The document provides an overview of how insurance companies work. It discusses key terms like insurer, insured, and premium. It explains that insurance companies collect premiums from customers, invest those funds, and use the money to pay claims when insured events occur. The document also outlines some common types of insurance like life, health, property, and car insurance. It discusses factors that determine insurance rates and gives examples of career paths within an insurance company.

![UPLOADED BY [email_address] How Insurance Companies Work ? Sami Ullah ID#9706 Maaz ID# 9702 Shah Junaid ID#9722 Naveed Afzal ID#9713 Imran ID# 9714 Qazi Fazli Rabi ID#4110 By](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdocumentsandsettingsadministrator-mr-8a4e314fe51bdesktopinsurance-100608160741-phpapp02/85/How-Insurance-Company-works-2-320.jpg)






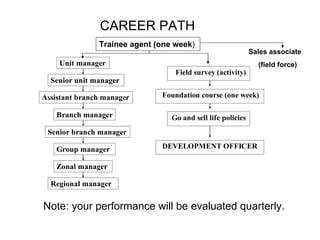
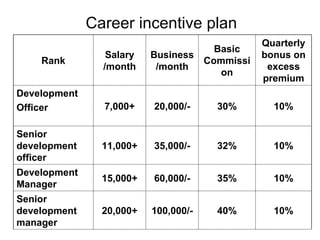
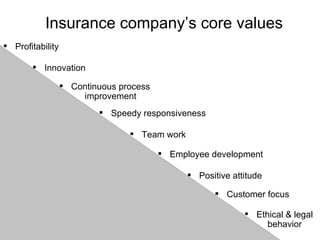














![Steps for Life insurance by Imran ID:9714 Feedback@ [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdocumentsandsettingsadministrator-mr-8a4e314fe51bdesktopinsurance-100608160741-phpapp02/85/How-Insurance-Company-works-26-320.jpg)











