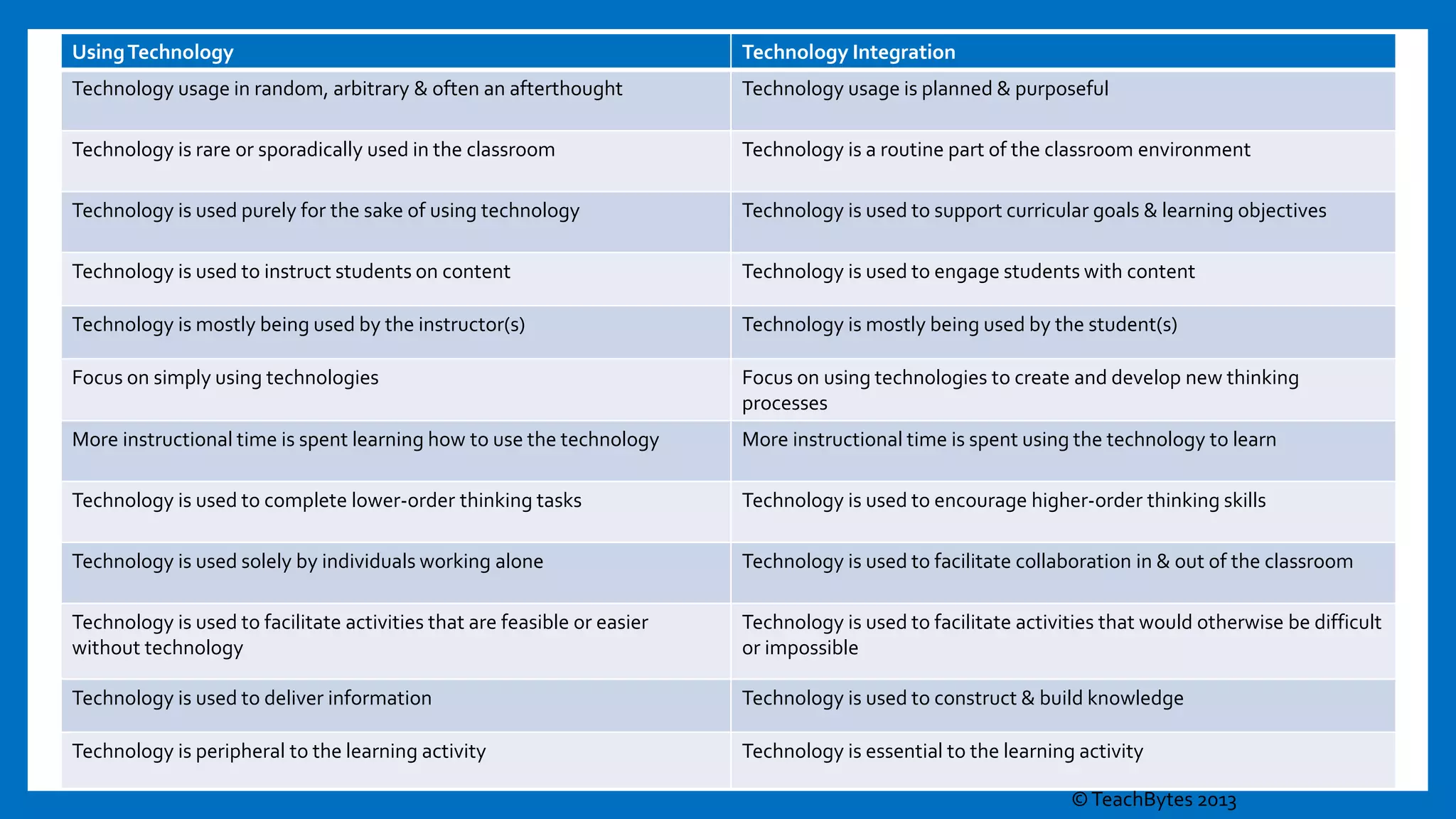
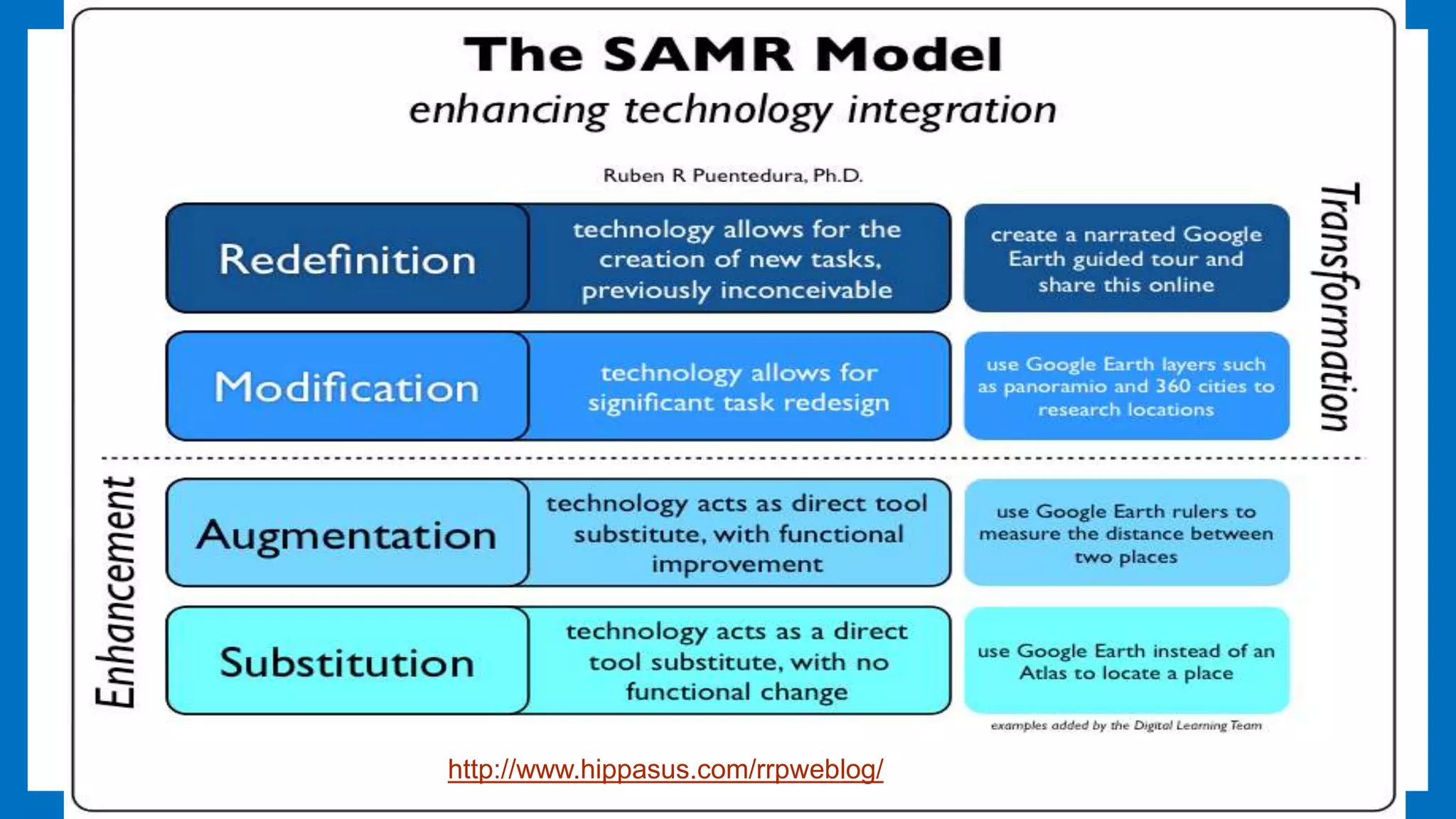
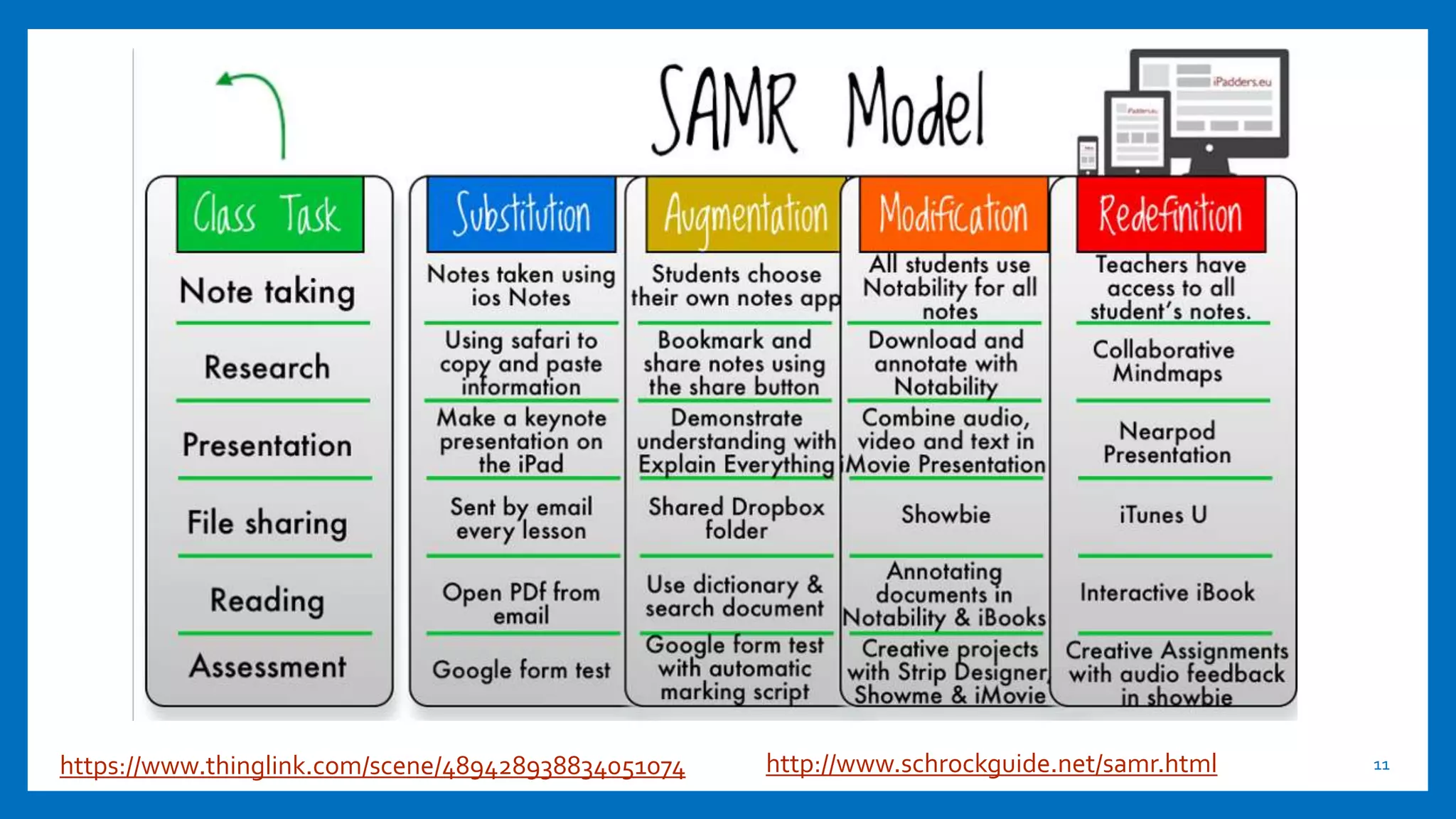
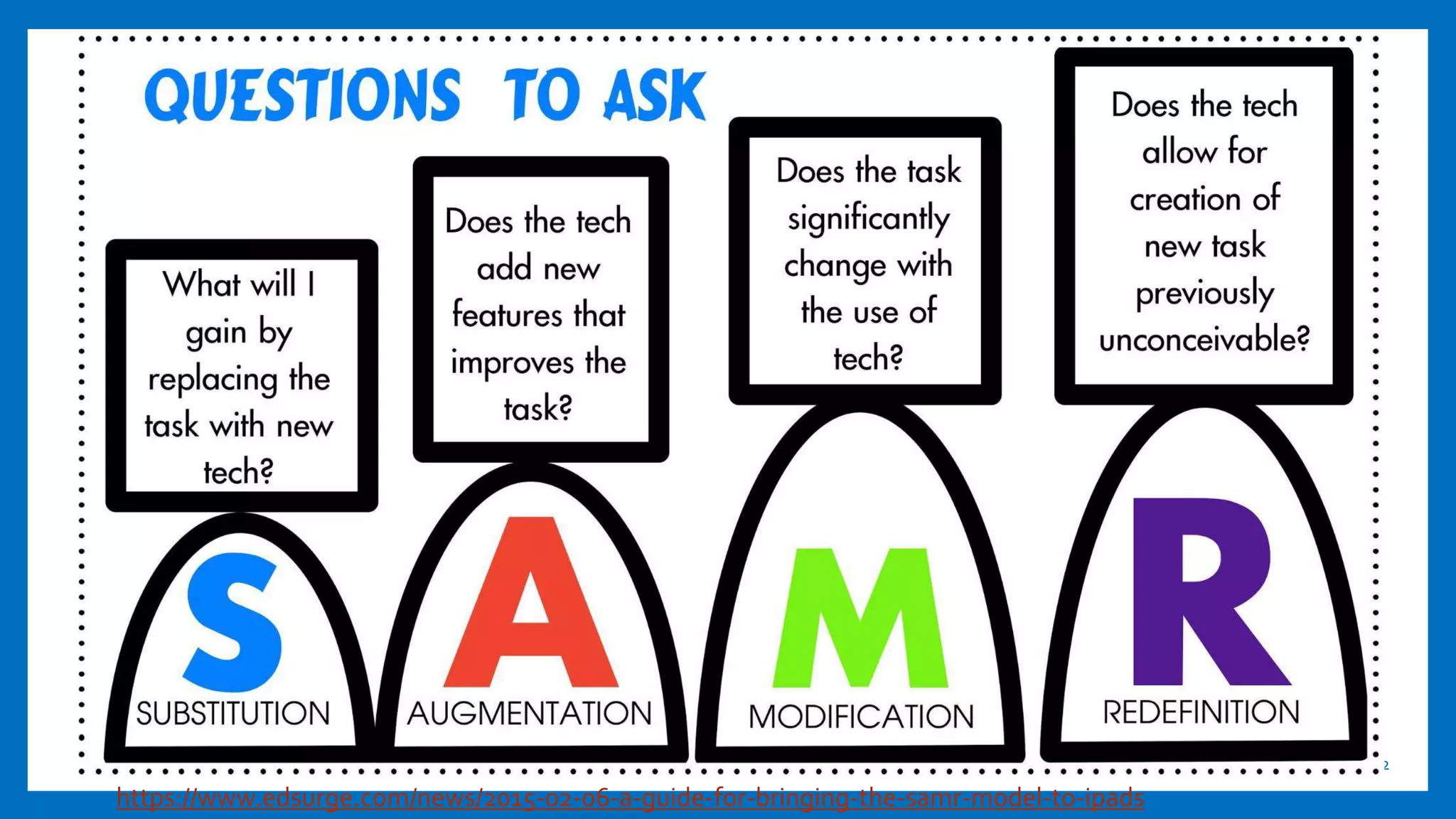
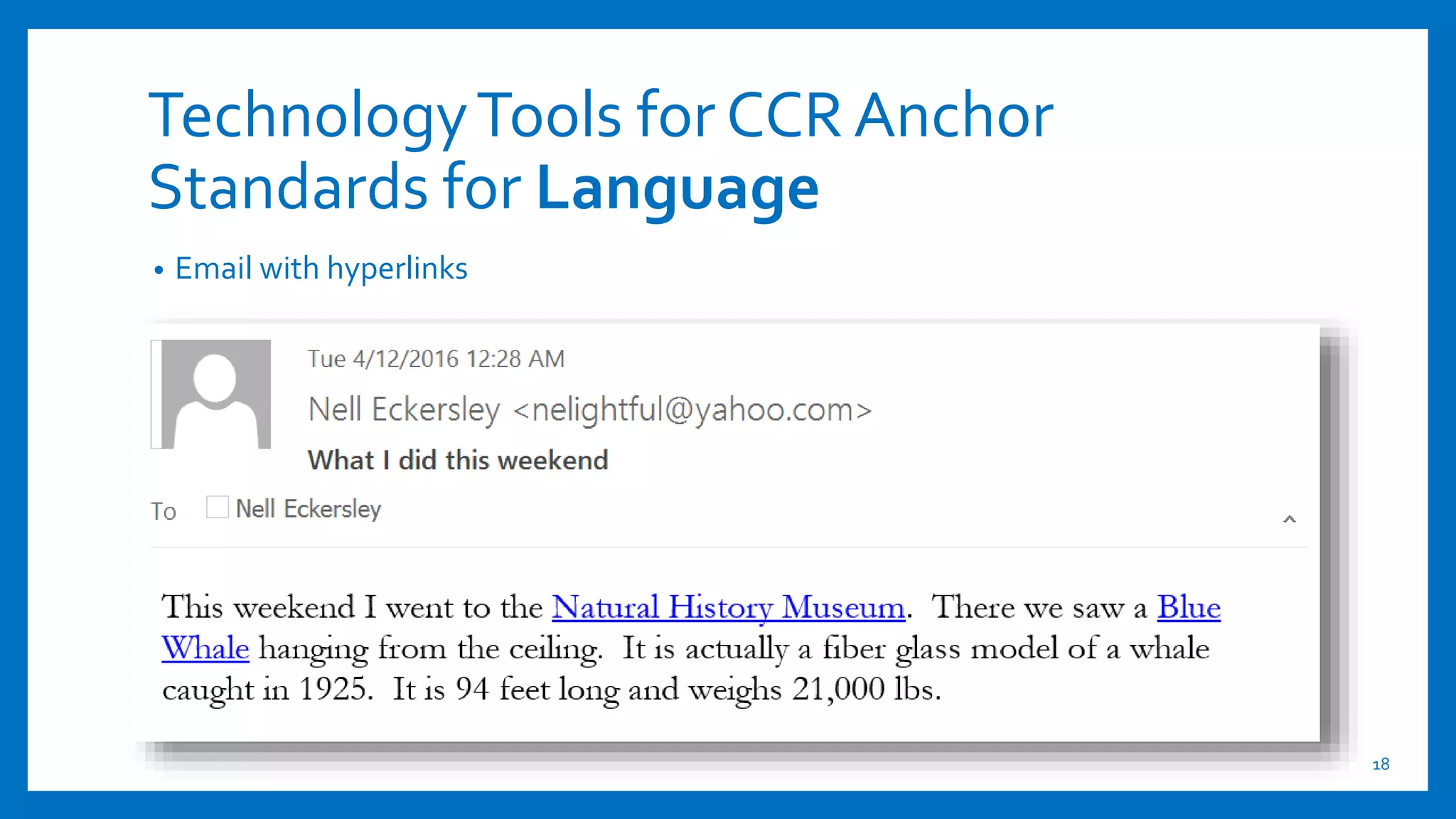
This document provides an overview of integrating technology to support the College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for English Language Arts. It includes discussions on the CCRS anchor standards for language, reading, speaking and listening, and writing. For each set of standards, examples of relevant technology tools are provided, such as Vocaroo for language standards and ReadWorks.org for reading standards. The document also covers shifts in the CCRS, such as building knowledge through nonfiction, and includes examples of how to apply the SAMR model to lesson planning using the standards. Contact information is provided for the presenters.