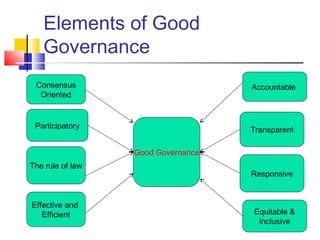
Governance refers to the rules and processes by which political actors interact to manage their affairs and provide public goods. There are three main conceptions of governance: as a synonym for public administration, related to new public management reforms, and a broader concept encompassing relations between political institutions. Good governance aims to safeguard democracy, human rights, and the economy through principles of participation, transparency, accountability, rule of law, responsiveness, and equity. It seeks to improve public administration, quality of life, institutional legitimacy, freedom of information, productivity, and organizational pluralism in governance.