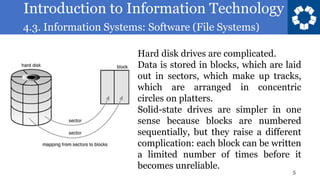
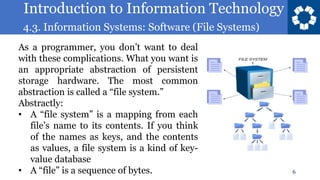
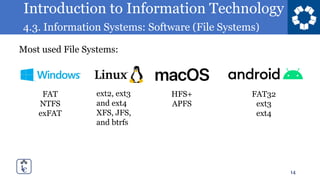
This document discusses file systems and how they provide an abstraction of data storage on hardware. It defines a file system as a mapping from file names to file contents, with files being sequences of bytes. It also notes that different operating systems commonly use different file systems like FAT, NTFS, ext2/3/4, and HFS+. Hard drives and solid state drives actually store data in more complex ways at the physical level.