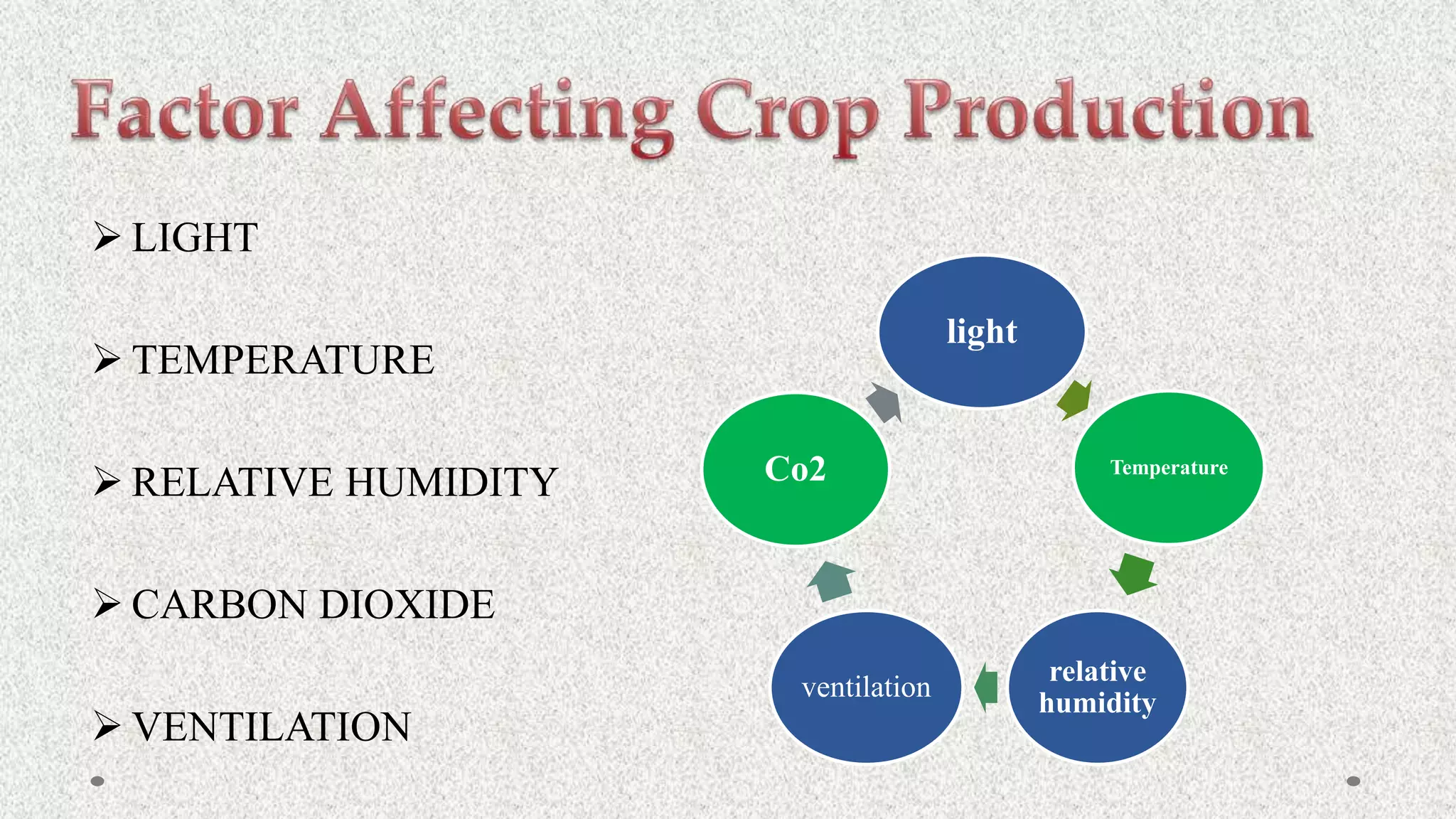
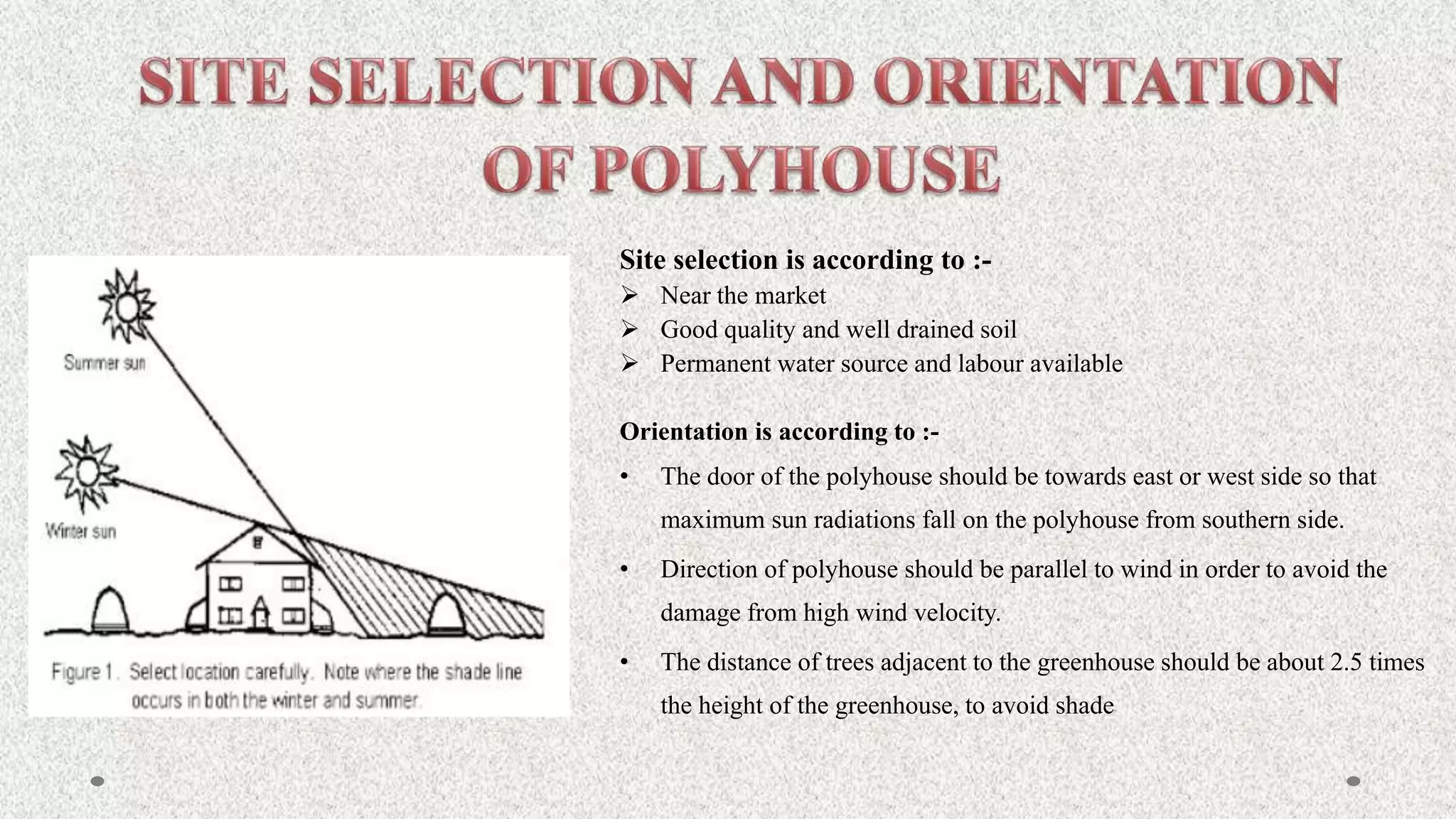
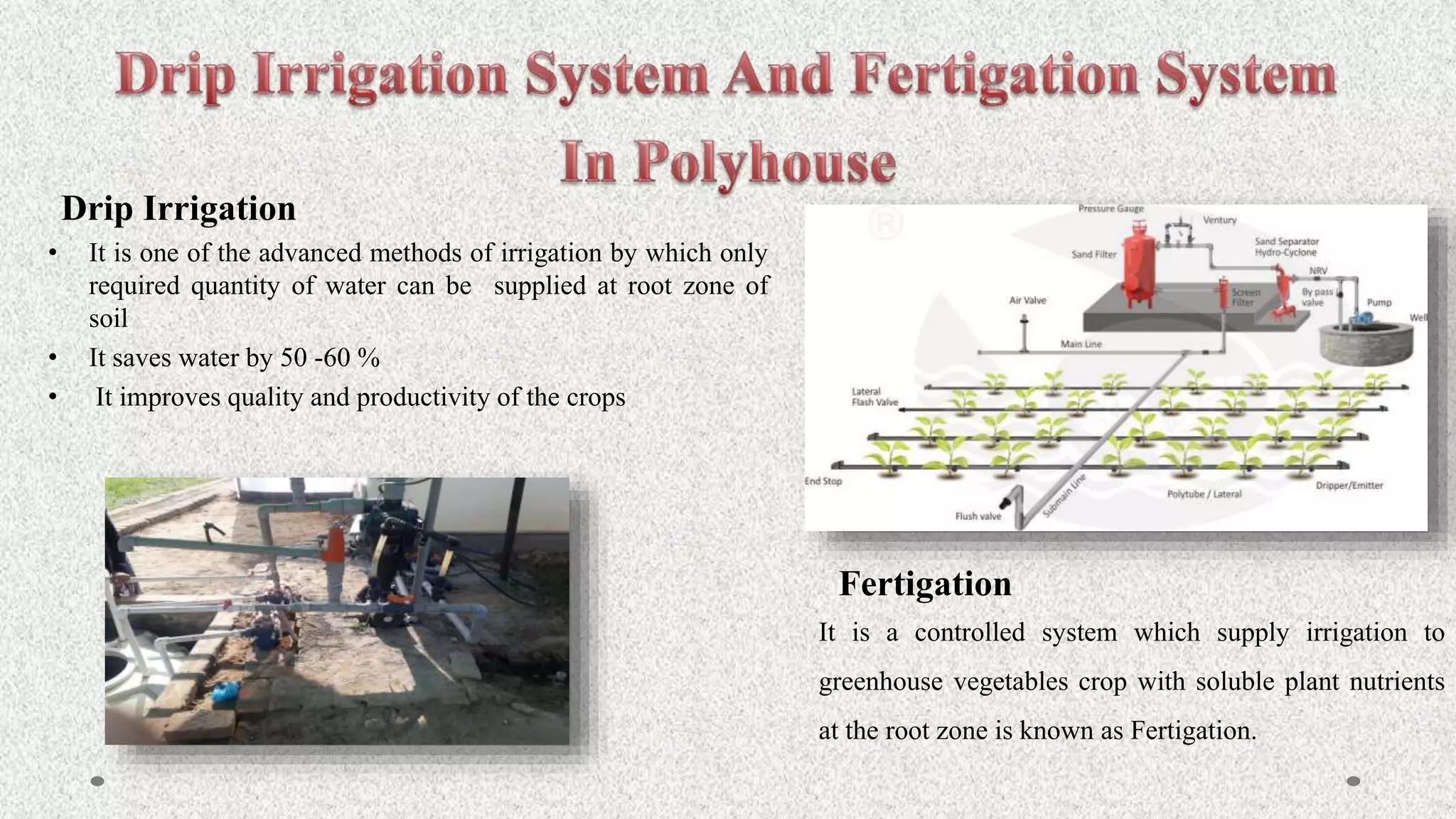
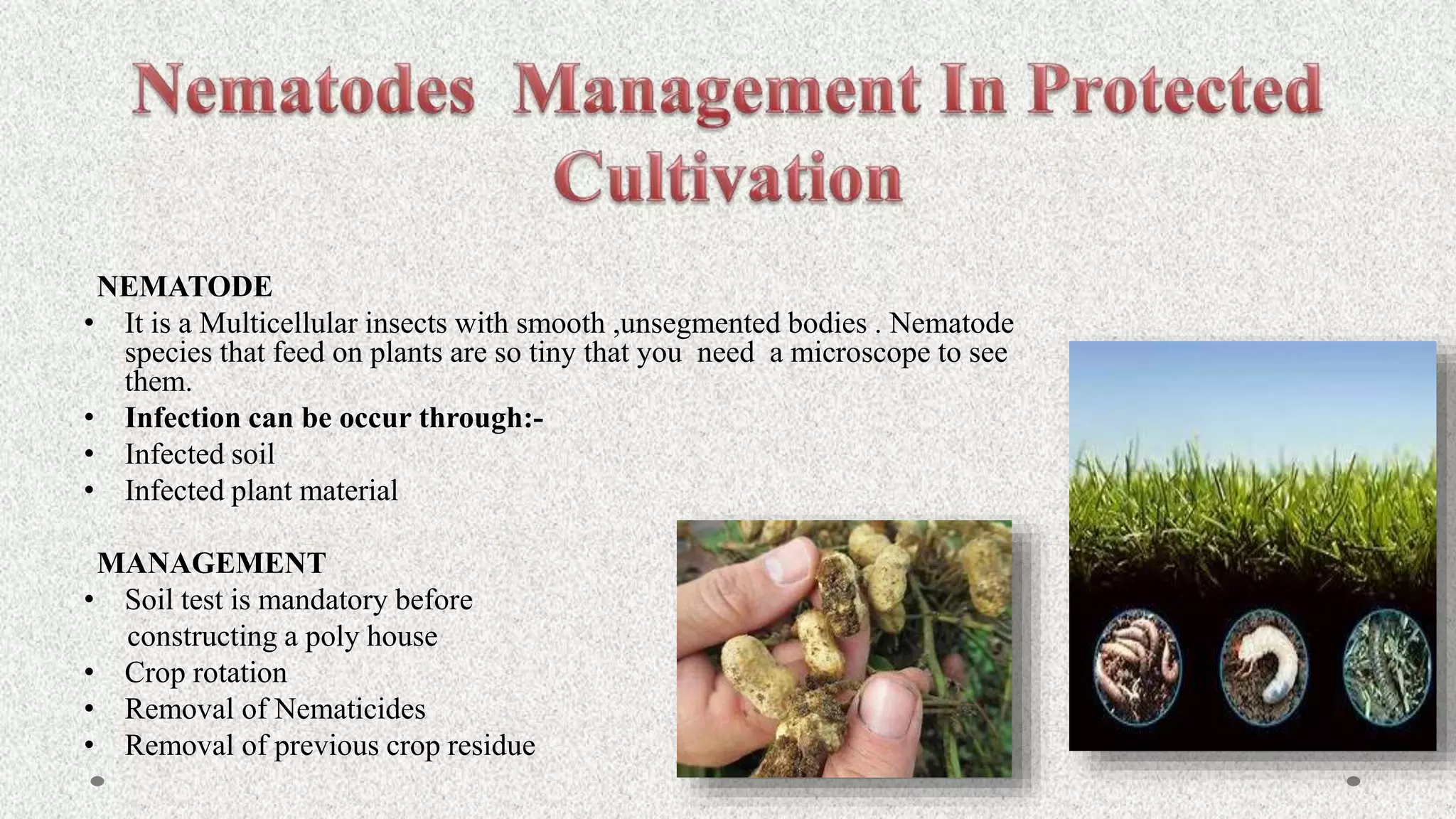
Vegetables are classified into root, stem, tuber, leafy, and seed vegetables. They are good sources of vitamins, minerals, fibers, and have antioxidant properties. Protected cultivation involves partially or fully controlling the microclimate around plants. Greenhouse technology is well-suited for vegetables, flowers, and nursery crops due to their small lifespans. Factors like light, temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide, and ventilation must be controlled in greenhouses.