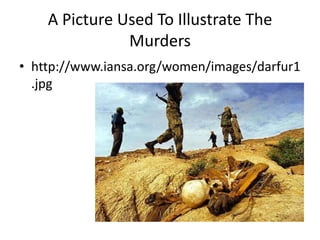
Forced migration in Darfur, Sudan has led to over 2 million people being displaced. Armed conflict between government forces, militias, and rebel groups has caused immense violence against civilian populations, forcing them to flee their homes for safety. The displaced populations face overcrowding and lack of resources in refugee camps in Chad, increasing tensions between the nations and risk of worsening conditions and conflict.