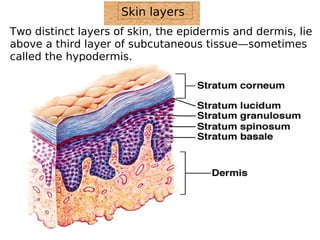
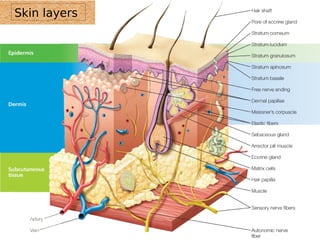
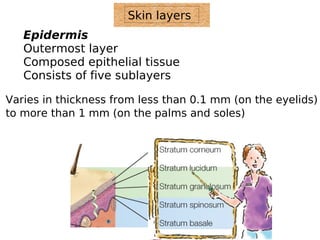
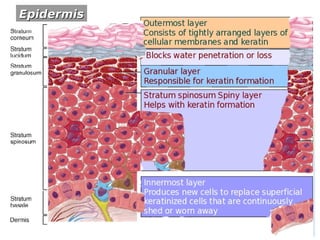
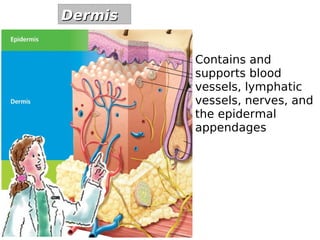
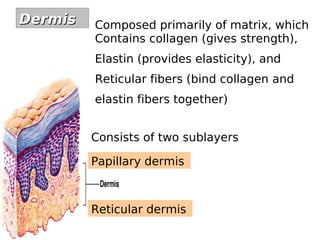
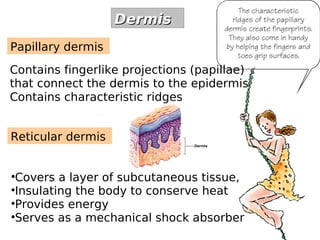
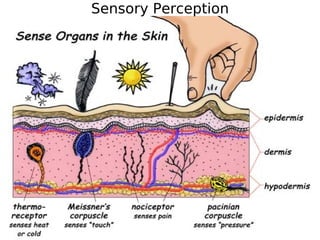
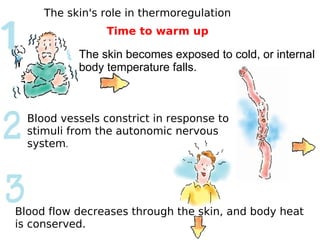
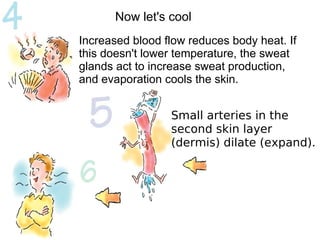
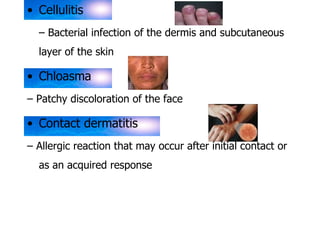
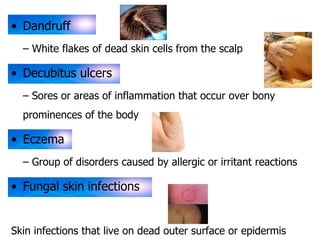
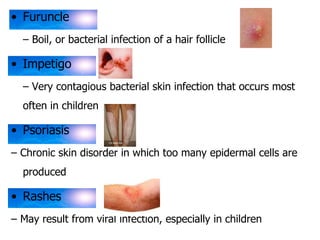
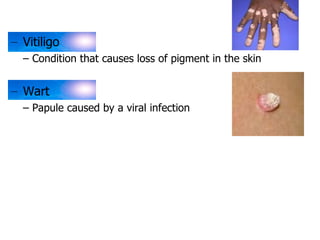
The skin has three layers - the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The epidermis is the outermost layer and varies in thickness, while the dermis lies below and contains collagen, elastin, and fibers. The subcutaneous tissue acts as insulation. The skin functions to protect the body, sense stimuli, excrete waste, and regulate temperature. It protects against damage and pathogens, and contains sensory receptors. Through sweating and blood flow regulation, it also helps control body heat. Common disorders of the integumentary system include acne, eczema, fungal infections, and psoriasis.