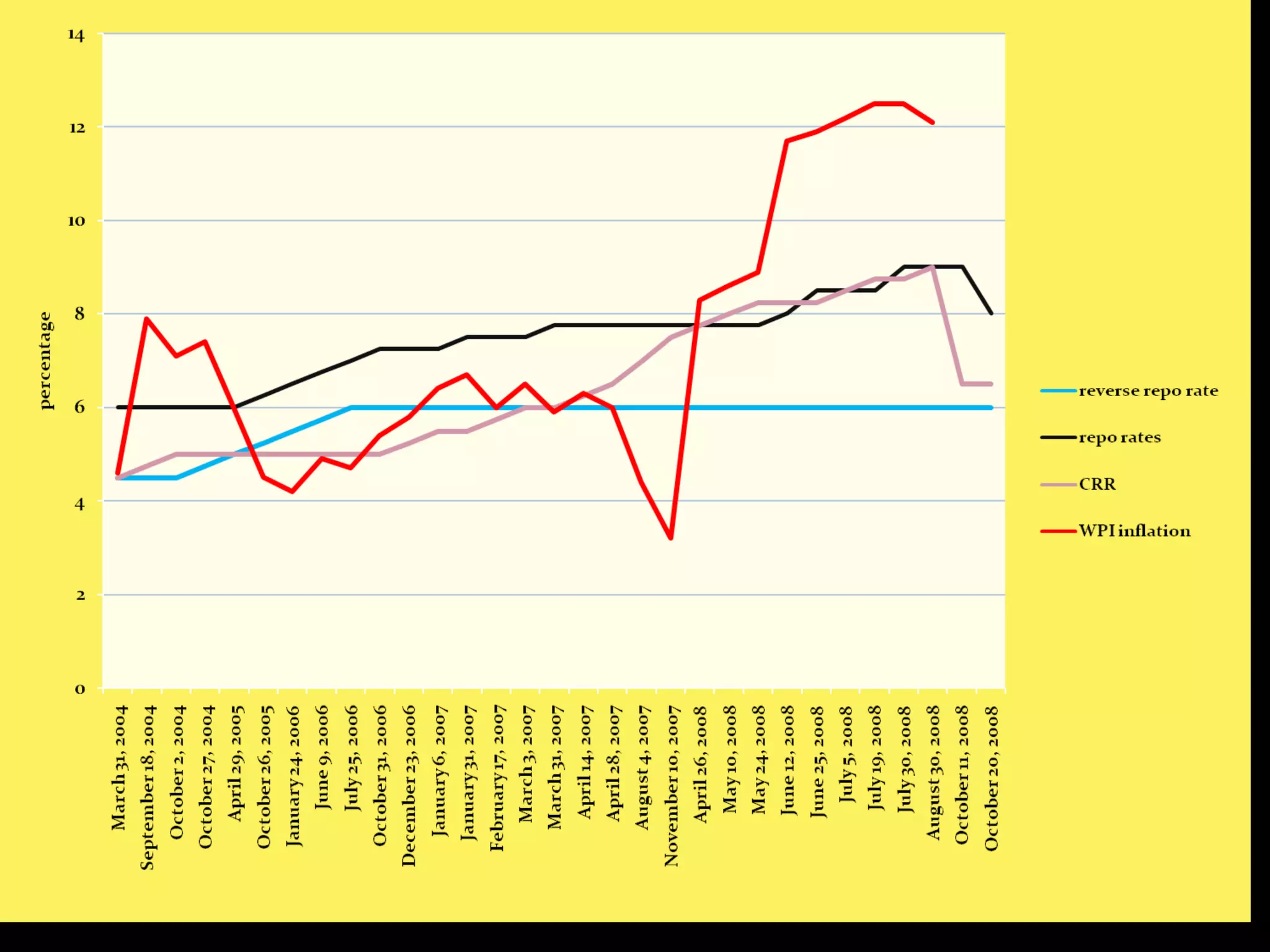
The document discusses tools used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to control the money market. It outlines key policy rates like the repo rate, reverse repo rate, and bank rate which RBI uses to influence liquidity and interest rates. Required reserve ratios like the CRR and SLR that require banks to hold a certain percentage of deposits in reserves are also mentioned. Current policy rates and lending/deposit rates are provided. The document concludes by stating that monetary policy involves managing money supply and interest rates to impact prices and employment, and that India follows an inflation targeting approach seeking to balance liquidity, inflation, exchange rates.