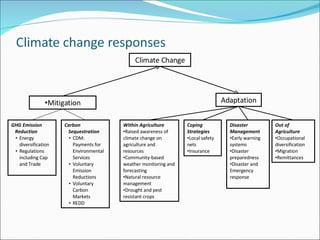
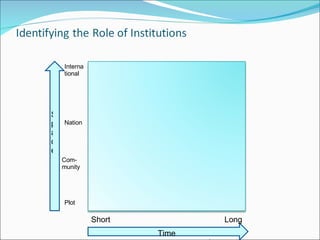
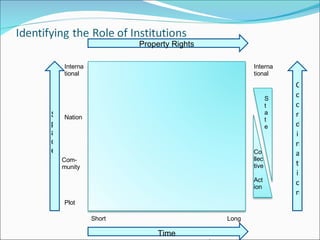
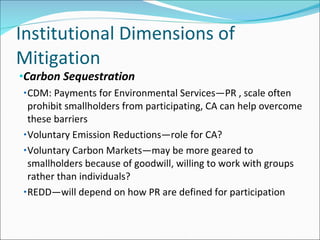
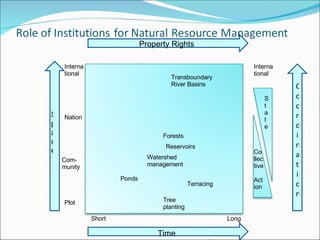
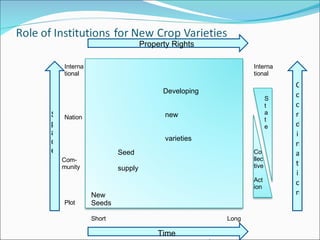
The document discusses climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies within agriculture. It outlines roles for community-based approaches in areas like weather monitoring, natural resource management, developing drought and pest resistant crops, local safety nets, and disaster management. It also discusses adaptation strategies outside of agriculture like occupational diversification and migration. The document concludes that institutional diversity increases resilience and that a range of local organizational forms and property rights regimes are needed. Both local and higher-level institutions are critical, with policies and mandates establishing standards and supporting a variety of strategies.