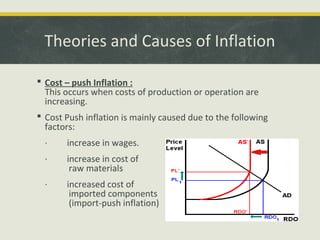
This document discusses inflation, defining it as a general increase in prices and a decline in the purchasing power of money. It outlines different types of inflation from creeping to hyperinflation. The main causes of inflation are described as too much demand and too little supply, which can be demand-pull or cost-push inflation. Effects include rising import prices, lower savings, and impacts on investment. Control measures discussed are monetary policy like interest rates and fiscal steps like tax increases. Present inflation rates in India are provided, ranging from -11% to 34% between 1969-2013, with an average of 7.7% over that period.