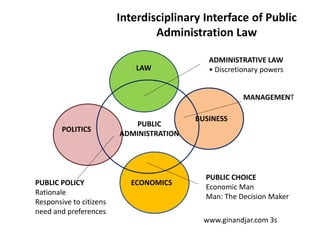
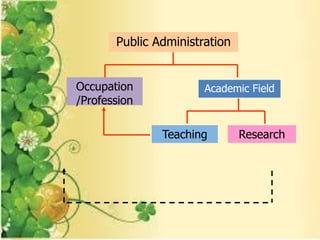
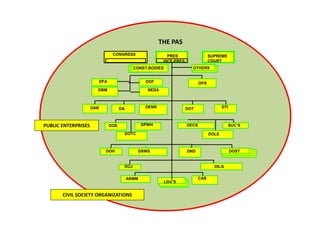
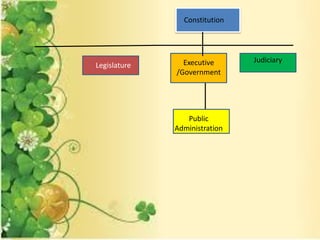
- Public administration is an interdisciplinary field that draws from various social sciences like political science, economics, and law. It aims to promote effective and efficient governance that is responsive to citizens' needs.
- The field has its roots in the late 19th century with Woodrow Wilson advocating for separating politics and administration, and for developing public administration as a self-conscious profession.
- It developed further in the 20th century with scholars and practitioners collaborating and experimenting to advance theories and practices of public administration.