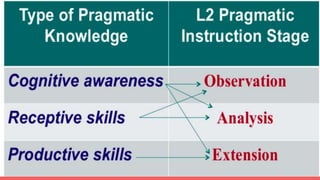
Interlanguage pragmatics examines second language learners' use and development of speech acts. Key concepts include speech acts, pragmatic failure, and factors influencing speech acts like power and social distance. Studies show learners progress through stages in speech act development, starting with formulaic utterances and progressing to more complex, indirect responses tailored to the social context. The Cross-Cultural Speech Act Realisation Project aimed to compare speech act realization patterns across languages and between native and non-native speakers. Research highlights the need for pragmatic instruction to go beyond textbook dialogs and incorporate observations of authentic language use.