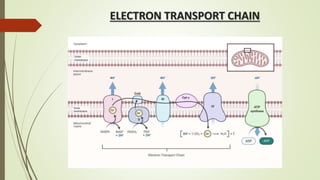
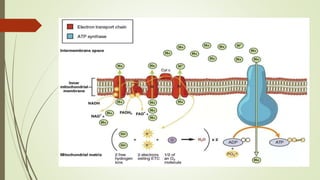
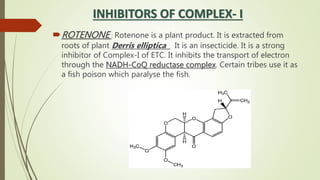
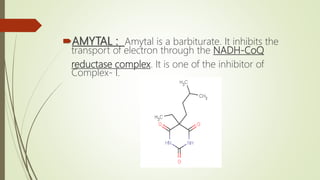
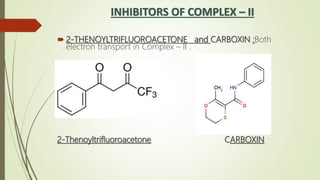
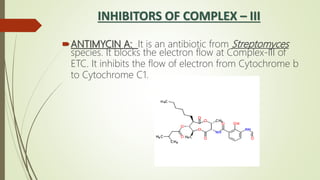
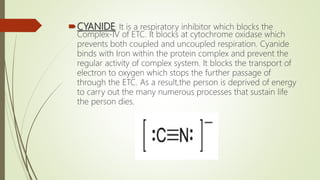
The document discusses inhibitors of the electron transport chain (ETC), which are agents that bind to specific components of the ETC, blocking the transfer of electrons and resulting in the accumulation of reduced forms. It details the four complexes involved in the ETC and identifies specific inhibitors for each complex, such as rotenone for complex I and cyanide for complex IV. Overall, these inhibitors can severely disrupt respiratory processes, leading to a lack of energy necessary for cellular functions.