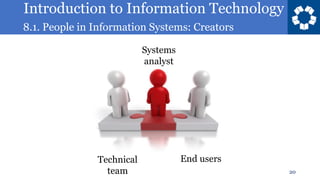
This document discusses different roles that people play in creating information systems. It describes systems analysts as identifying business needs and designing systems to address them. Programmers then write the code to build the systems based on designs. Computer engineers design the underlying hardware and software technologies, with roles in hardware, software, systems integration, and networking. Creators generally have technical backgrounds in fields like computer science and mathematics.

![Introduction to Information Technology
8.1. People in Information Systems: Creators
2
[Getting to know about PGCC]
How many locations does
PGCC have? Where are they?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int101008-1-231114172707-0ae75dc4/85/INT-1010-08-1-pdf-2-320.jpg)