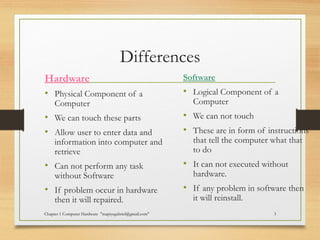
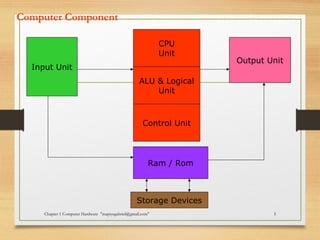
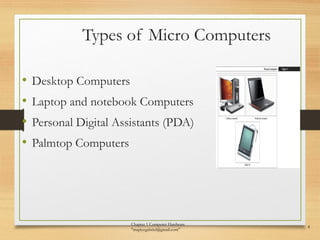
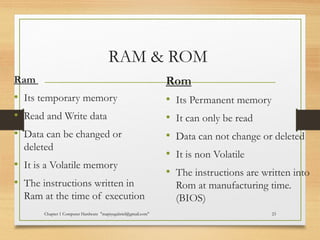
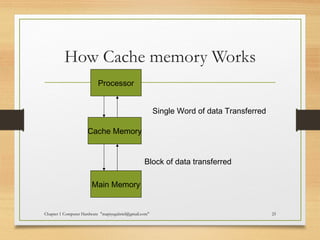
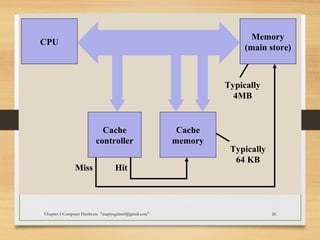
The document discusses the key components of computer hardware. It describes the differences between hardware and software, with hardware being the physical parts that can be touched, and software being the logical instructions. The main components of a computer system are then outlined as the input, output, memory, CPU, and secondary storage units. Several types of computers are also defined based on size, including microcomputers, mainframes, supercomputers, mini computers, and embedded systems. Common examples are provided for each type along with their typical uses. Memory and storage technologies like RAM, ROM, cache, hard disks, optical disks, and USB drives are further explained.