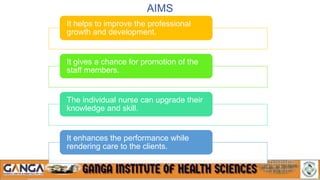
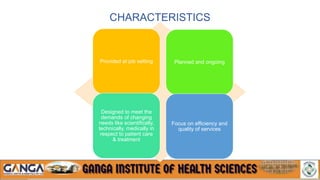
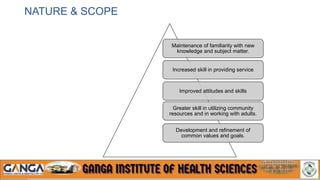
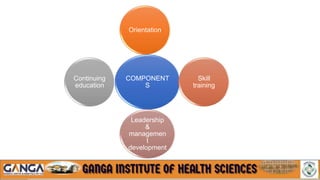
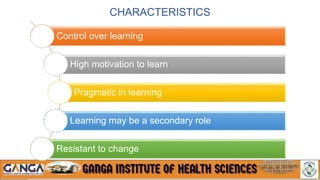
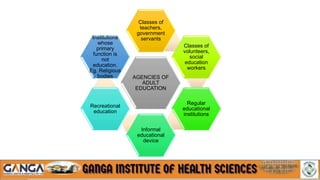
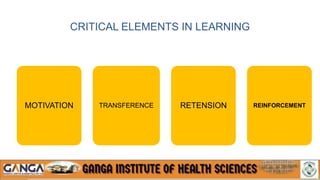
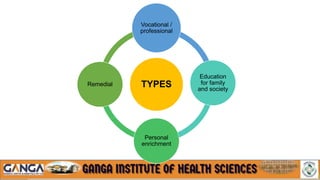
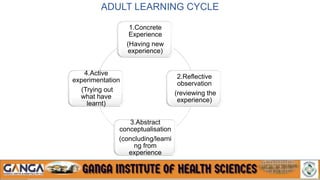
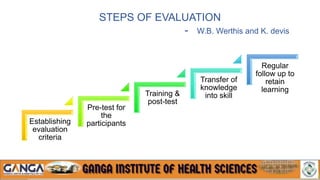
The document provides an overview of in-service education and adult learning principles. It defines in-service education and discusses its aims, characteristics, nature and scope. It also explains the principles of adult learning, including characteristics of adult learners and important considerations in teaching adults. Finally, it outlines various components of in-service education like orientation, skill training, leadership development and continuing education, as well as methods for planning, implementing and evaluating in-service education programs.