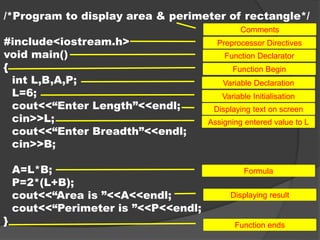
Programming languages are designed to communicate with machines like computers. Programs are sets of instructions written in a programming language following its syntax to serve some purpose. C++ was developed in the 1980s as an object-oriented programming language. OOP views a problem in terms of objects rather than procedures. A programming language's character set includes letters, digits, symbols, and whitespace that it can recognize as valid characters. The smallest units of a program are tokens like keywords, identifiers, literals, operators, and punctuators.

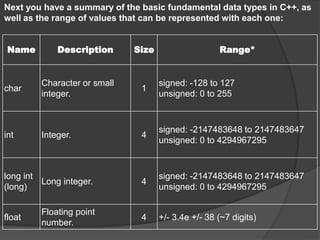
![Character set: A set of valid characters that a
language can recognize.
Letters: A to Z, a-z.
Digits: 0 to 9
Special Symbols: Space + - * / ^ ( ) { } [ ] = < > ,
‘ “ $ . ; : % ! & ? _(Underscore) # <= >= @
White Spaces: Blank Space, Horizontal Tab (à),
Carriage return(J), Newline, Form Feed
Other Characters: C++ can process any of the
256 ASCII characters as data or as literals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-170816041425/85/C-3-320.jpg)

![Literals : (Often referred to as constants) are data
items that never change their values during a
program run.
Operators: Operators are tokens that trigger some
computation when applied to variables and other
object in an expression. They are
I/o : << and >>
Arithmetic : +, - , * , / , %
Increment/Decrement : ++ , - -
Relational : ==, <, >, <=, >=, !=
Logical : &&, ||, !
Conditional : ?
Punctuators : Also known as separators. They
enhance a program’s readability. For eg
[ ] , { } , ( ) , ; , : , * , = , #](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-170816041425/85/C-5-320.jpg)