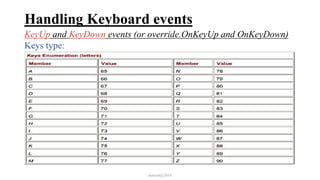
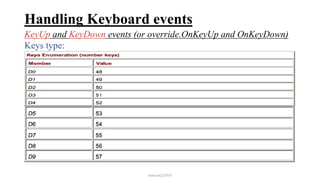
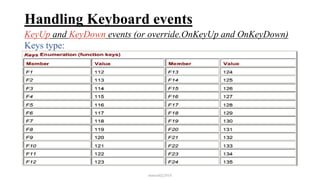
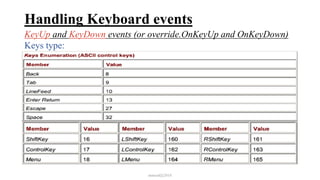
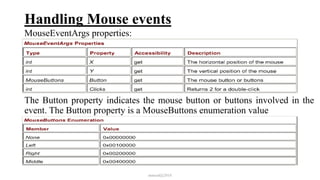
This document discusses how to handle events in Visual C# .NET framework 4.5. It explains that GUI classes have predefined events that developers implement by attaching event handlers using delegates. It then provides examples of handling events from the Form, Control, and Mouse classes, describing properties like PaintEventArgs, KeyEventArgs, and MouseEventArgs that provide information about the events. It discusses overriding methods like OnPaint, OnKeyPress, OnKeyUp, and event handler methods.