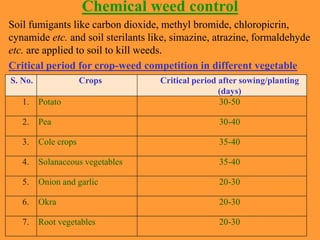
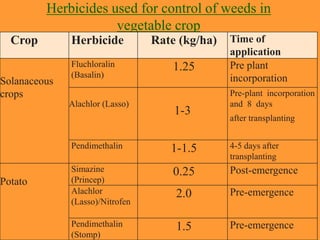
This document discusses weeds and methods of weed control in vegetable crops. It states that weeds compete with crops for resources like water, nutrients and light, reducing yields. Important weeds in different vegetable crops are described, including annual, biennial and perennial varieties. Methods of weed control discussed include physical/mechanical methods like tilling, hoeing and hand weeding; chemical methods using herbicides; cultural methods like mulching; and integrated weed management. Specific herbicides and their application times are also outlined for different vegetable crops.