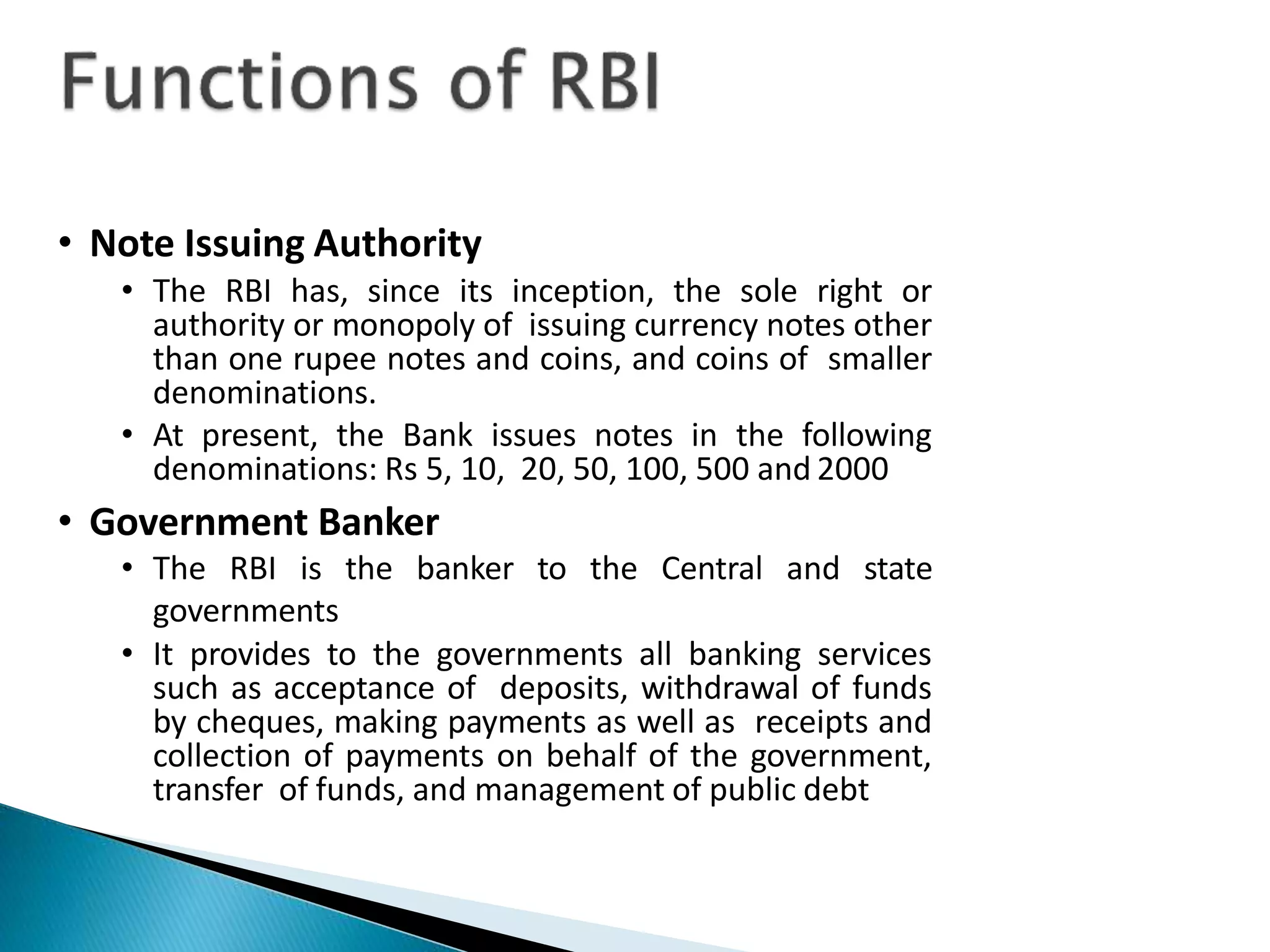
The document discusses the key components and functions of India's financial system. It notes that the financial system links savers and investors to facilitate wealth creation and economic development. The main constituents of the financial system include banks, non-banking financial institutions, money markets, capital markets, primary markets, and secondary markets. It then outlines the roles of important regulatory bodies like RBI, SEBI, and IRDA. The RBI acts as the central bank and regulates monetary policy, banking system, payment systems, and financial markets. SEBI regulates securities markets and aims to protect investors.