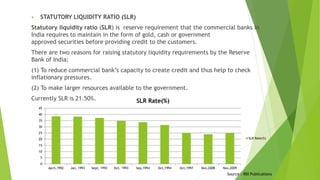
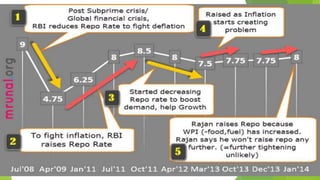
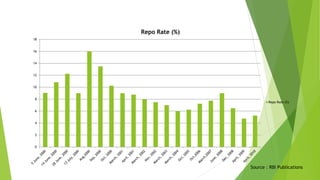
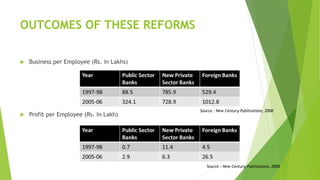
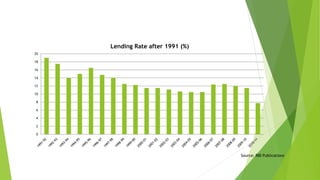
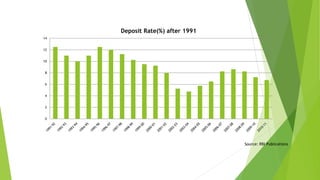
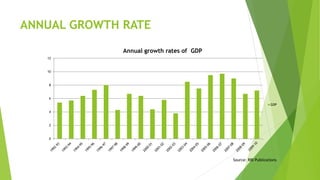
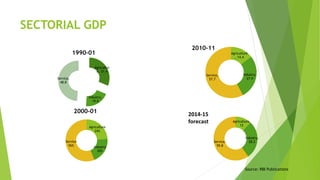
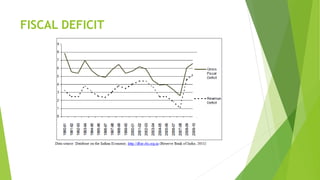
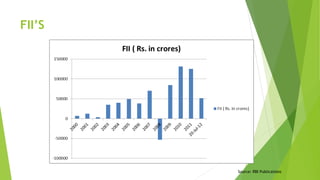
The document discusses India's monetary and banking reforms post-liberalization. It outlines the objectives of monetary policy in India including price stability, economic growth, full employment, and balance of payments equilibrium. It then describes the evolution of monetary policy frameworks and tools used, including key interest rates, cash reserve ratios, statutory liquidity ratios, and open market operations. Banking reforms introduced prudential norms, capital adequacy norms, and interest rate deregulation to increase efficiency and competitiveness in the banking sector. Overall, the reforms aimed to increase stability, reduce inflation, and boost economic growth.