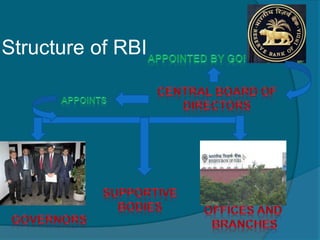
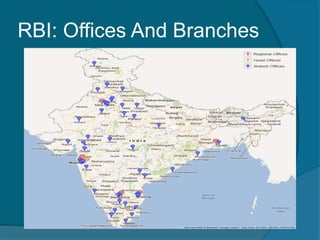
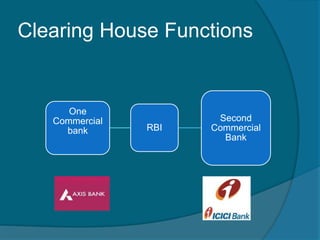
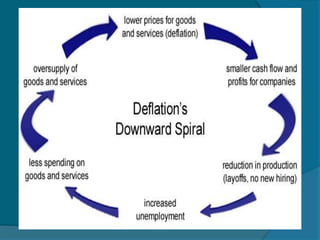
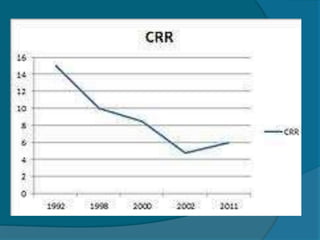
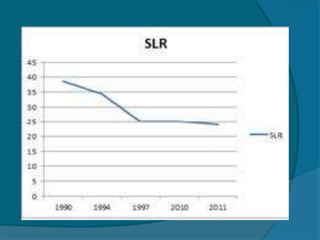
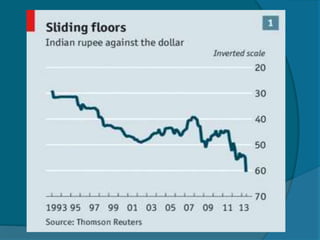
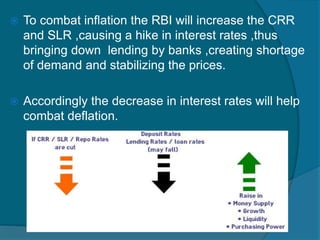
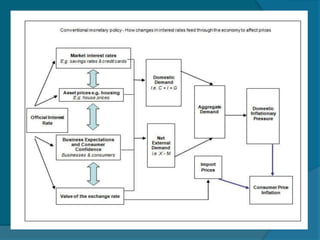
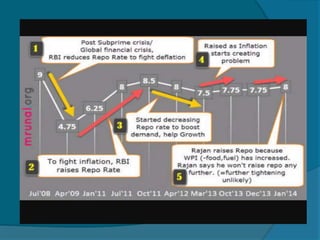
The document provides information about the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), including that it was established in 1935, initially as a privately owned bank in Calcutta. It summarizes that the RBI was nationalized in 1949 and moved to Mumbai in 1937. It also outlines the RBI's roles such as being the banker to the government, controlling credit and money supply through various quantitative and qualitative tools to influence inflation and economic growth.