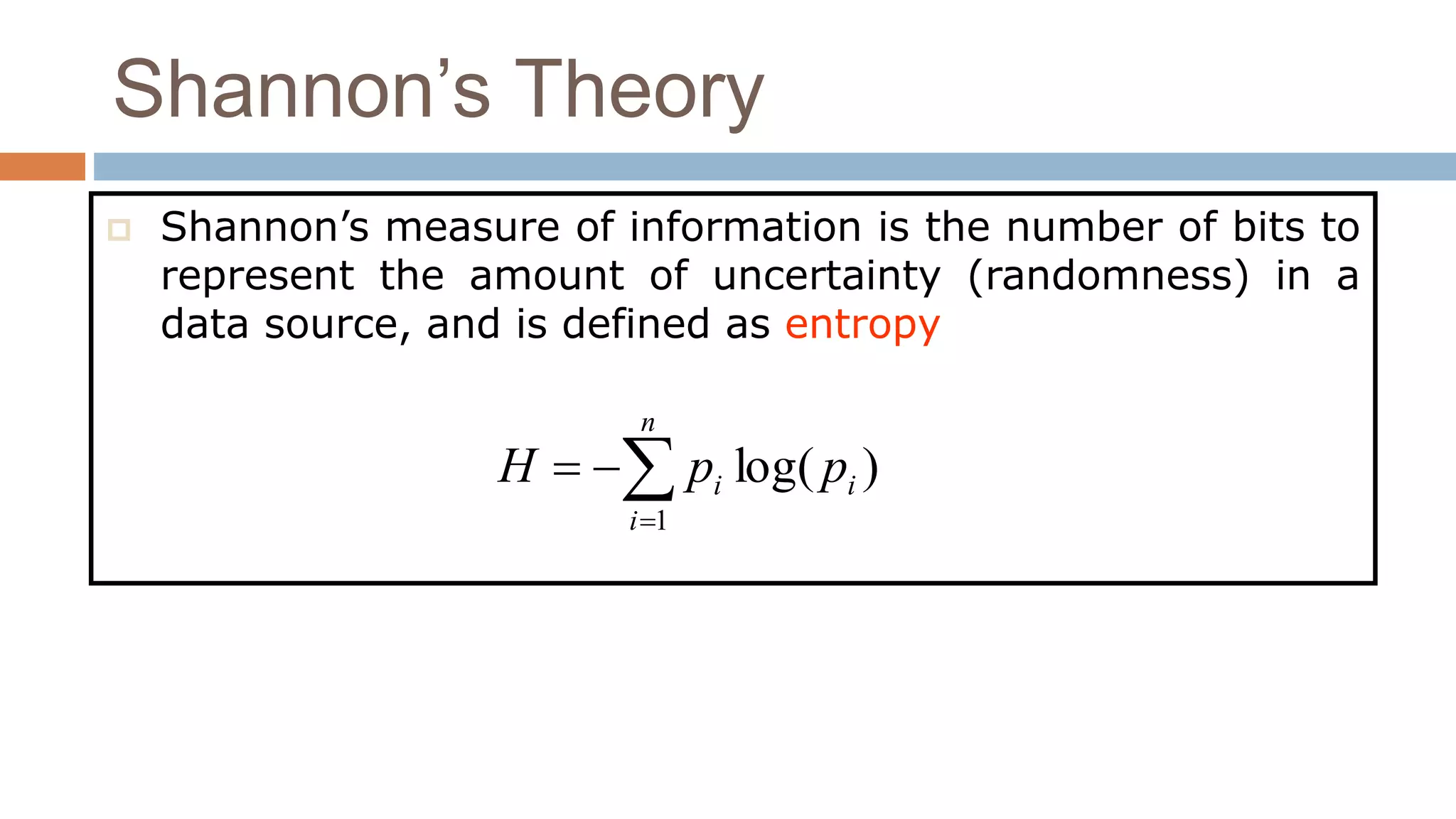
This document provides an overview of information theory as it relates to cryptography and network security. It discusses the foundations of information theory, including its history, definition, Shannon's theory, and Huffman coding. It also outlines some key measures in information theory like entropy, mutual information, and channel capacity. Finally, it lists some application areas of information theory such as data compression, channel coding, cryptography, and more.