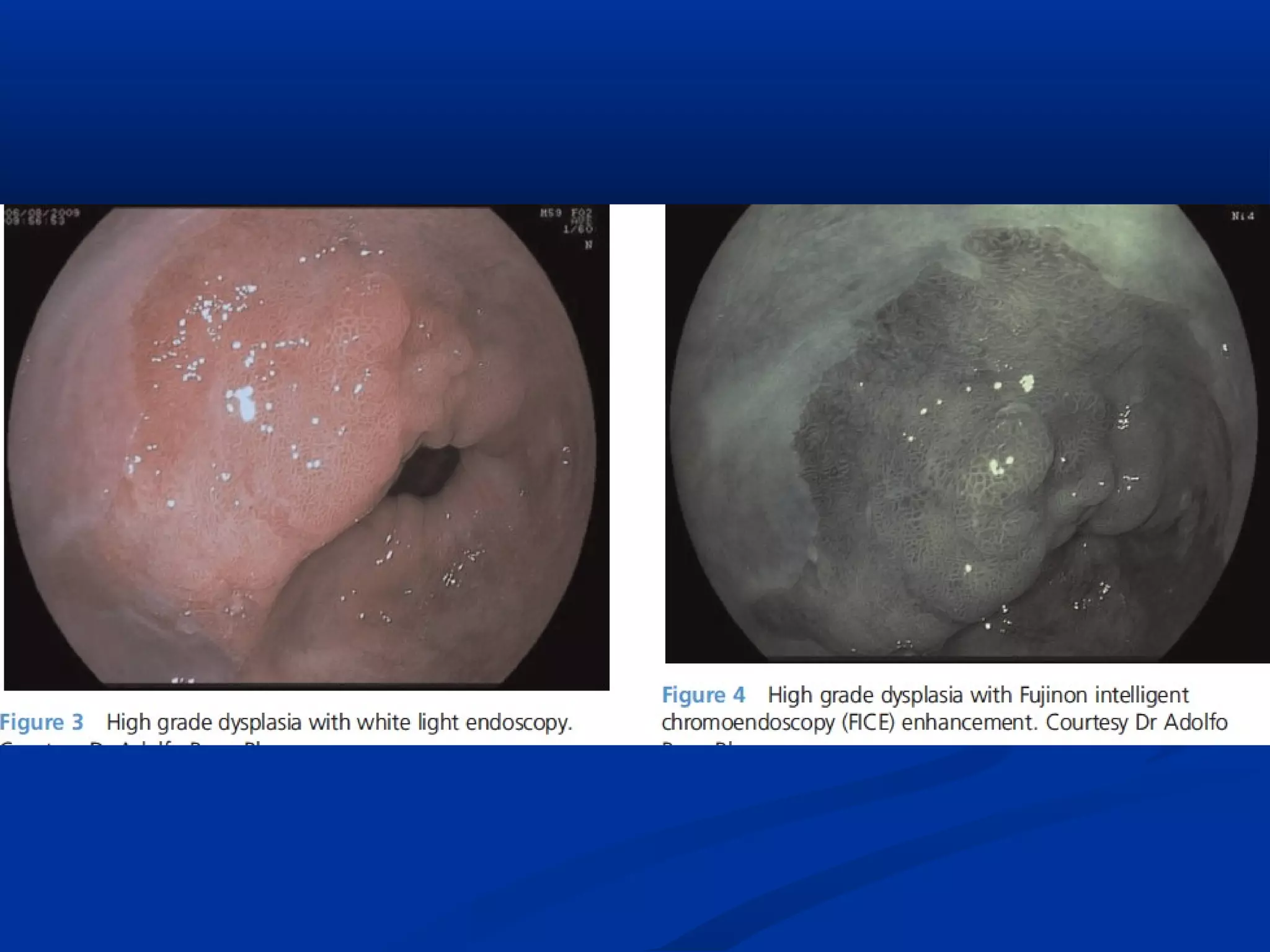
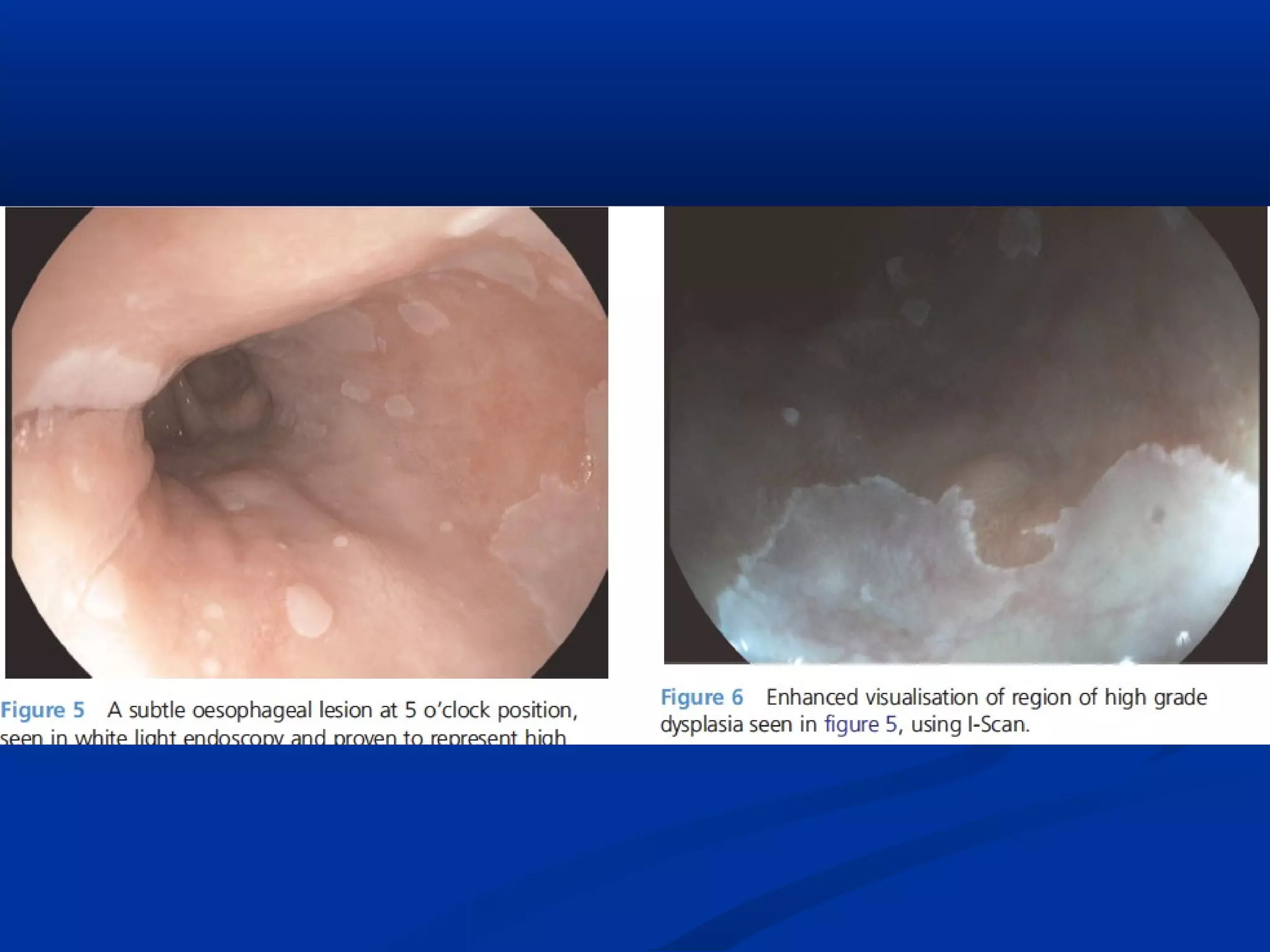
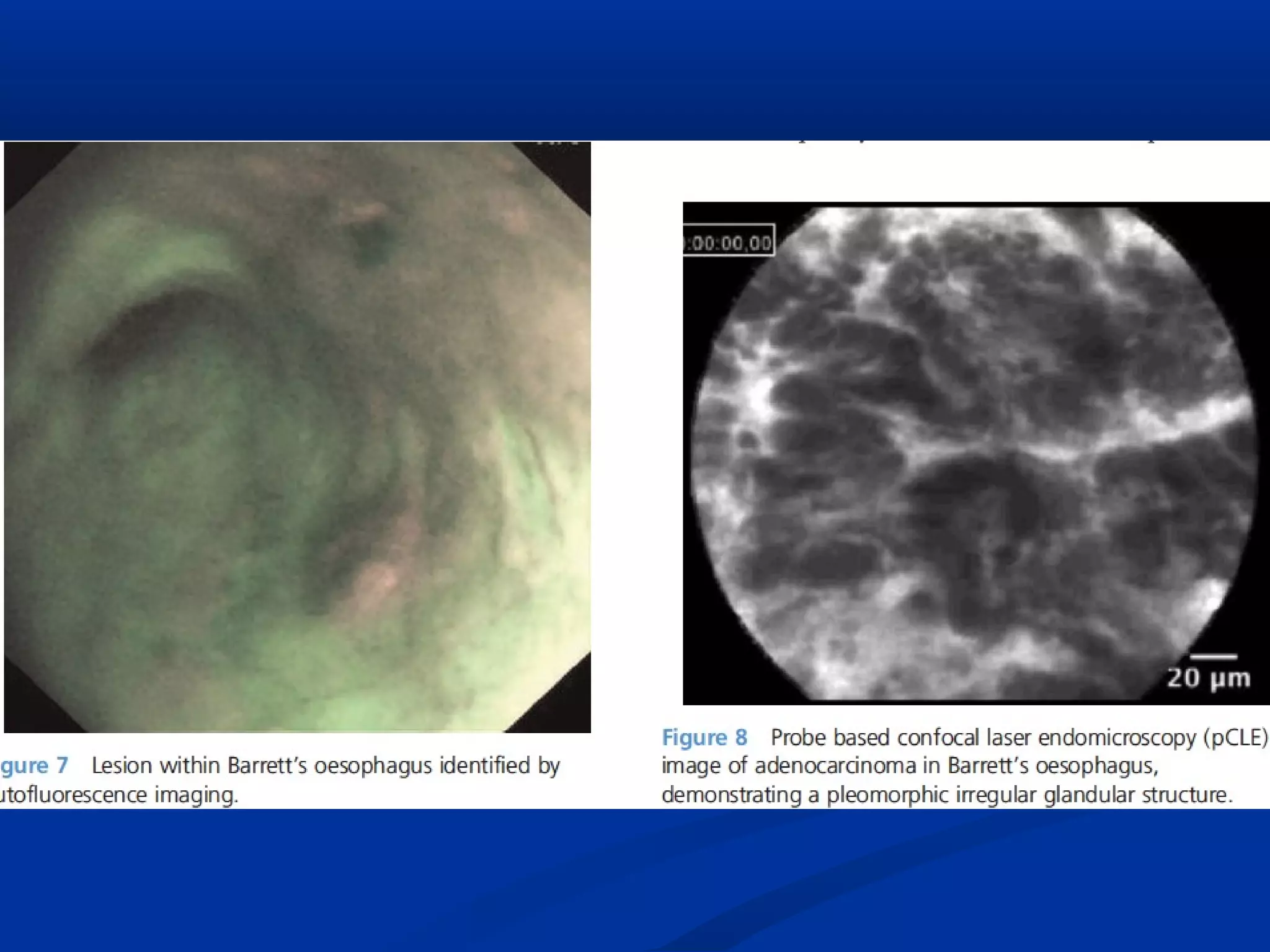
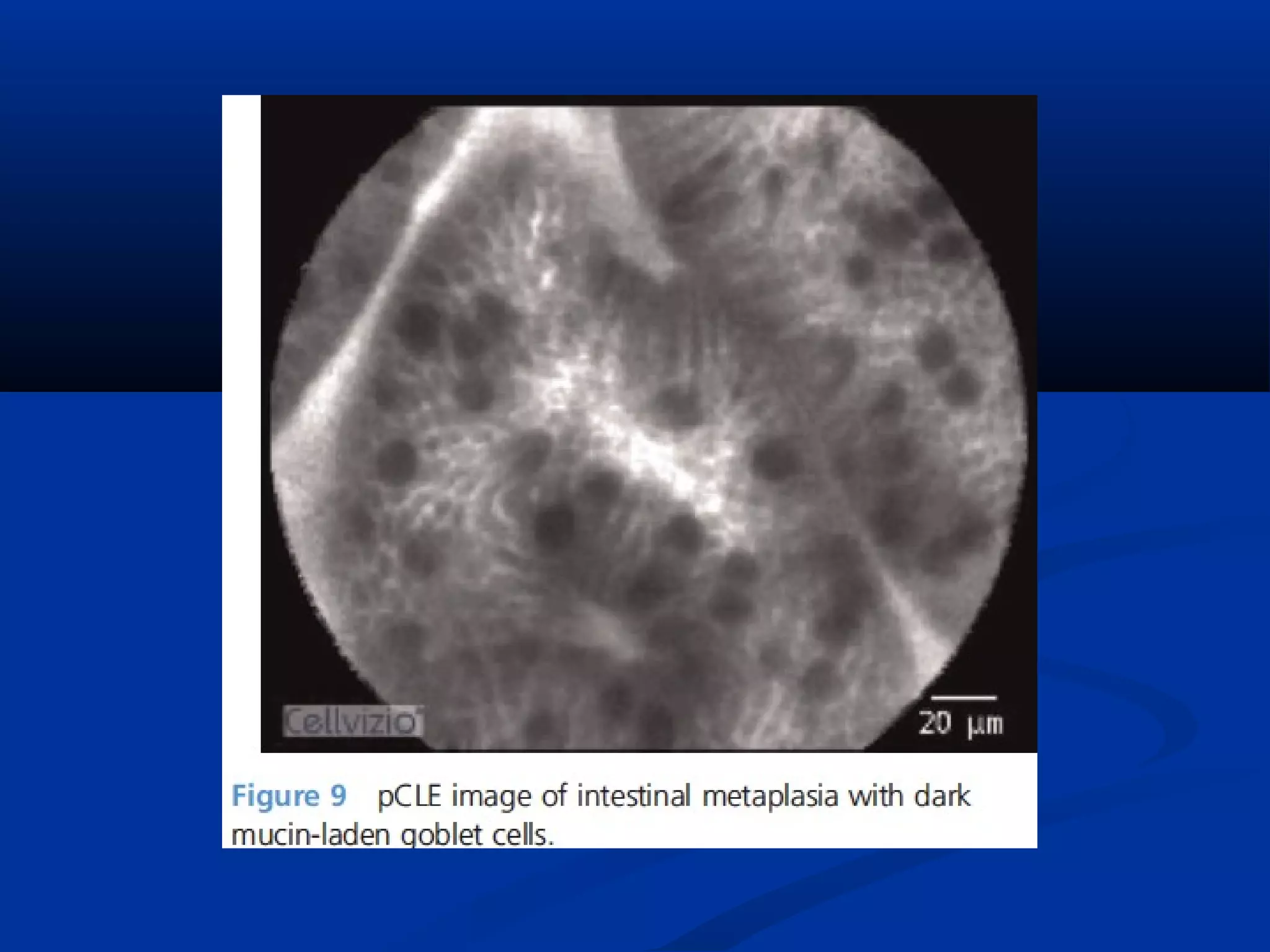
This document discusses various advanced imaging techniques used in gastrointestinal endoscopy to identify early pathology and lesions. It describes technologies like high-definition white light endoscopy, narrow-band imaging, autofluorescence imaging, and confocal laser endomicroscopy. While these techniques have shown promise in clinical trials, most are only widely available in tertiary hospitals. Optical imaging provides improved diagnostic capability and enables real-time "optical biopsies," representing progress toward more effective detection and management of treatable early gastrointestinal diseases.