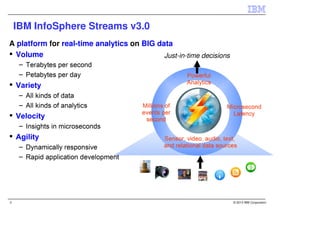
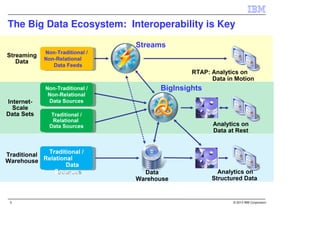
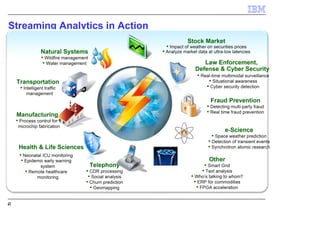
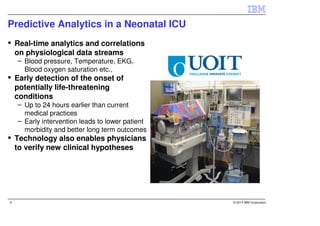
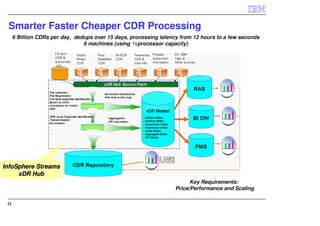
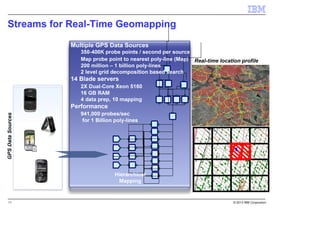
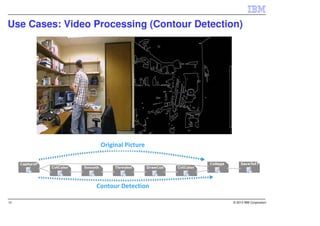
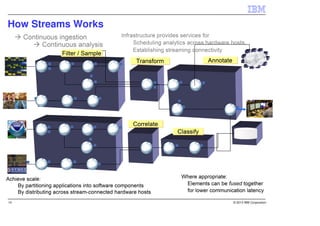
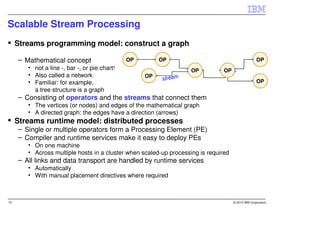
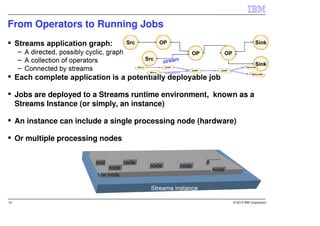
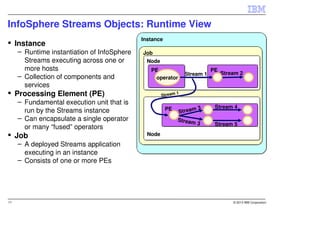
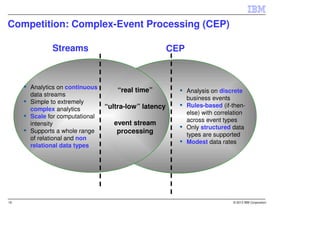
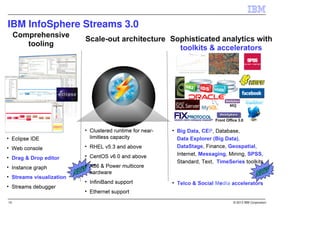
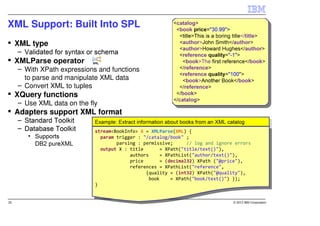
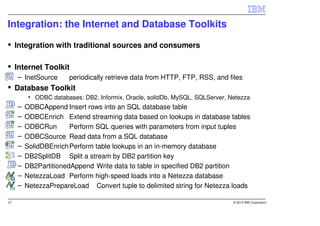
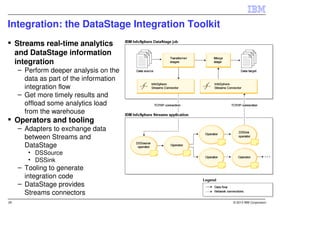
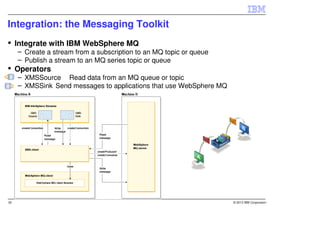
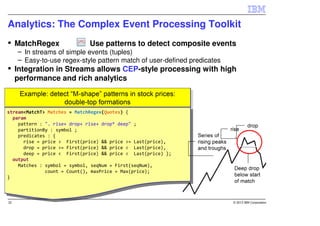
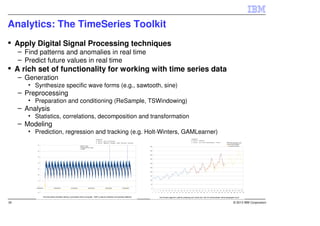
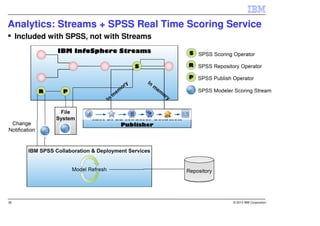
IBM InfoSphere Streams is a platform for processing streaming data in real-time. It allows for the construction of application graphs where data continuously flows between operators. The platform can handle high data volumes and varieties, providing low-latency analysis. It includes various pre-built operators and toolkits for integration, analytics, text processing, and more. Streams supports the development of applications across multiple nodes in a cluster and can automatically distribute and parallelize processing.