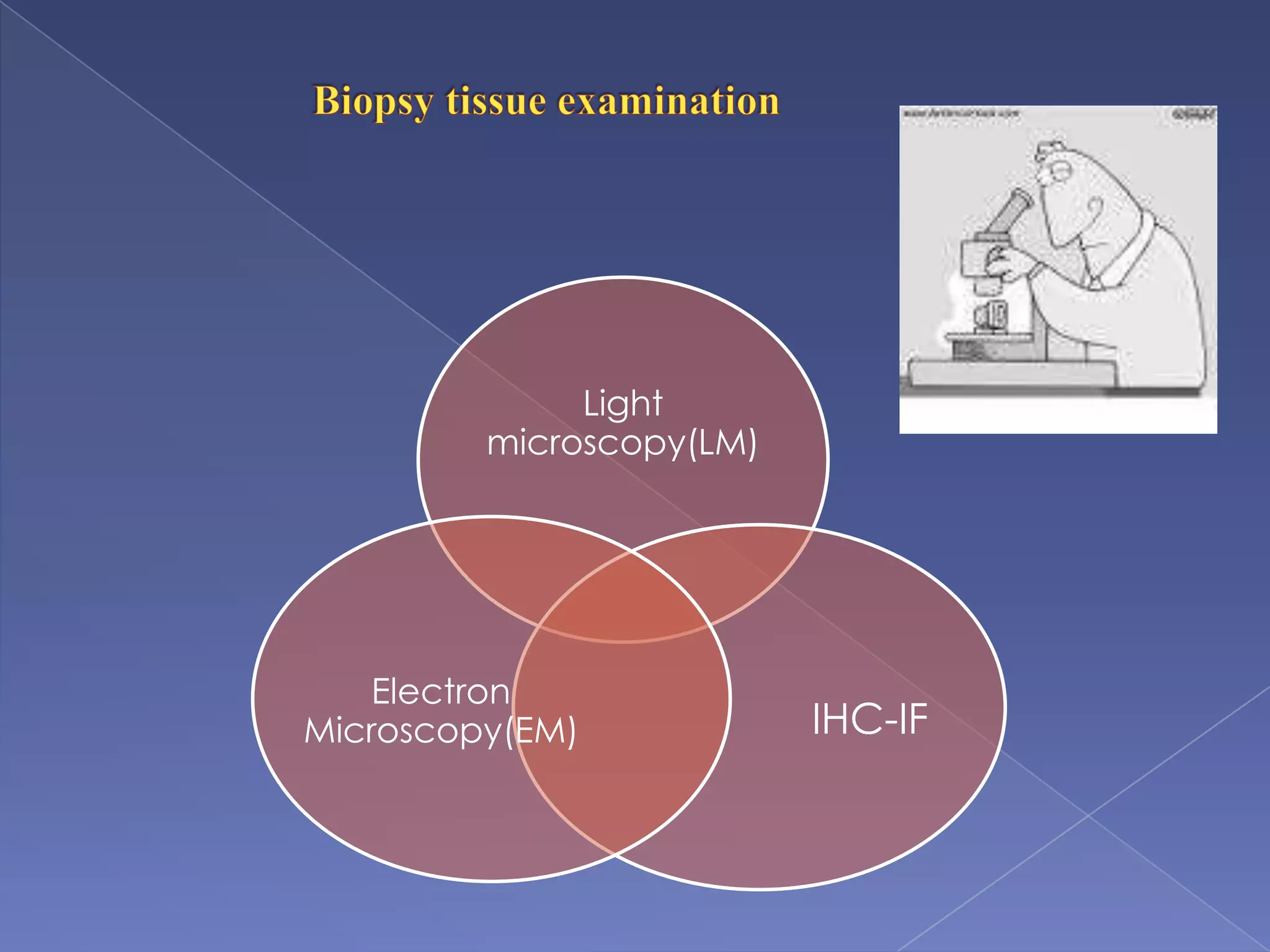
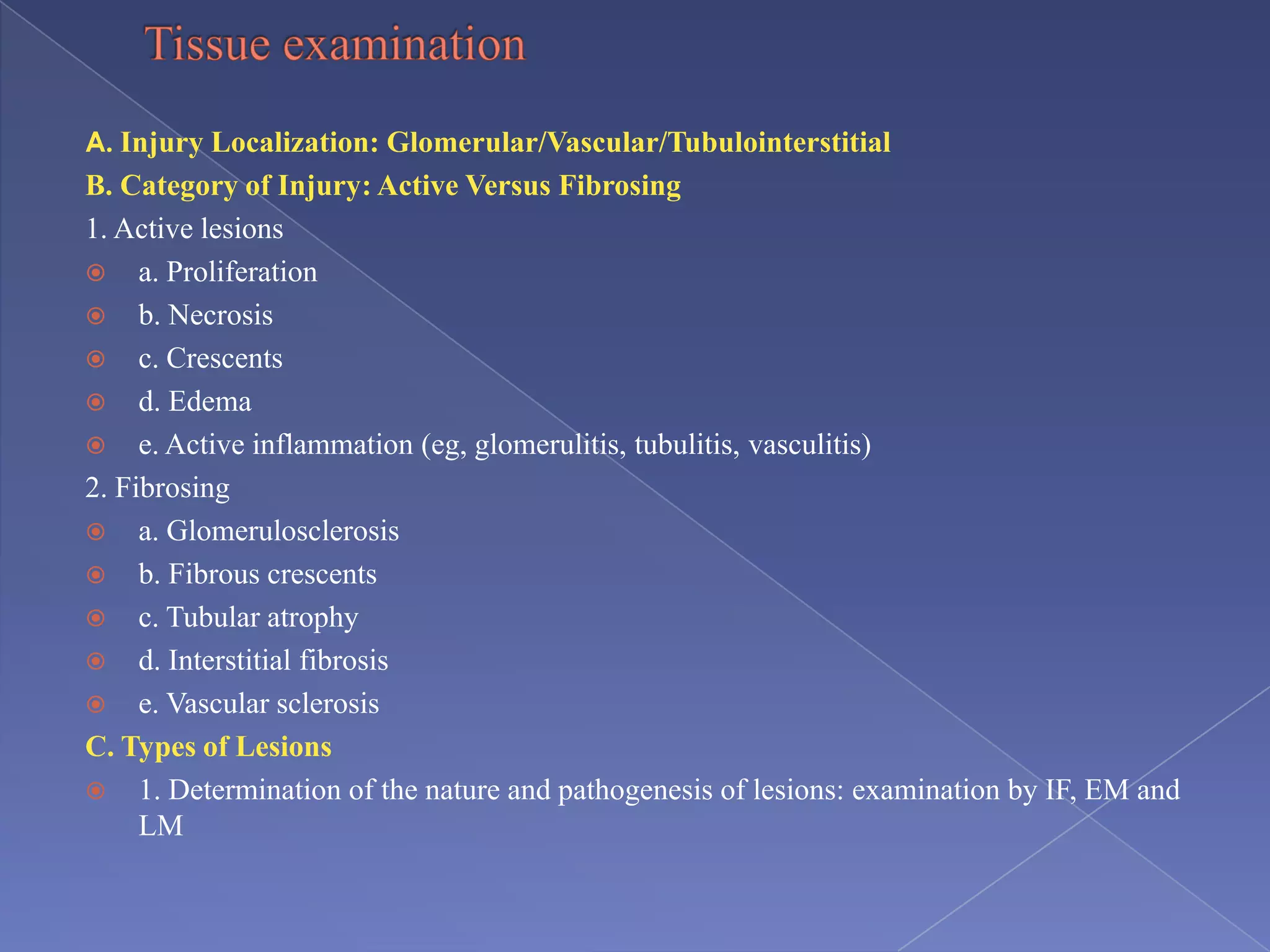
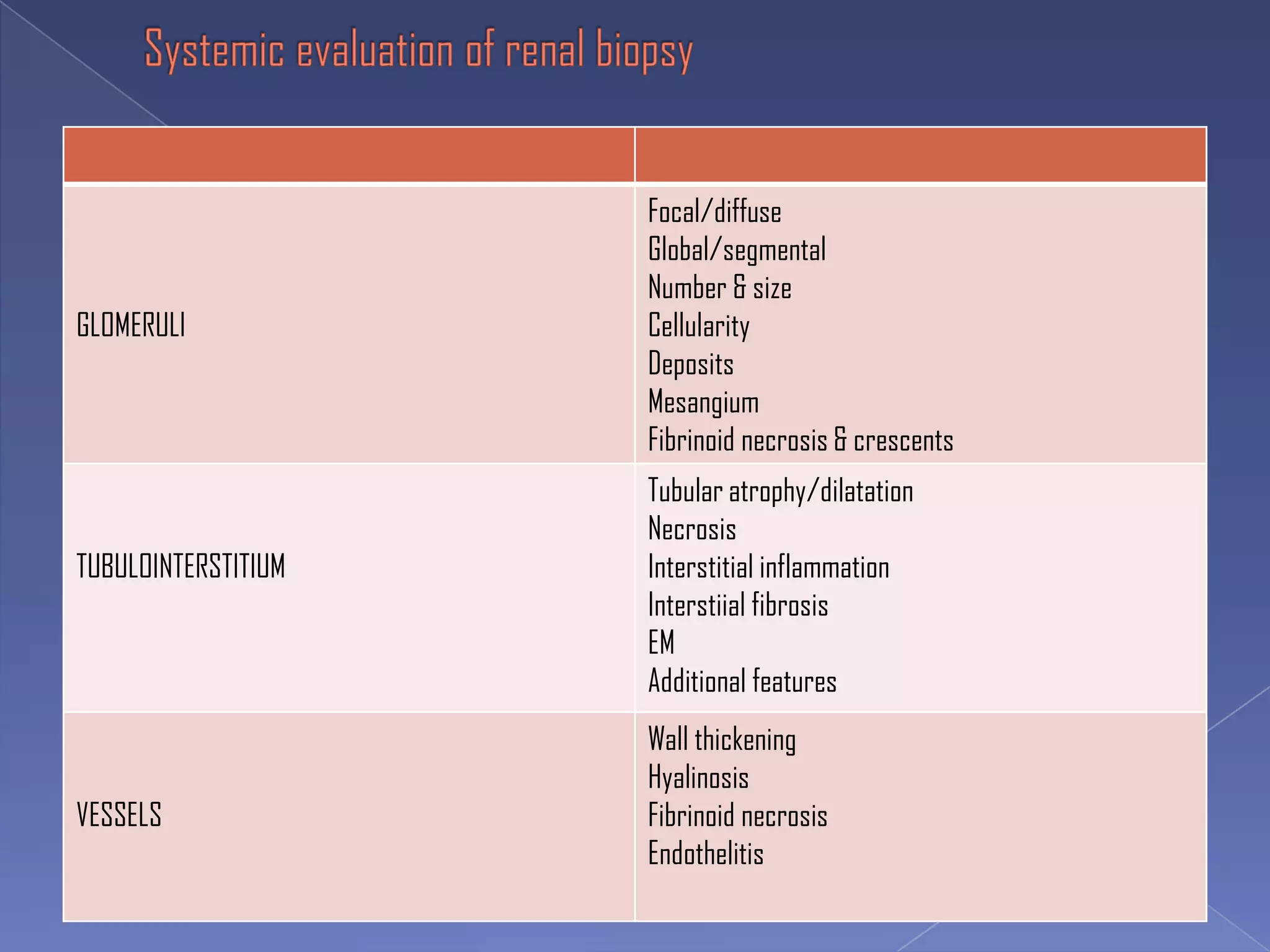
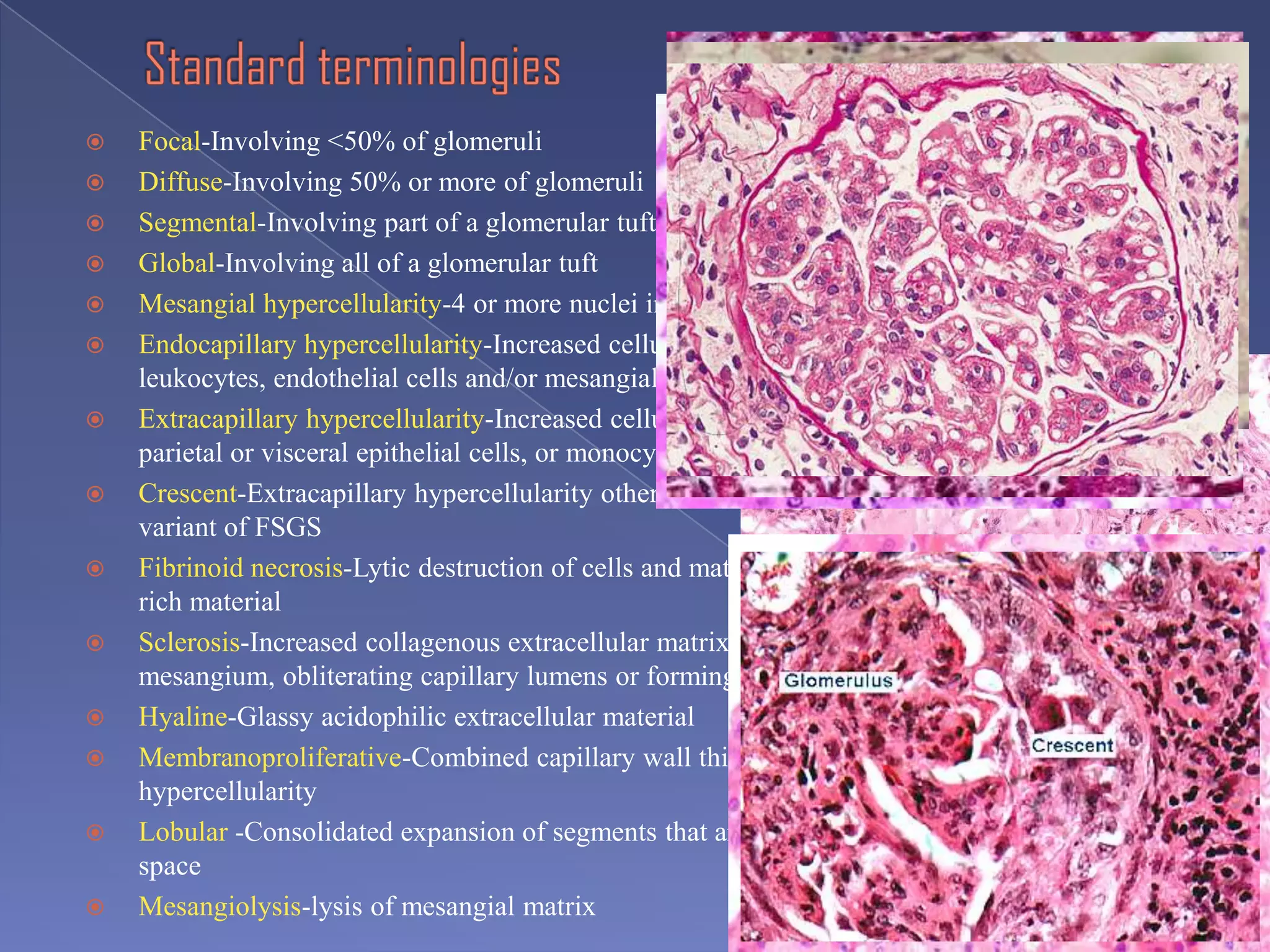
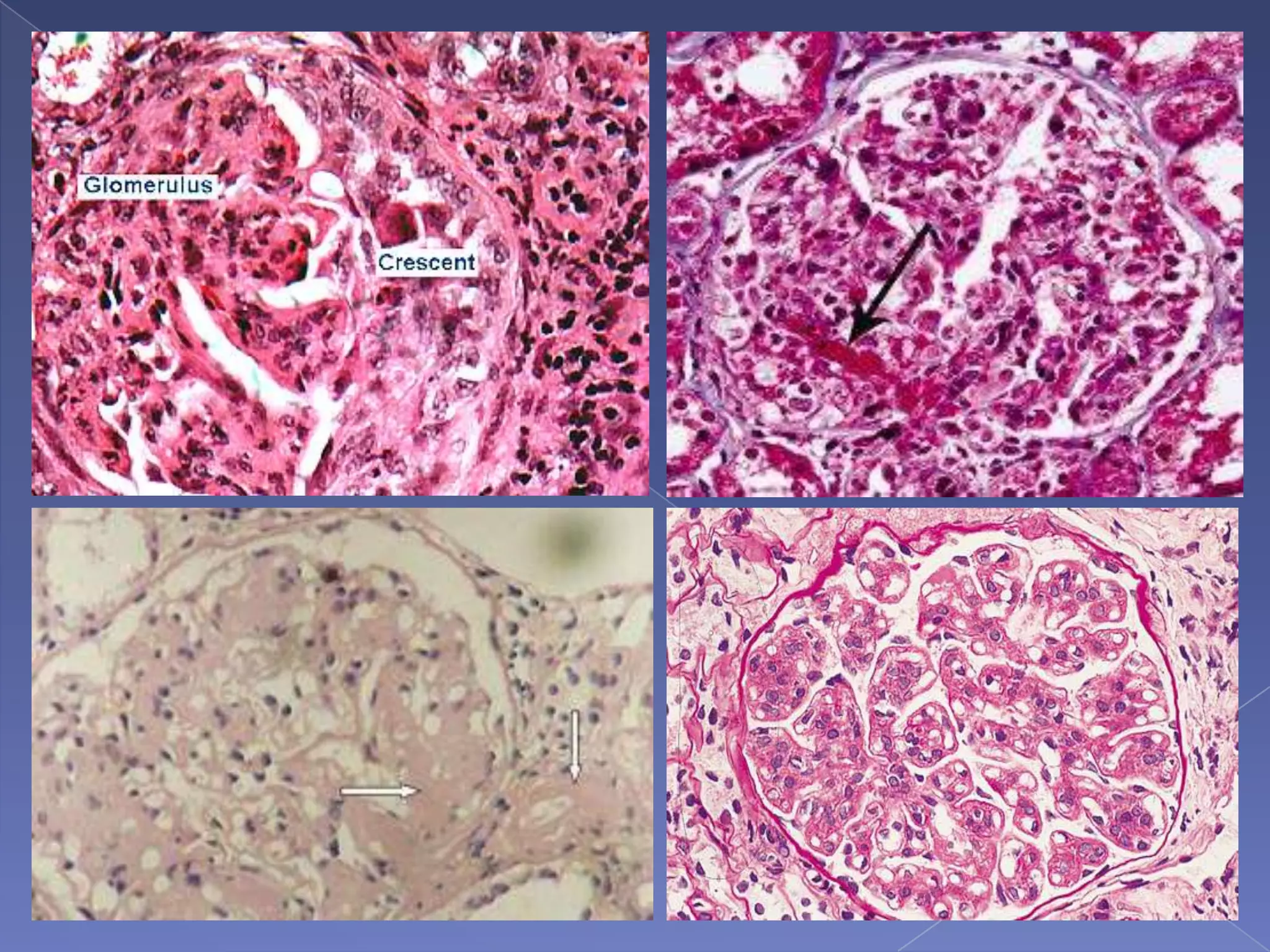
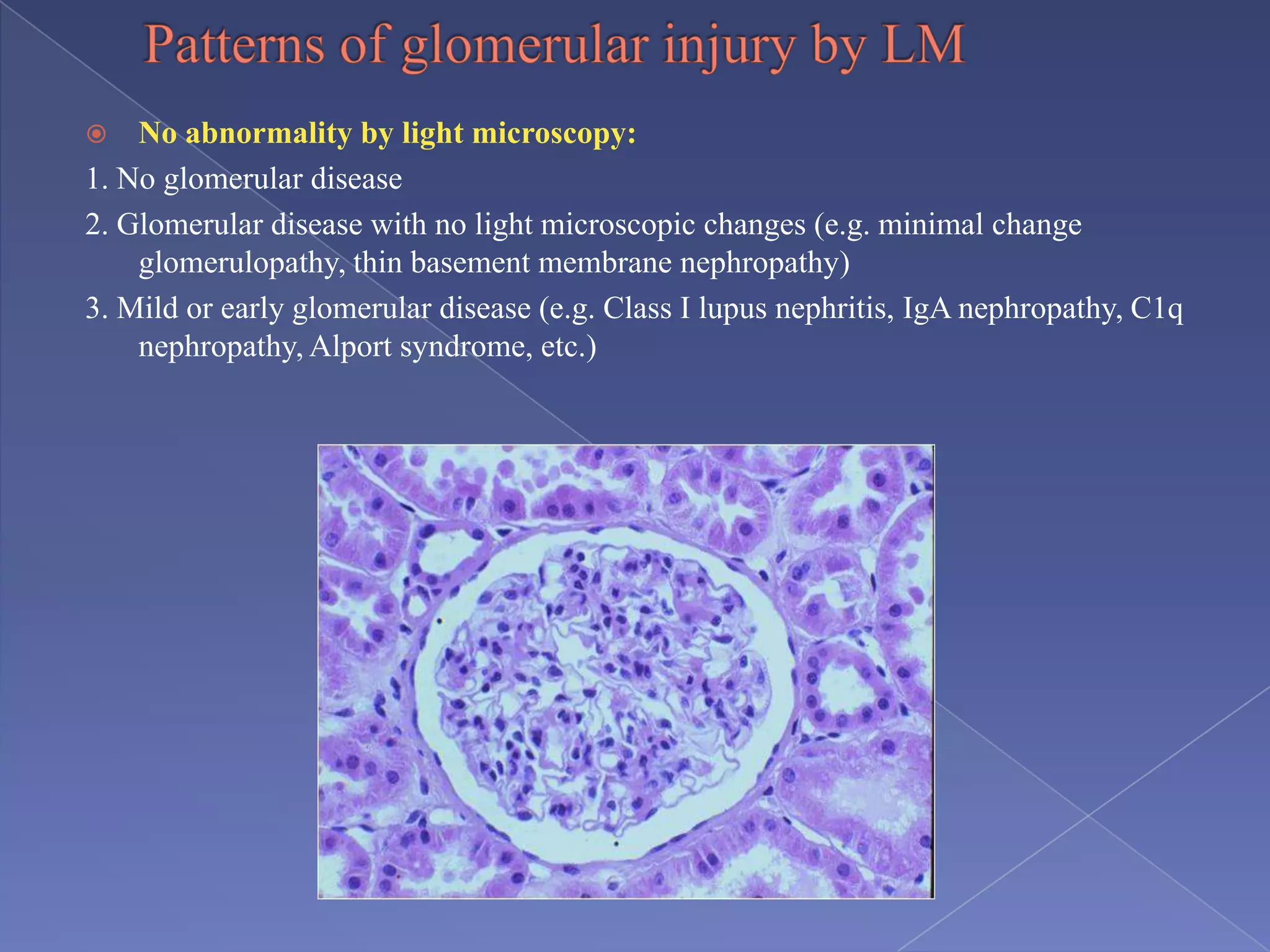
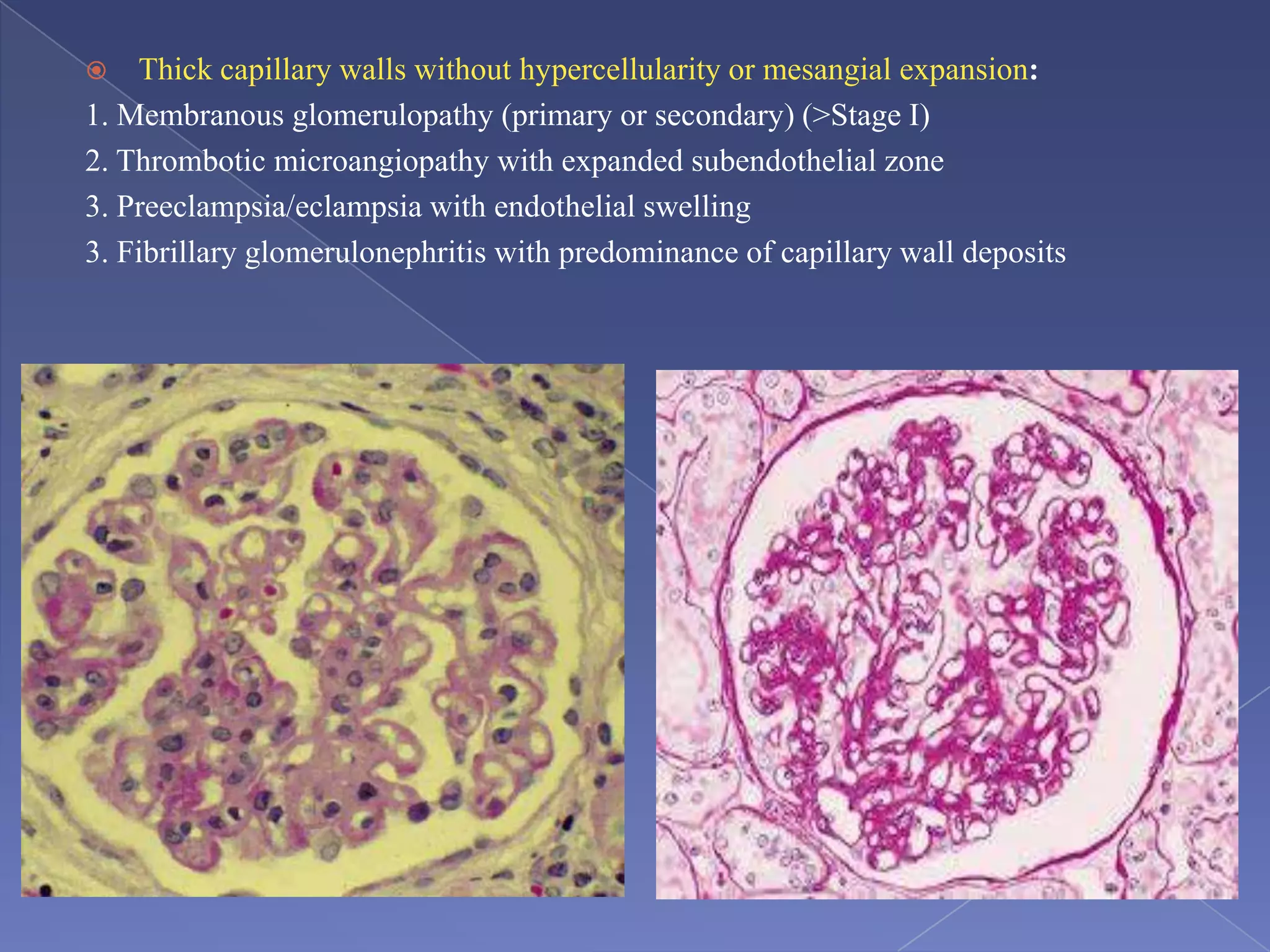
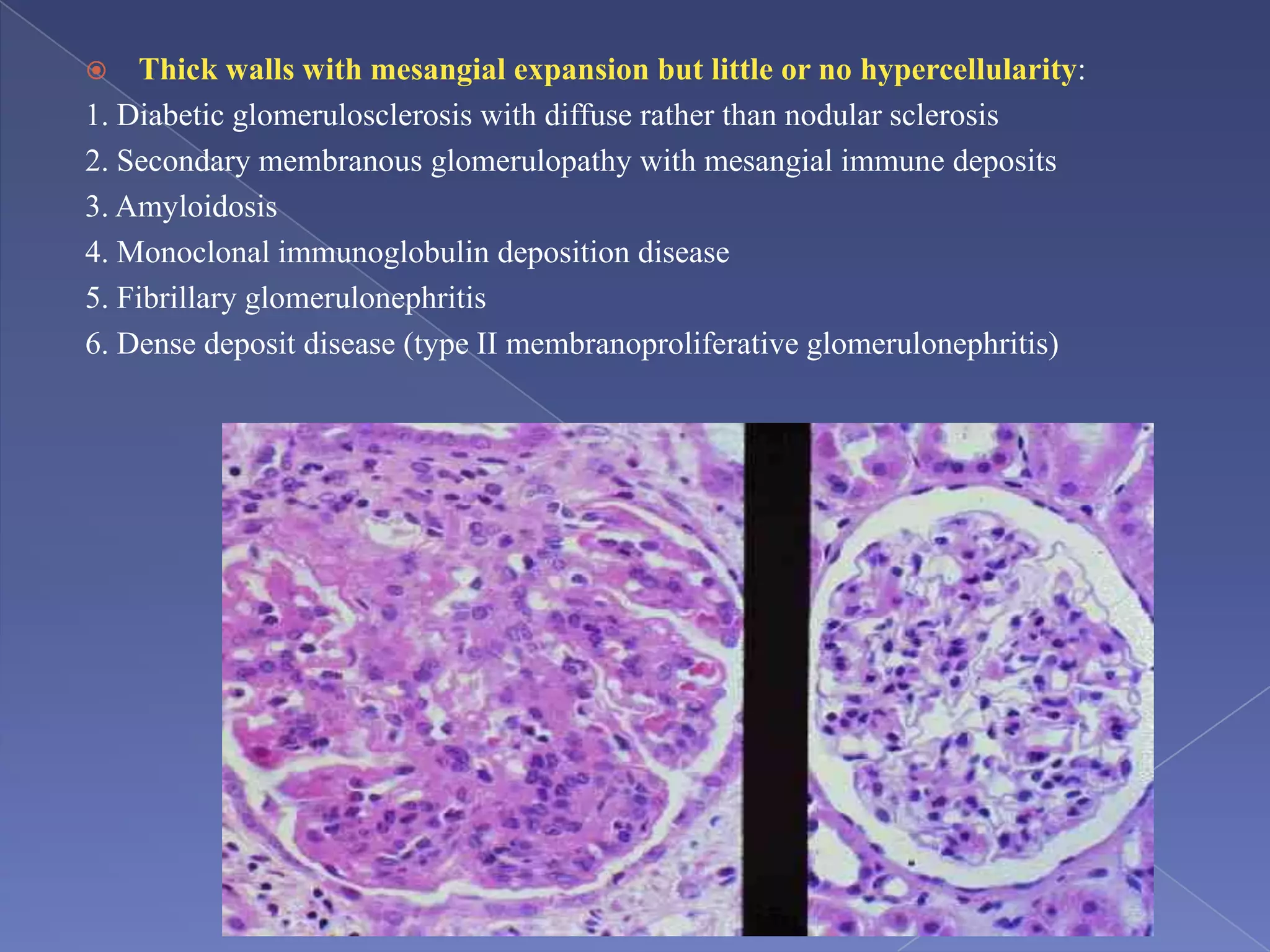
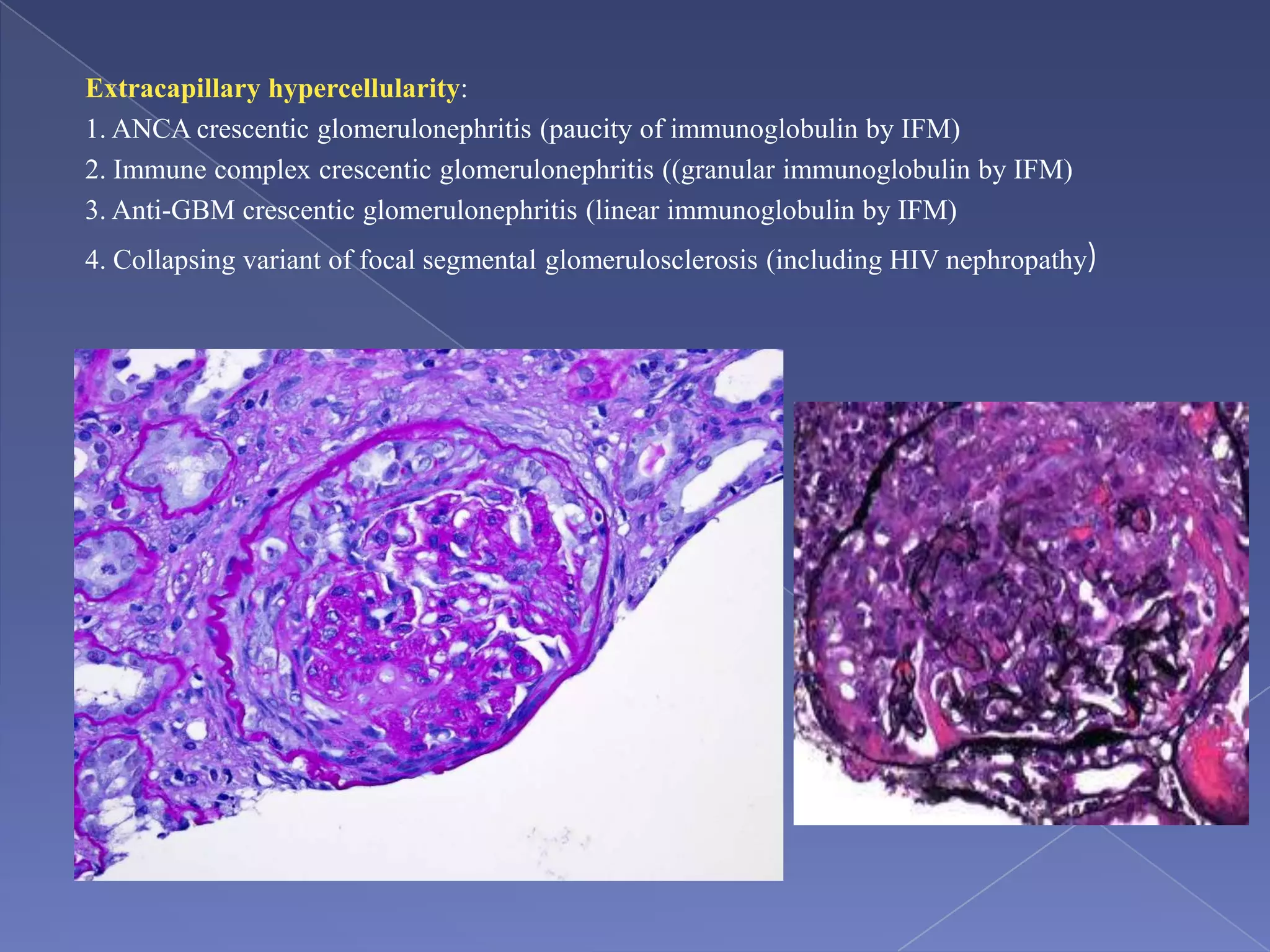
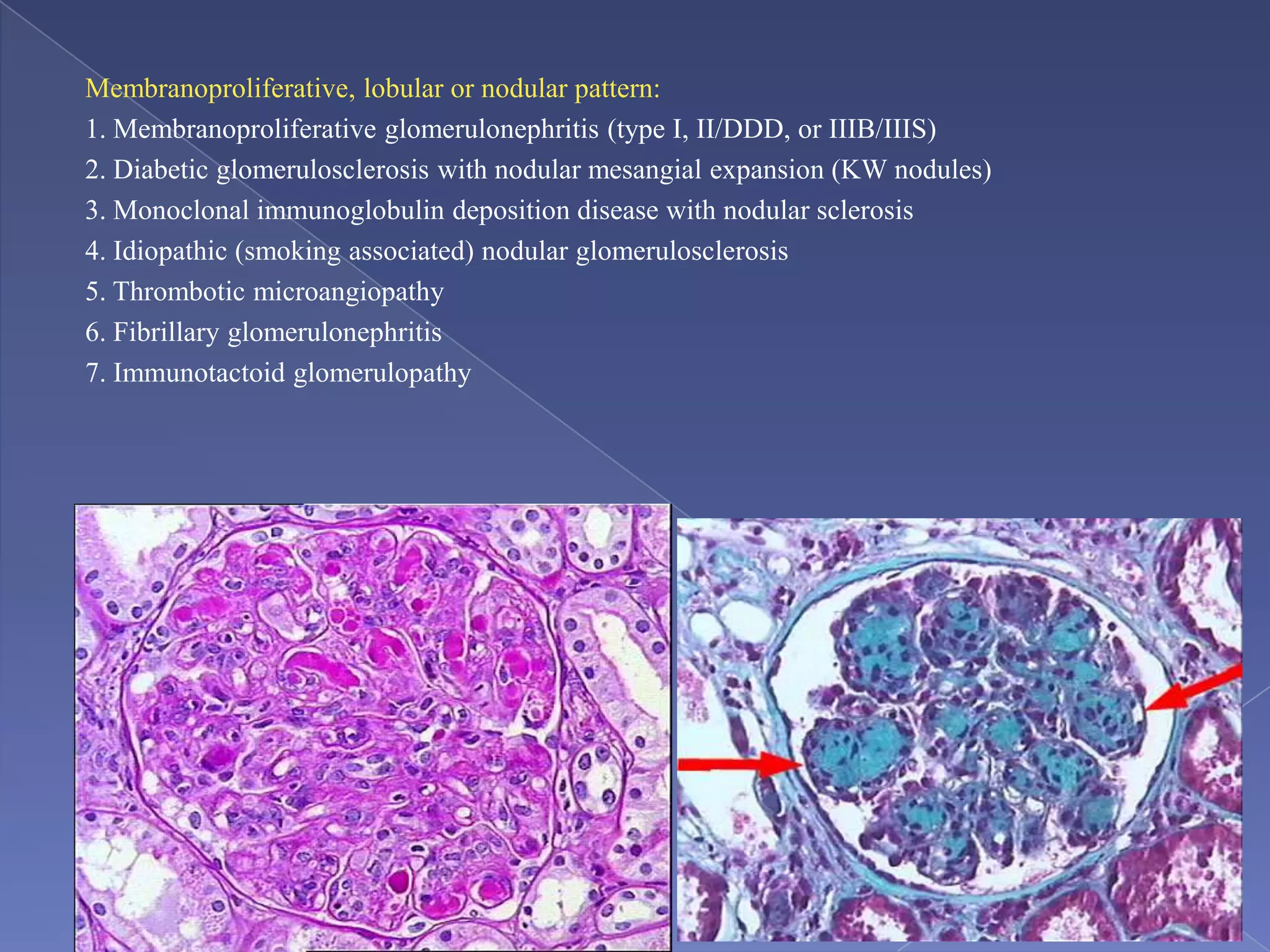
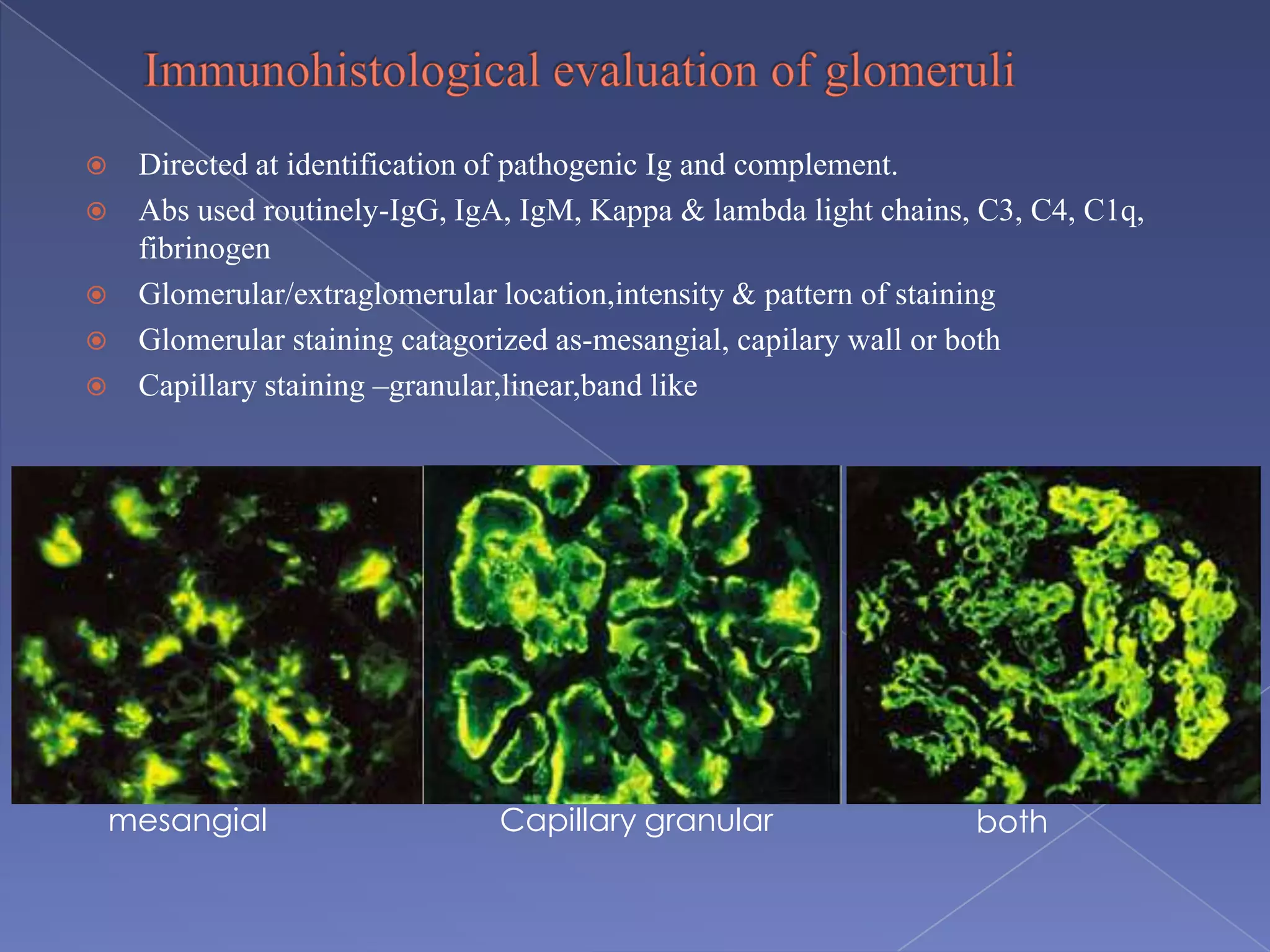
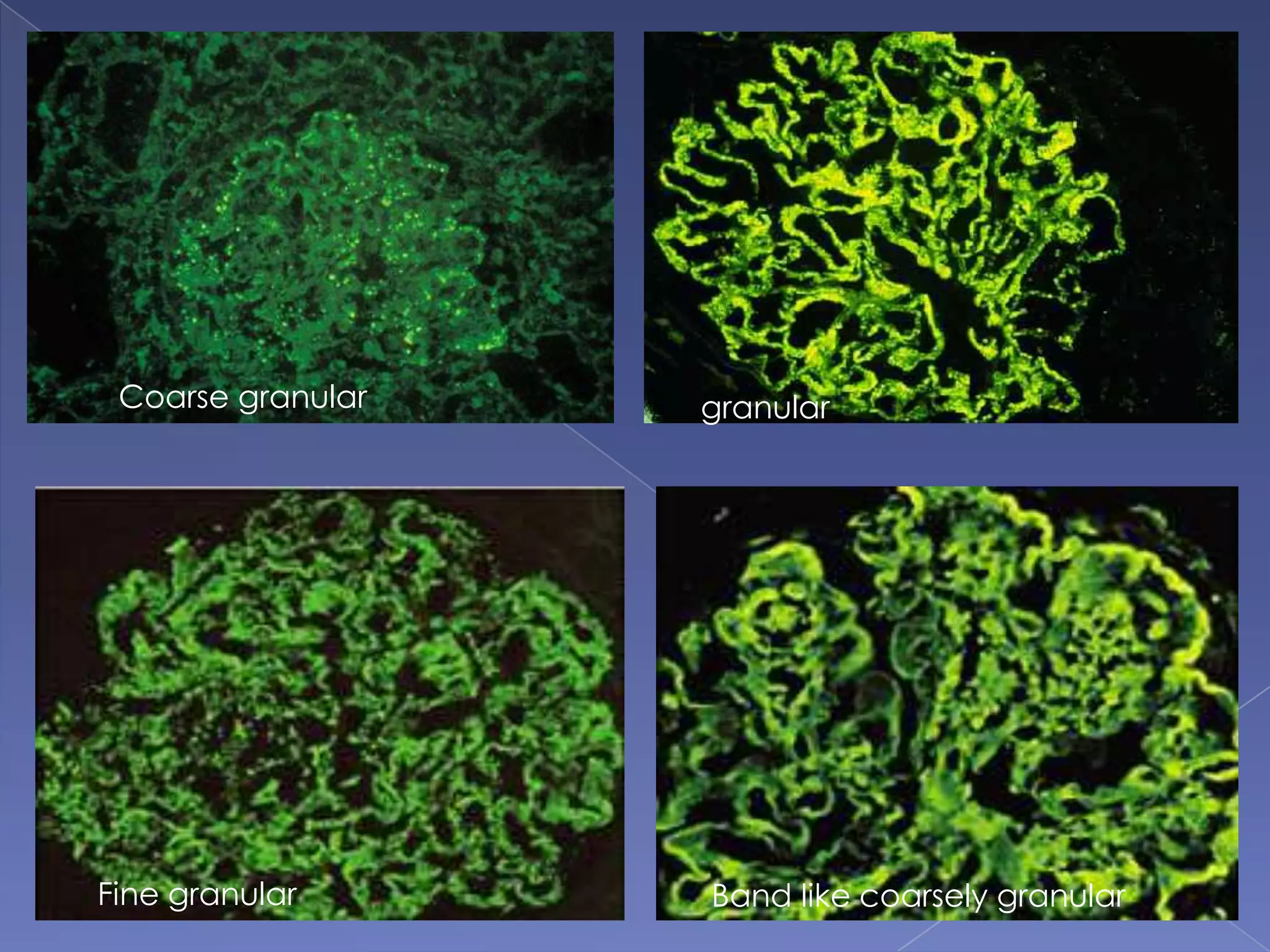
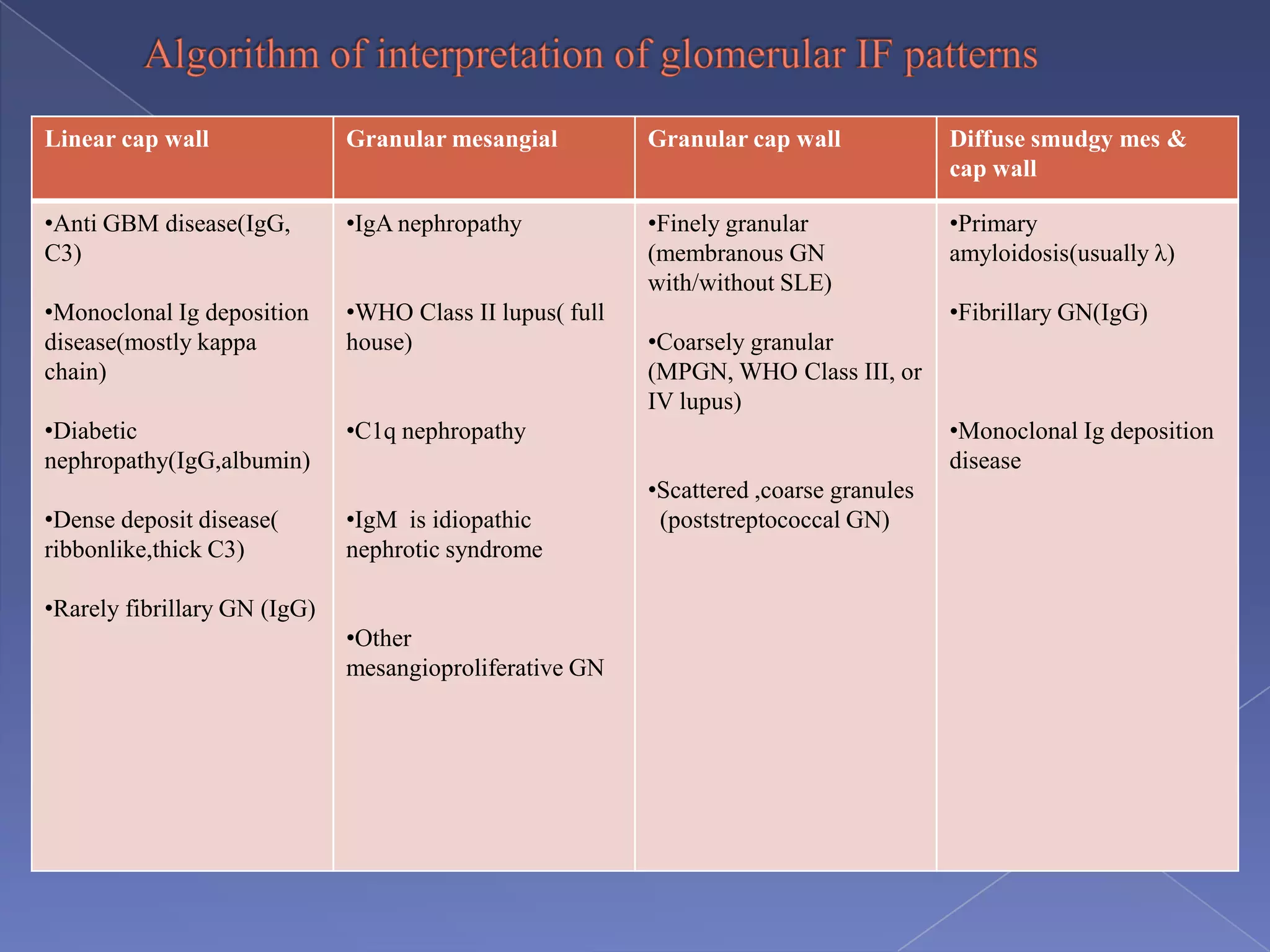
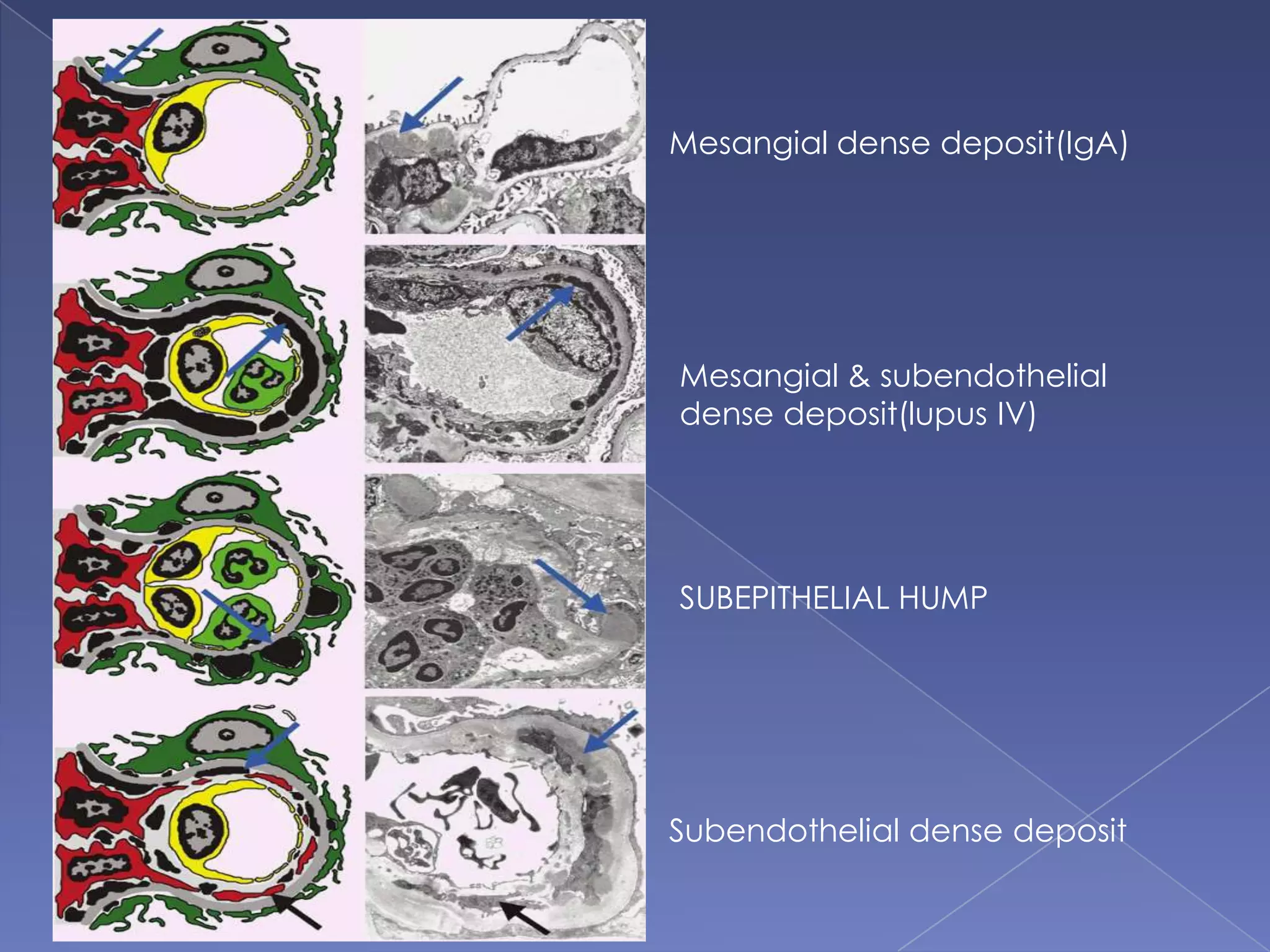
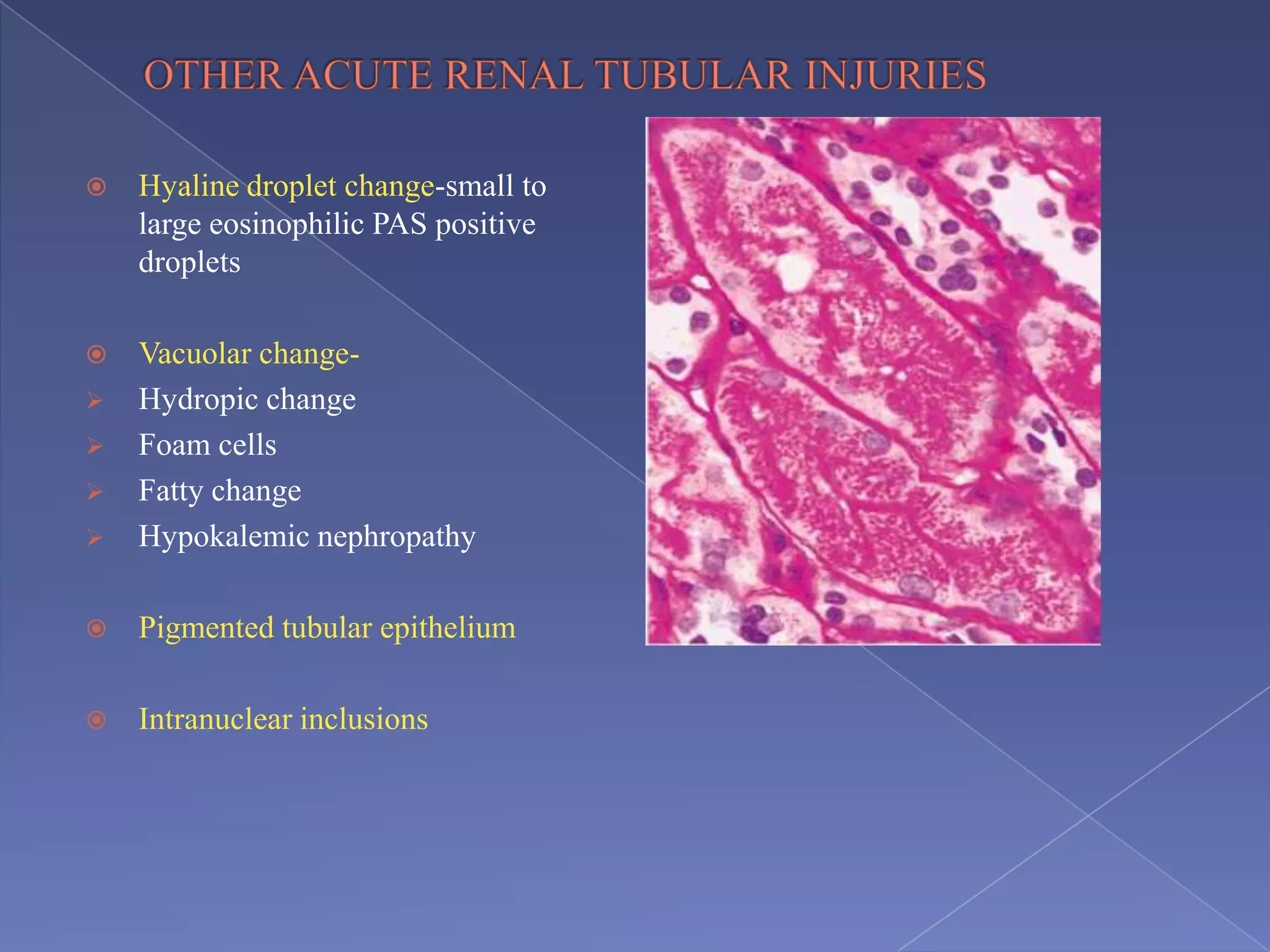
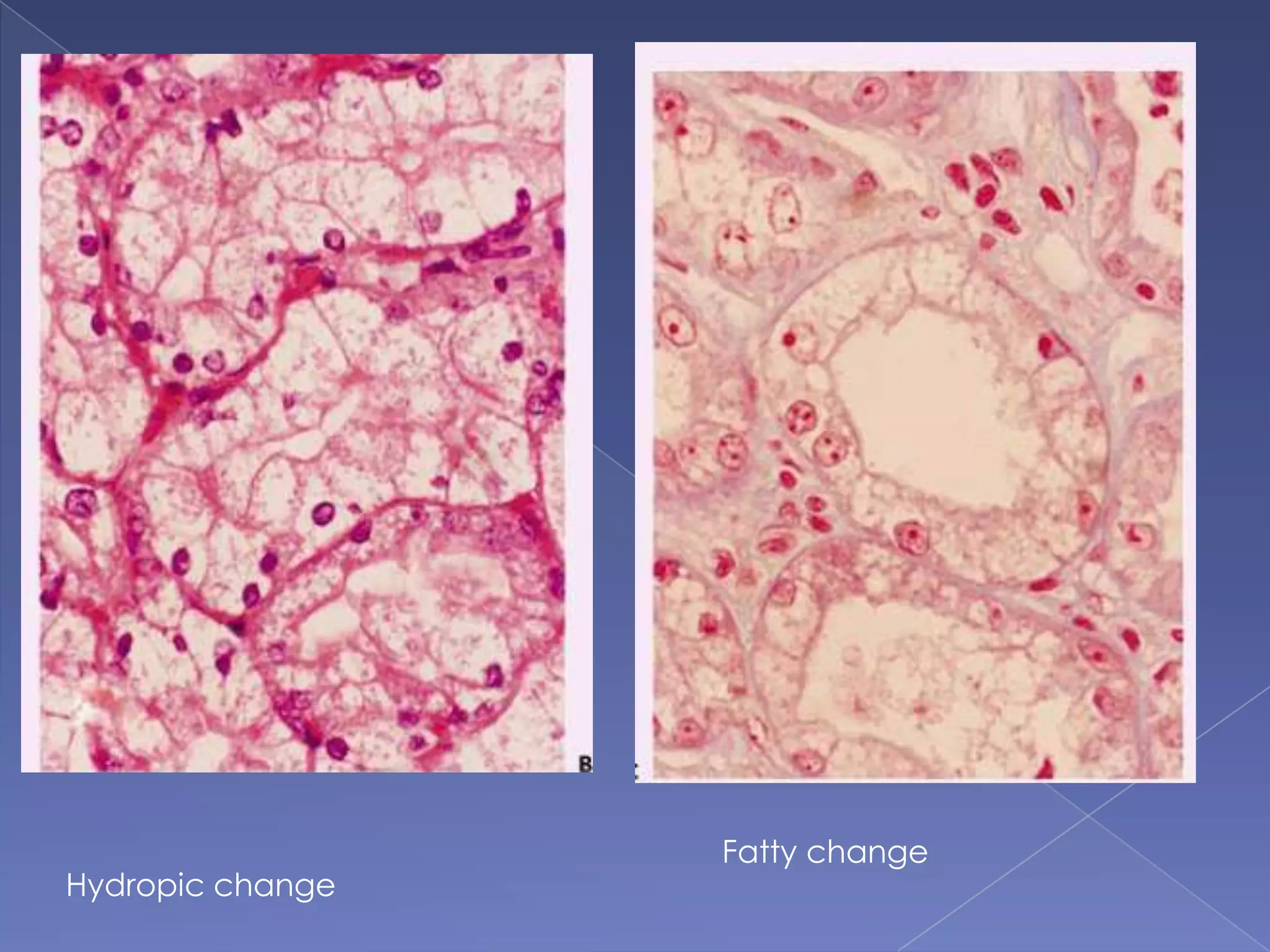
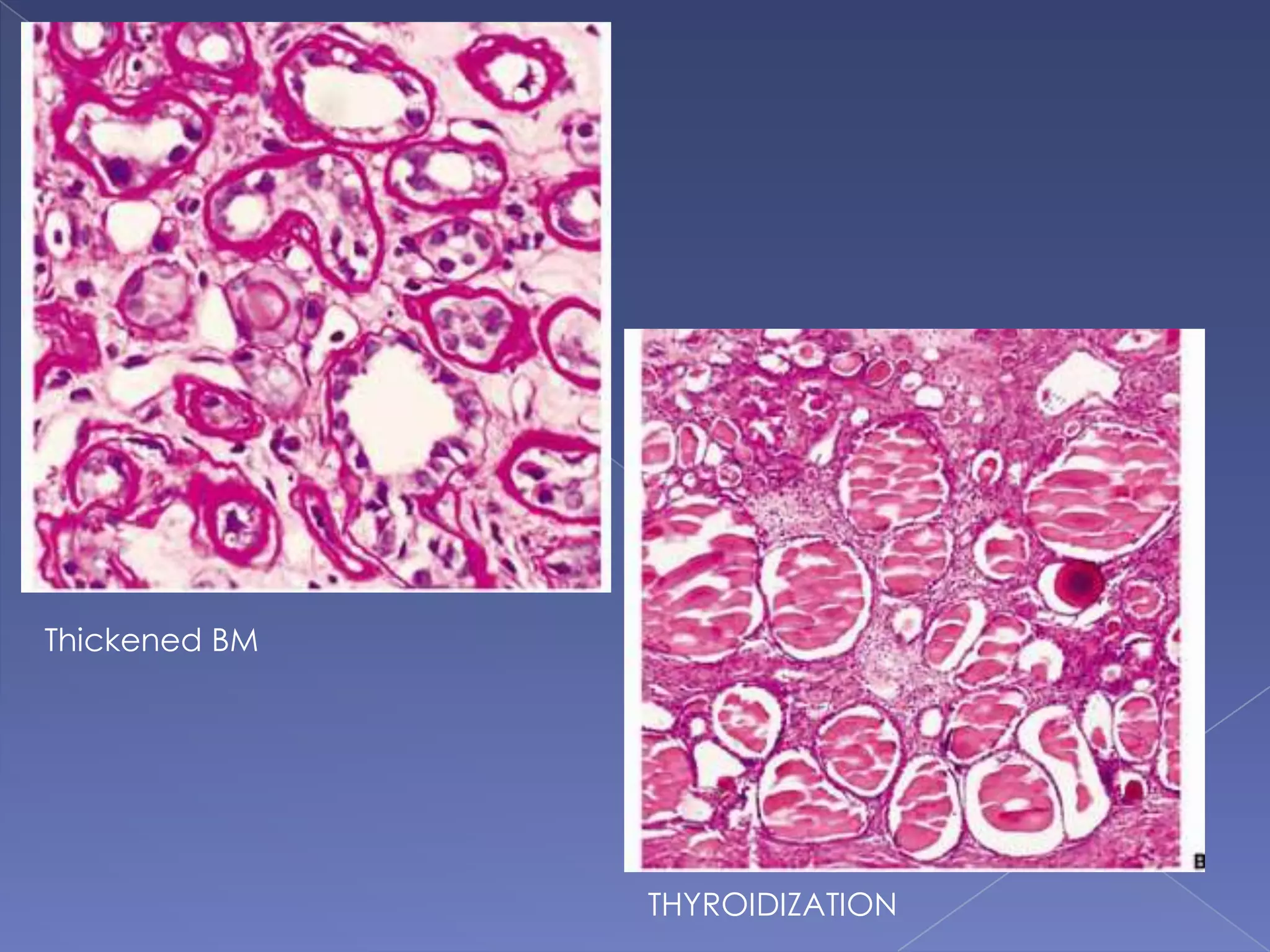
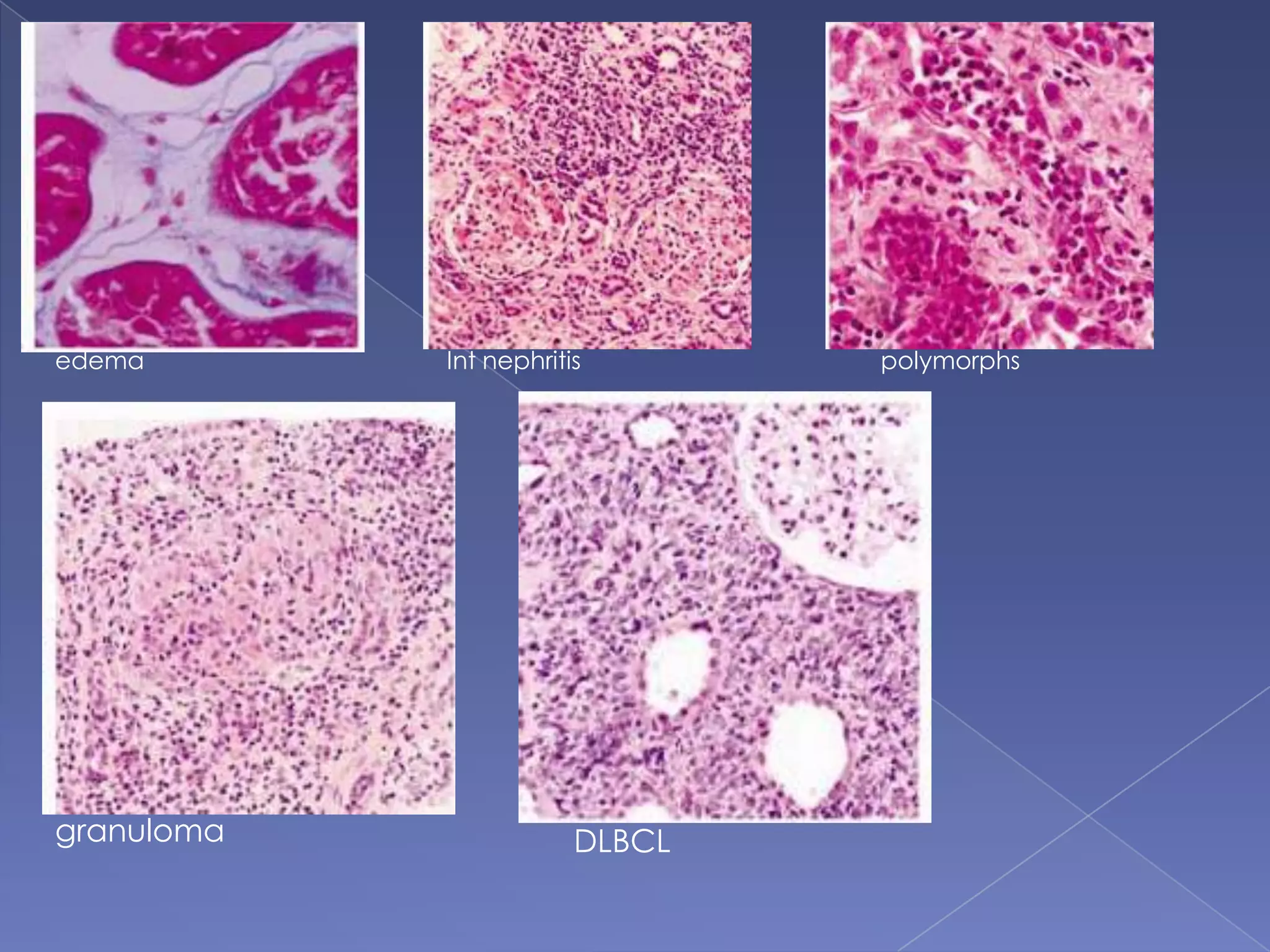
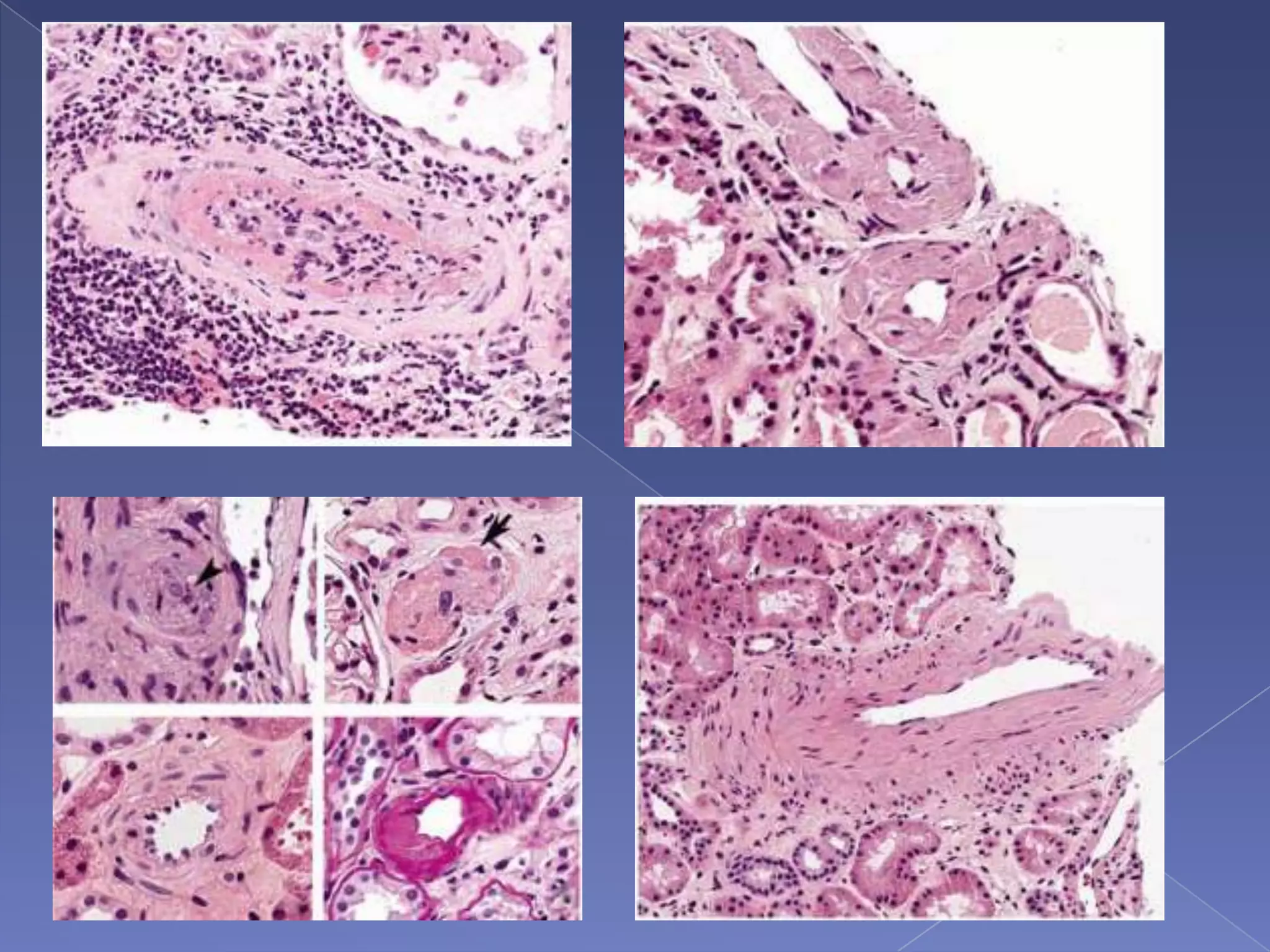
The kidney is a bean-shaped organ that plays important roles in excreting waste, regulating fluids, and balancing ions. It contains millions of nephrons, the functional units that filter blood to form urine. A renal biopsy examines kidney tissue under microscopy to diagnose conditions affecting the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, or blood vessels. The biopsy sample is prepared through fixation, sectioning, and staining to analyze by light microscopy, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy. This allows characterization of lesions by their location, category of injury (active vs fibrotic), and identification of pathogenic antibodies or complement deposits to determine the specific cause of kidney disease.