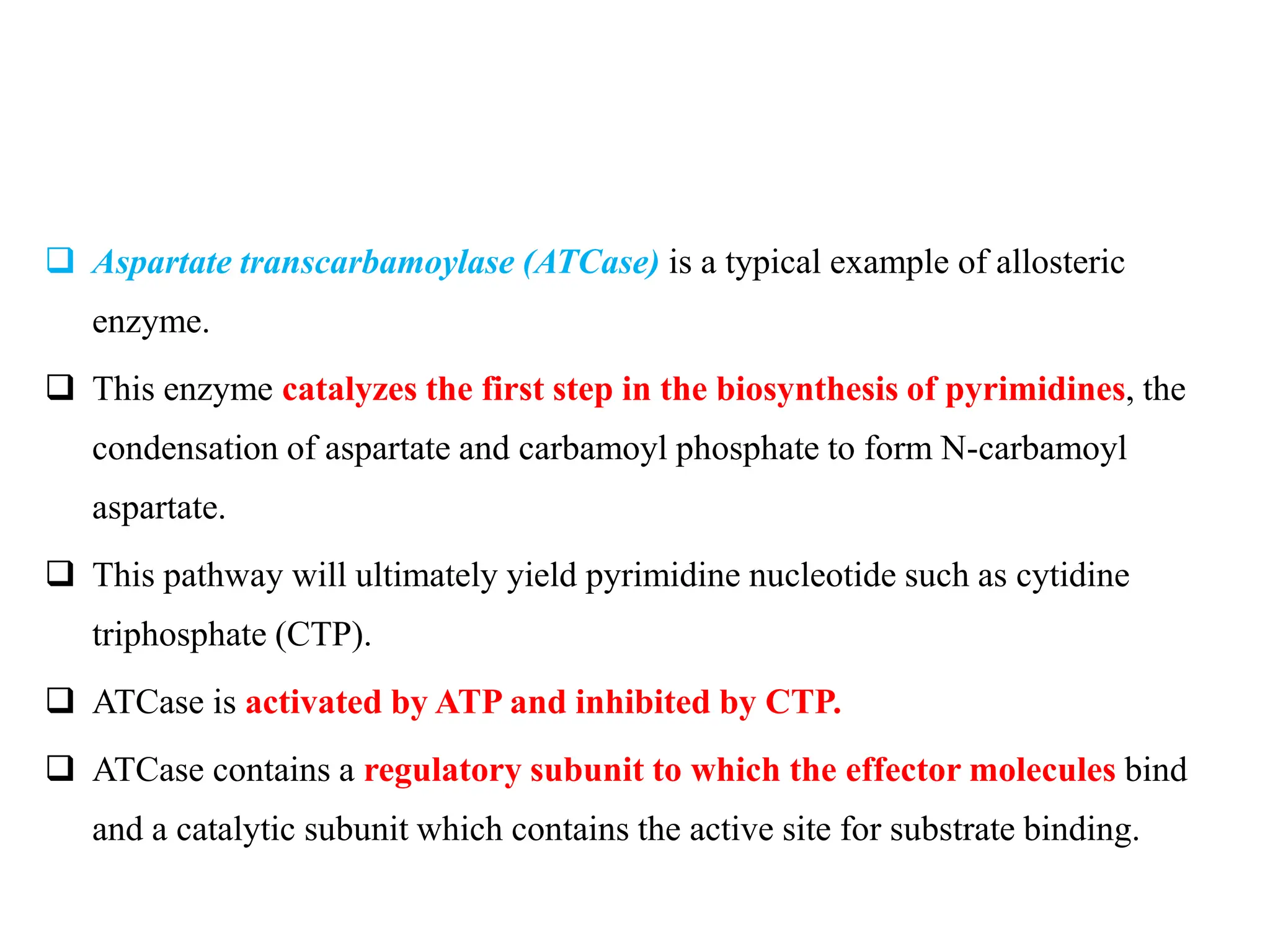
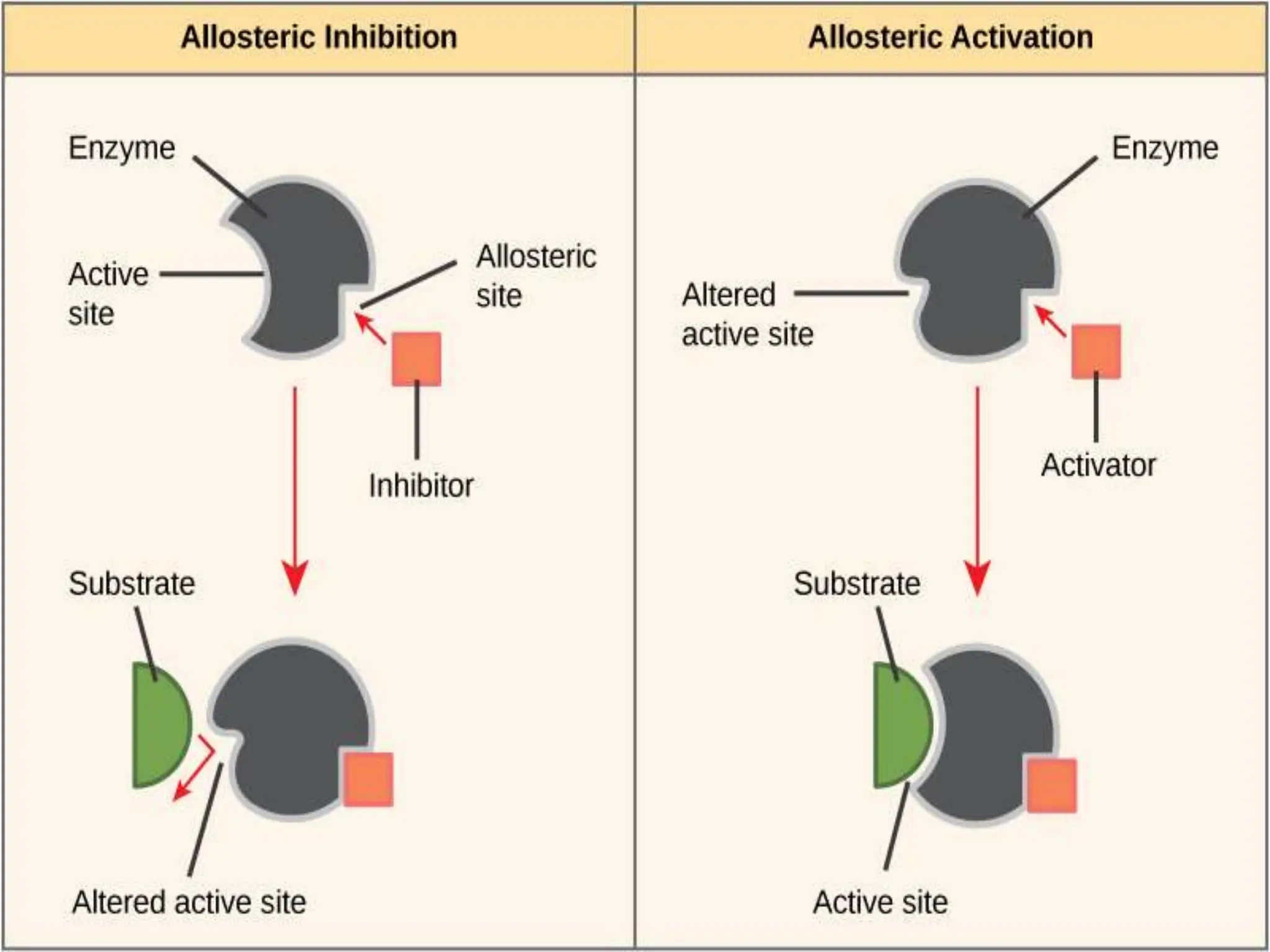
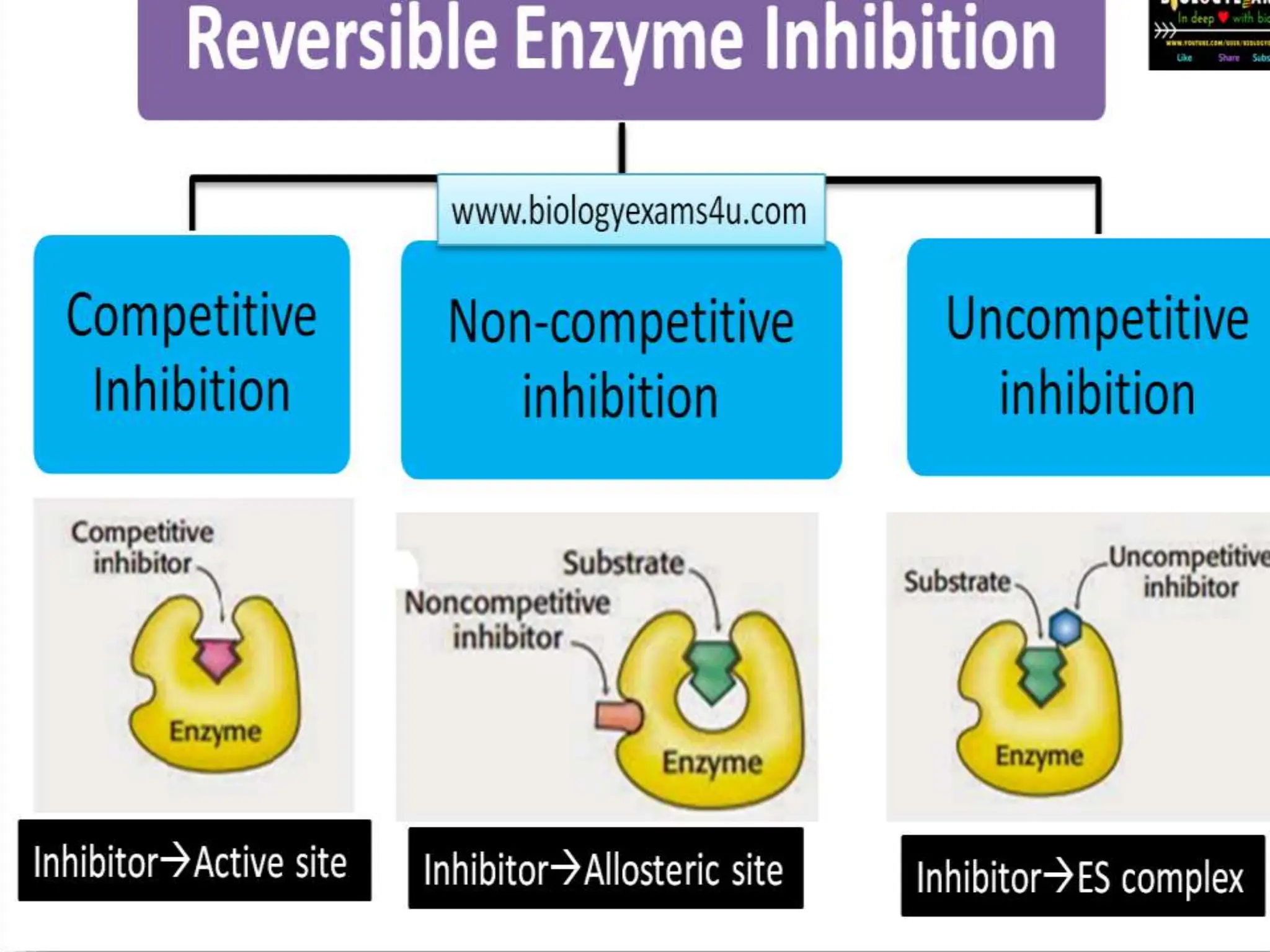
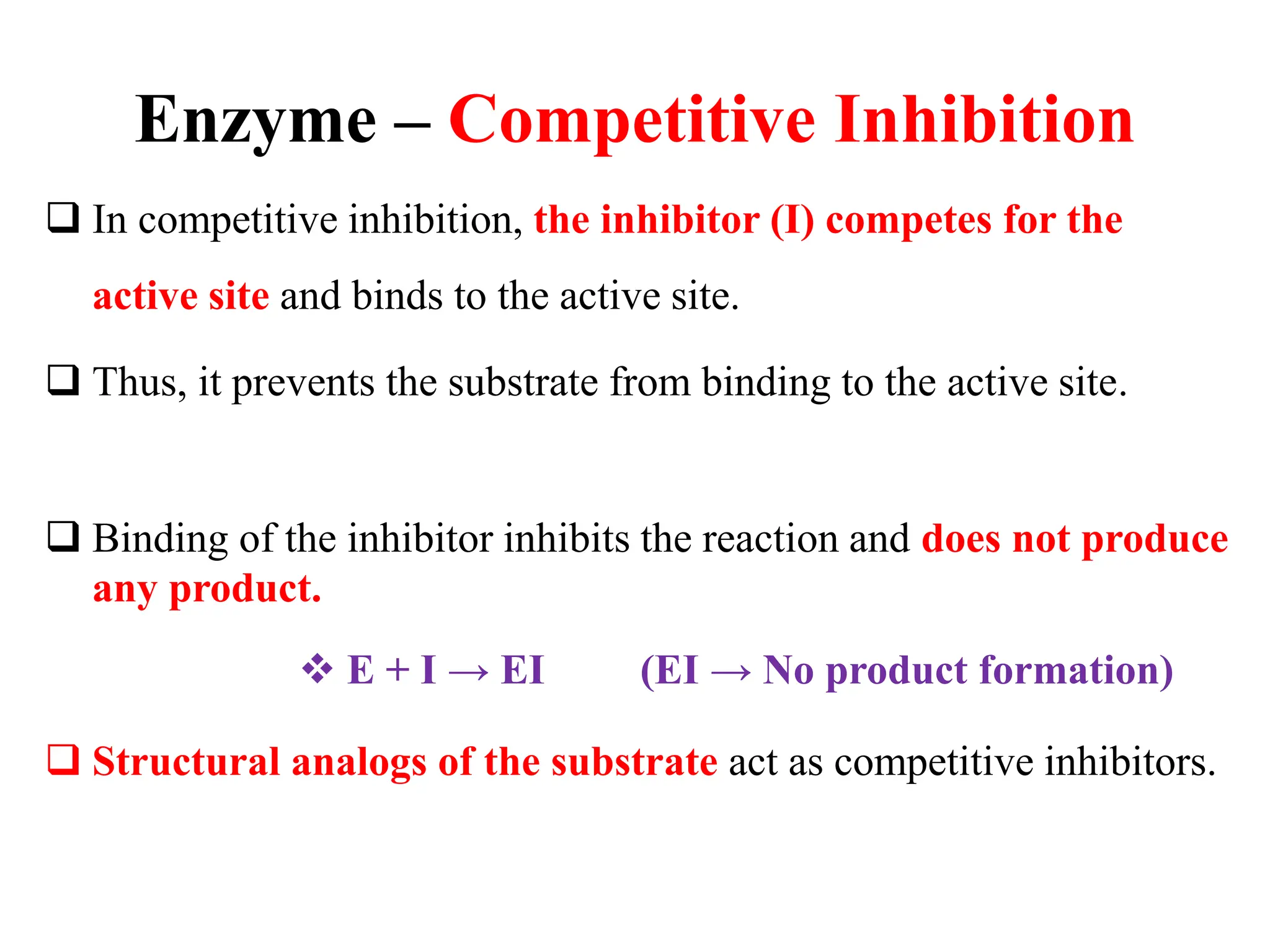
This document discusses enzyme inhibition. It explains that enzymes can be inhibited through reversible or irreversible inhibition. Reversible inhibition includes competitive, non-competitive and uncompetitive inhibition which influence the enzyme's kinetic parameters like Vmax and Km in different ways. Allosteric enzymes have additional regulatory sites and exhibit cooperative kinetics. Aspartate transcarbamoylase is provided as an example of an allosteric enzyme regulated by feedback inhibition.

















![ Thus, allosteric enzymes are usually composed of multiple binding
sites and often shows sigmoidal graph of initial rate versus [S] and
therefore do not obey MichaelisMenten kinetics.
The kinetic properties of allosteric enzymes are often explained in terms
of a conformational change between a low-activity, low-affinity “tense”
or T state and a high-activity, high-affinity “relaxed” or R state.
These structurally distinct enzyme forms have been shown to exist in
several known allosteric enzymes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymeinhibition-210420044925-240322103320-ce690b04/75/Enzyme-inhibition-in-brief-and-their-examples-21-2048.jpg)