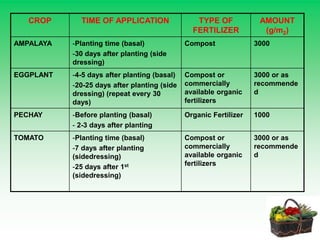
The document provides information on organic vegetable production. It discusses preparing the growth media, establishing organic nurseries by preparing seedbeds and land, and planting seedlings. It also covers performing plant care activities like irrigation, pest and disease control using organic methods, improving soil fertility, and applying fertilizers. Specific cultural practices are mentioned for different crops like tomato staking, pole sitao trellising, and ampalaya trellising. Weed control through manual removal and mulching is also described.