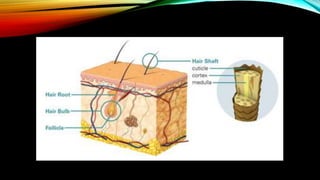
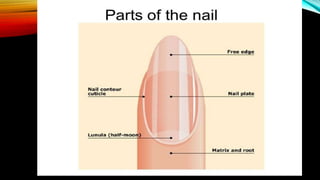
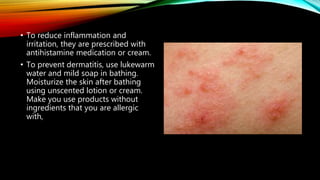
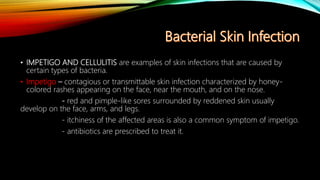
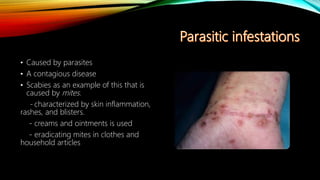
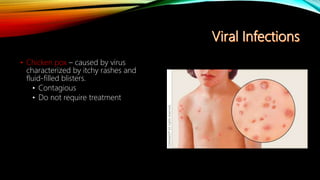
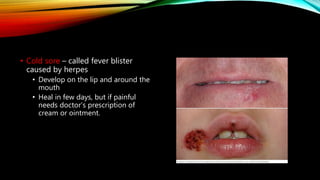
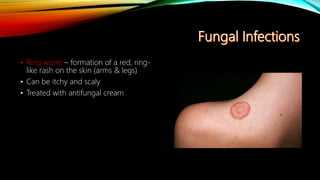
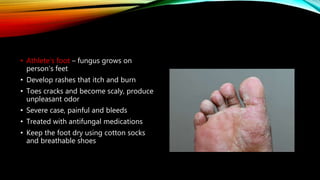
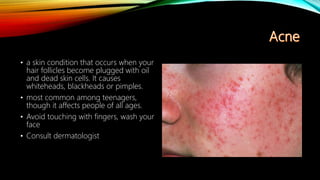
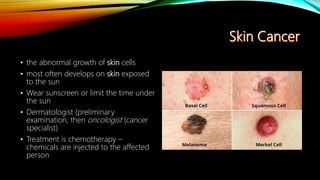
The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and associated glands. It protects the body from microbes and regulates temperature. The skin is the largest organ and has three layers - the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The dermis contains blood vessels, sweat and oil glands, and sensory receptors. The hypodermis contains fat and connective tissue. Diseases like dermatitis, impetigo, and cellulitis can infect the skin. Proper hygiene and a healthy lifestyle help maintain skin health.