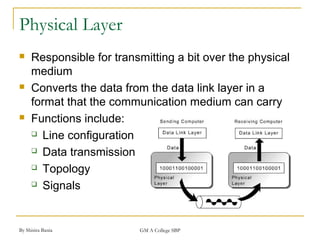
The document discusses key concepts in networking including line configurations, topologies, network types, transmission modes, the hierarchical network model, and the OSI model. It provides details on the point-to-point and multipoint line configurations, five basic topologies (bus, star, ring, tree, mesh), three main network types (LAN, MAN, WAN), and three transmission modes (simplex, half-duplex, full-duplex). It also describes the three layers of Cisco's hierarchical network model (core, distribution, access) and the seven layers of the OSI model.