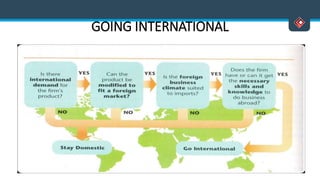
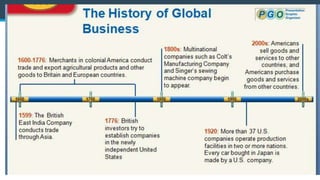
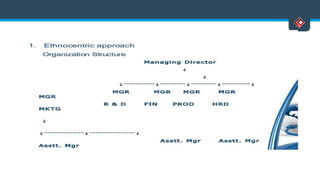
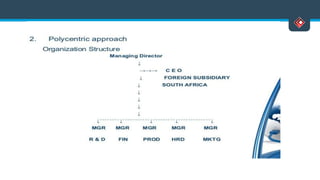
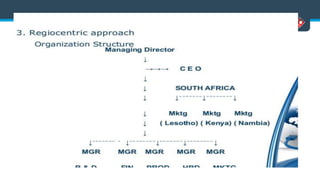
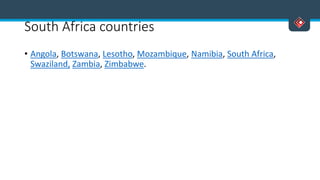
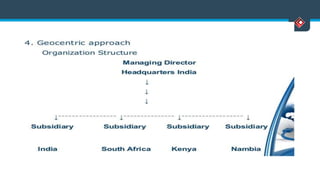
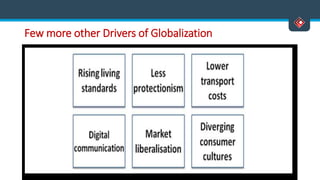
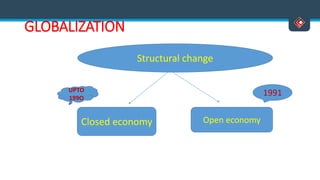
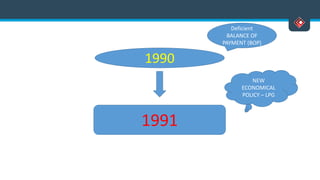
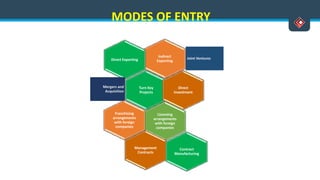
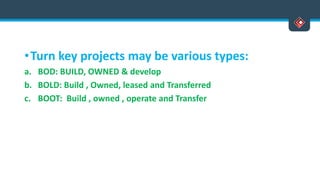
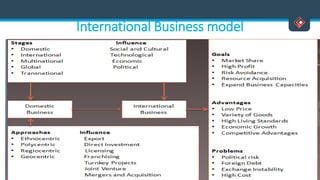
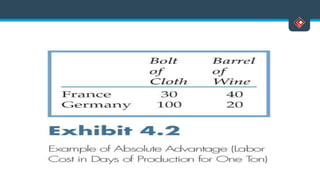
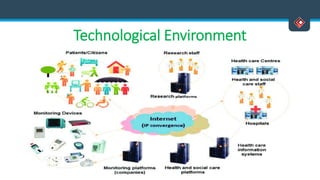
This document discusses various aspects of international business. It begins by defining business and international business. It then discusses the key drivers of internationalization including profit advantages, competition, and access to resources and technology. The document outlines the stages of internationalization from domestic to multinational to global companies. It also discusses the different orientations companies can take including ethnocentric, polycentric, regiocentric, and geocentric. Finally, it discusses factors that have increased globalization like regional trade agreements, declining trade barriers, and increased foreign direct investment.