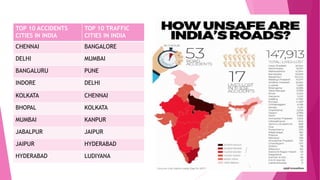
The document discusses Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS), which integrate information and communications technology into transportation infrastructure and vehicles to enhance safety, reduce congestion, and improve fuel efficiency. It highlights various technologies used in ITS, such as wireless communications, sensing technologies, and electronic toll collection, while addressing the pressing need for improved road safety in India due to high road fatalities and traffic congestion. The document calls for collaboration between stakeholders to deploy ITS effectively and enhance the overall efficiency of the transportation system.