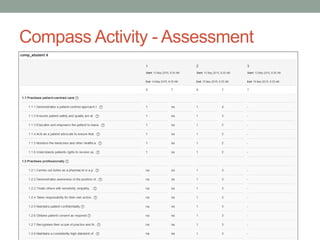
The document outlines various competency frameworks for different fields, including sales, nursing, and programming, highlighting key competencies required for effective performance. It details tasks related to software development, assesses student performance in both programming and English through specific tasks, and emphasizes the importance of competency-based education in Moodle. Additionally, it discusses patient-centered care and provides insights into effective educational practices and learning frameworks within Moodle.