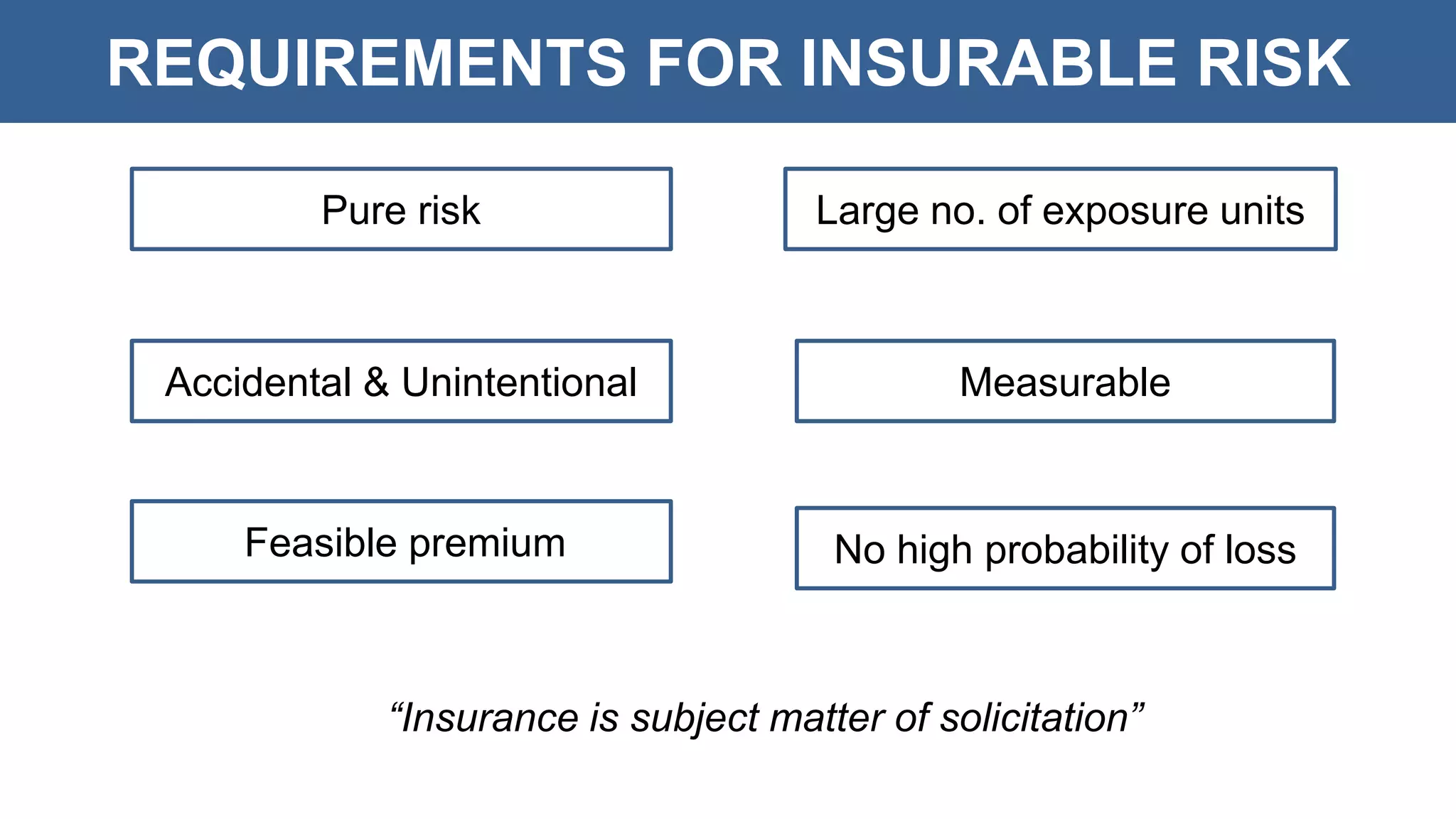
The document discusses general insurance concepts including basic terminology, requirements for insurable risk, and principles of insurance. It defines key terms like insurance, insurer, insured, premium, policy, risk, peril, and hazard. The six requirements for a risk to be insurable are outlined. The seven principles of insurance are explained in detail, including indemnity, insurable interest, utmost good faith, contribution, average, subrogation, and proximate cause. Finally, the document categorizes insurance into life, general, fire, health, motor, and marine types.