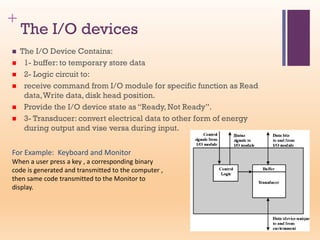
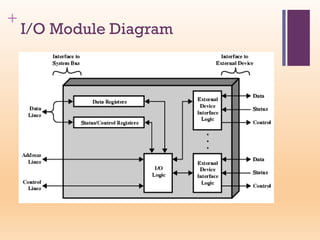
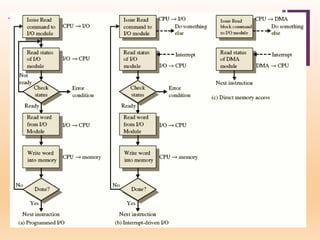
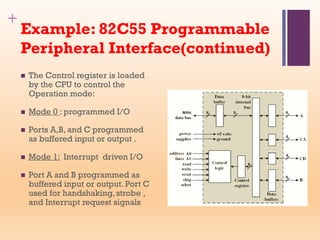
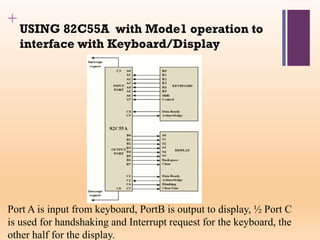
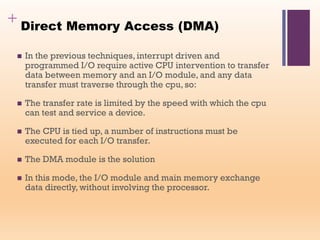
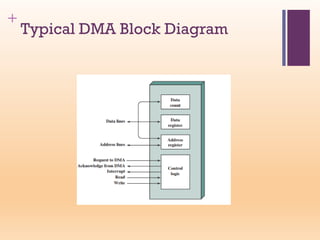
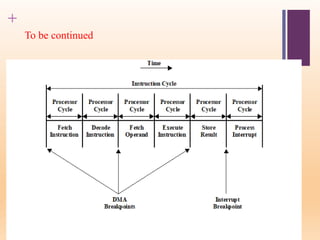
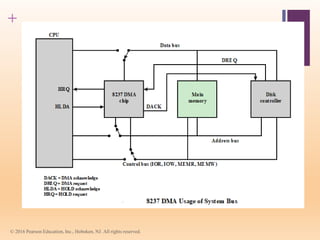
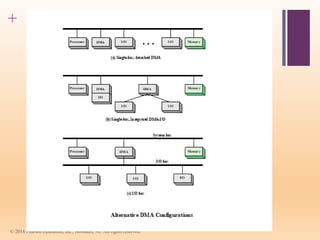
This document discusses input/output (I/O) in computer systems. It defines I/O as the transfer of data between a computer's CPU and memory and external peripheral devices. Peripherals connect to the computer via I/O modules and operate more slowly than the CPU and RAM. The document outlines different types of peripherals and describes generic I/O module functions like controlling data transfer and buffering. It also explains the three main I/O techniques: programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA), where the I/O module transfers data directly between memory and peripherals without CPU involvement.