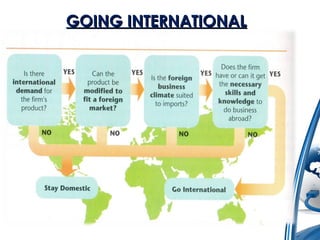
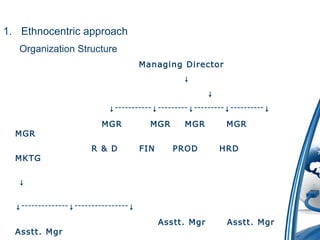
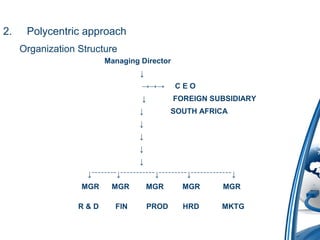
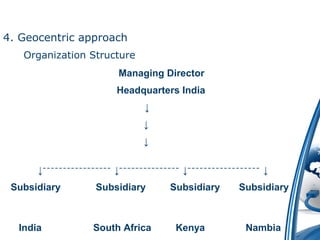
The presentation outlines the fundamentals of international business, focusing on its definitions, nature, scope, features, importance, various approaches, motivations, entry strategies, and barriers. It emphasizes the significance of adapting to global markets and highlights the roles of international organizations like GATT and the IMF. The document also addresses the advantages and disadvantages of engaging in international business and the reasons behind its recent growth.