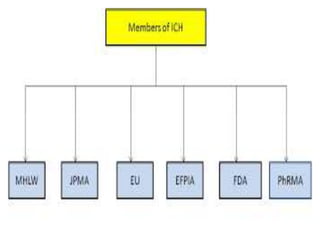
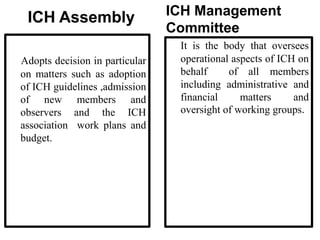
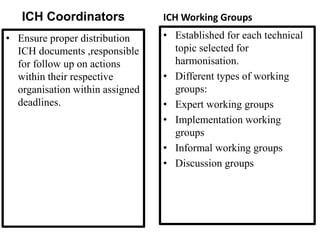
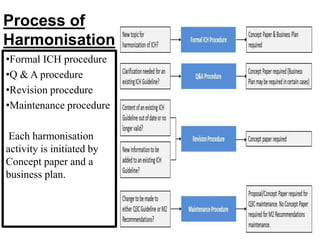
The document discusses the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH), an international body that aims to harmonize technical requirements for pharmaceutical product registration among regulators in Europe, Japan, and the United States. The ICH seeks to reduce duplication of clinical trials, accelerate drug development and licensing, and make safe and effective therapies more widely available. It has produced over 50 harmonized guidelines covering quality, safety, efficacy, and multidisciplinary topics to standardize pharmaceutical development and evaluation globally.