This document provides an overview of key concepts about computers and their uses:
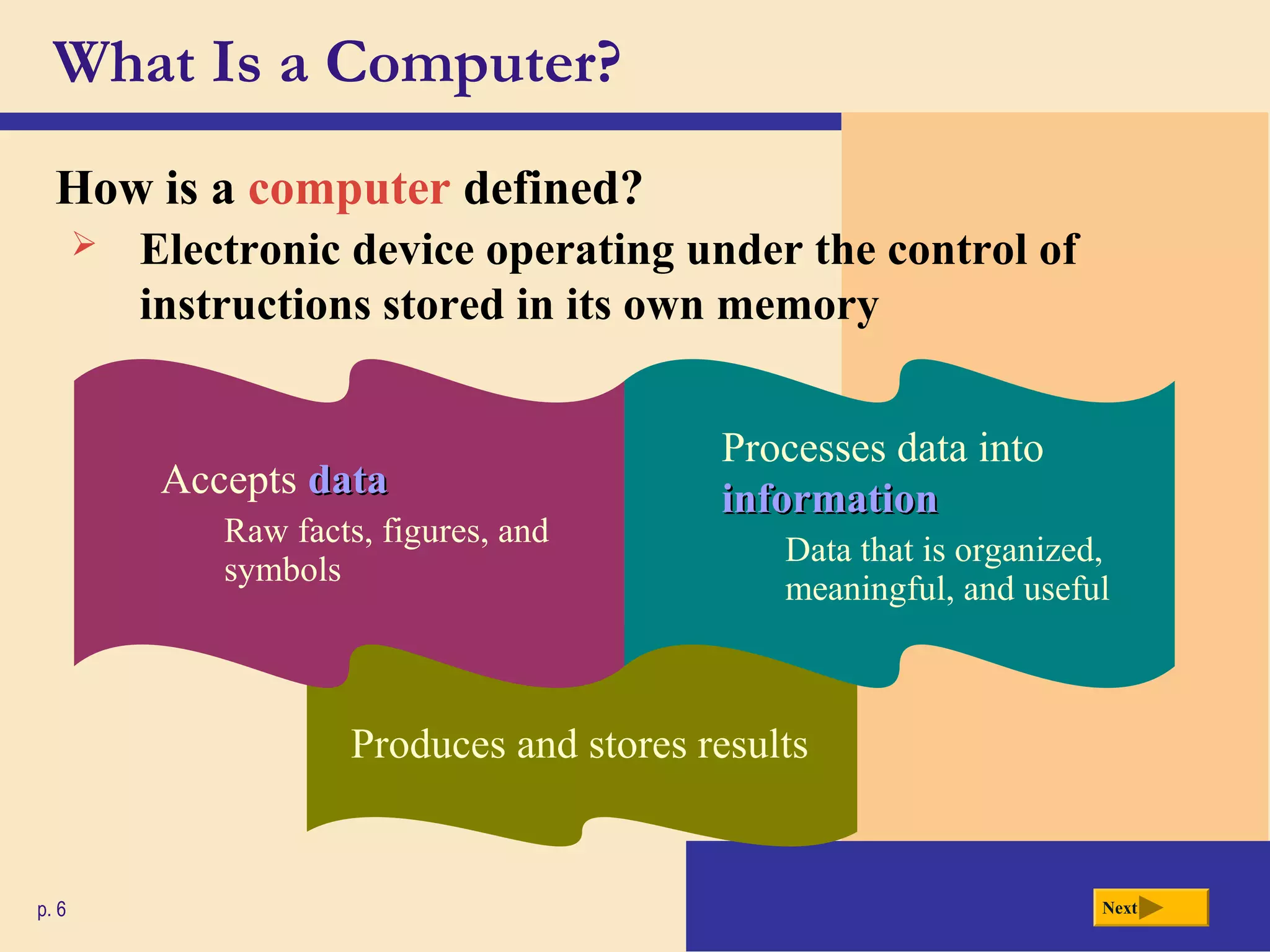
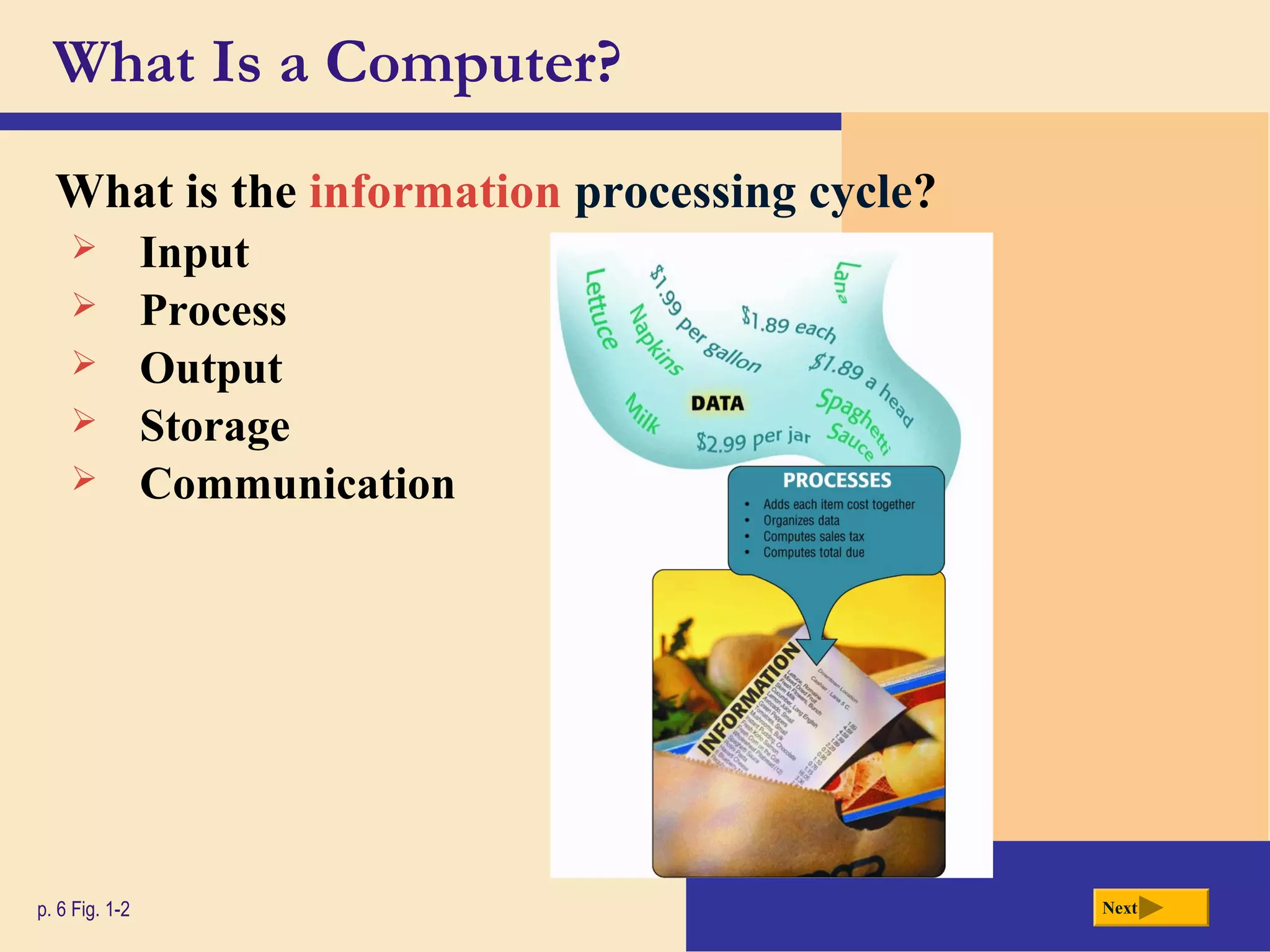
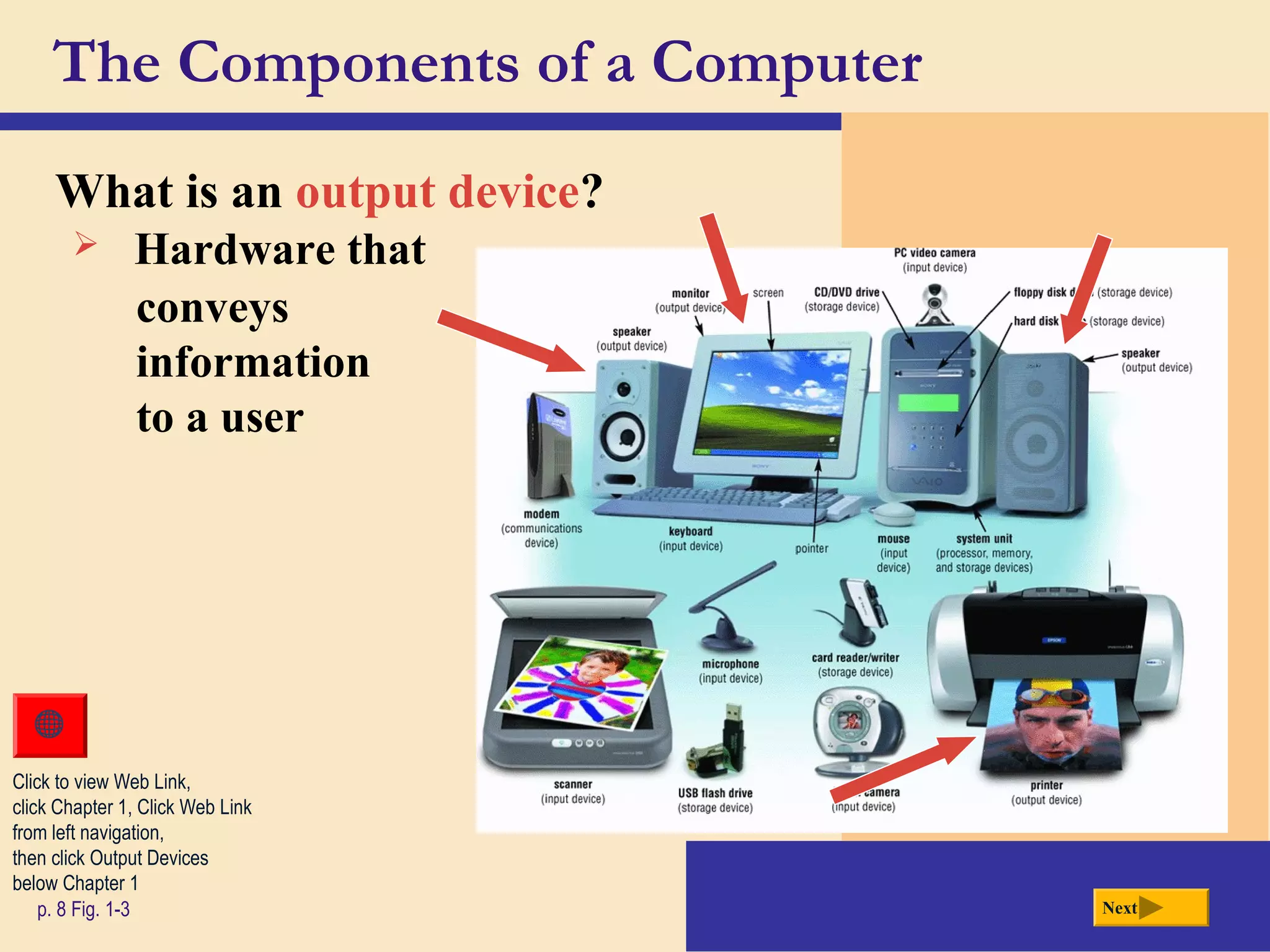
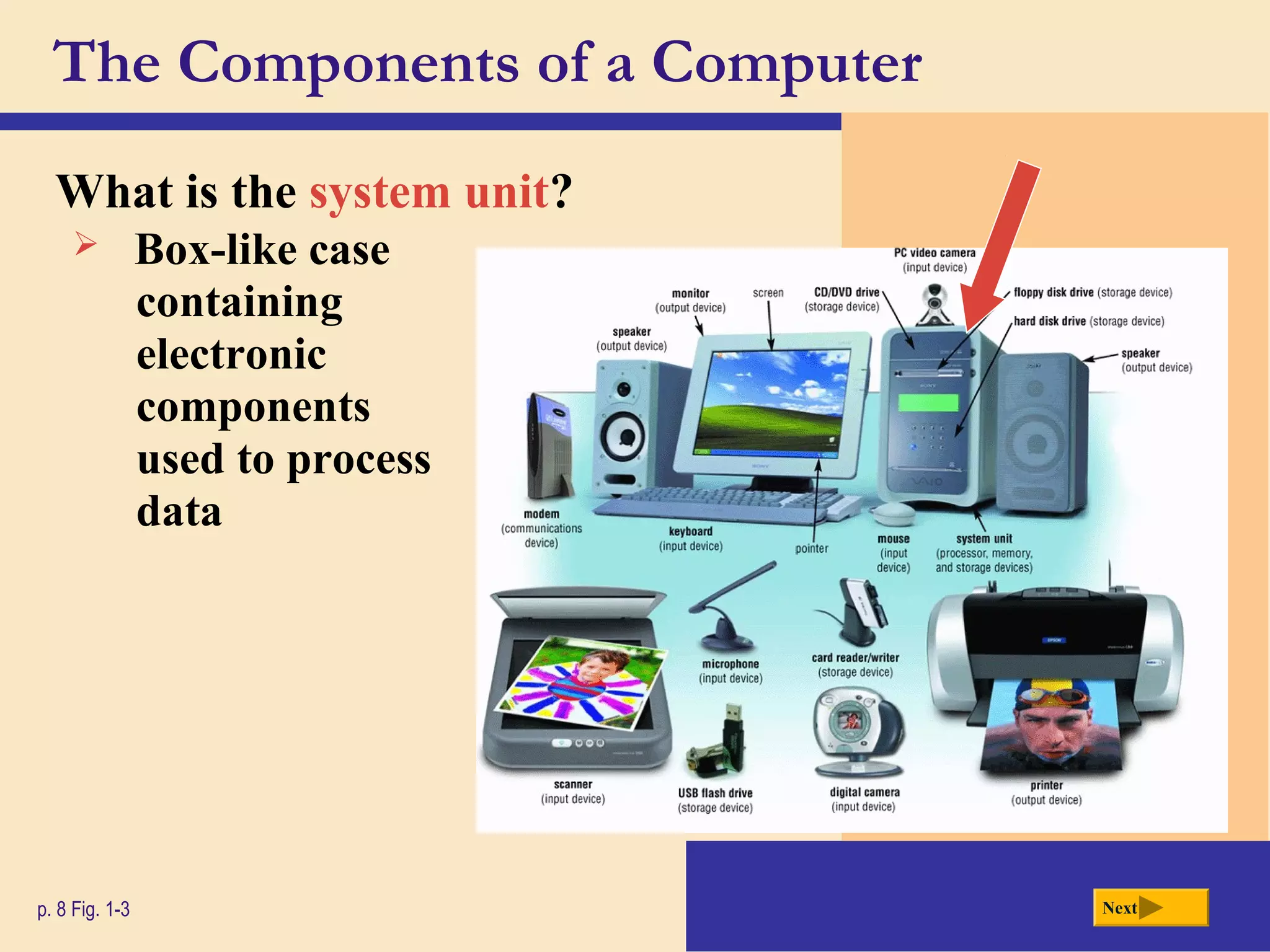
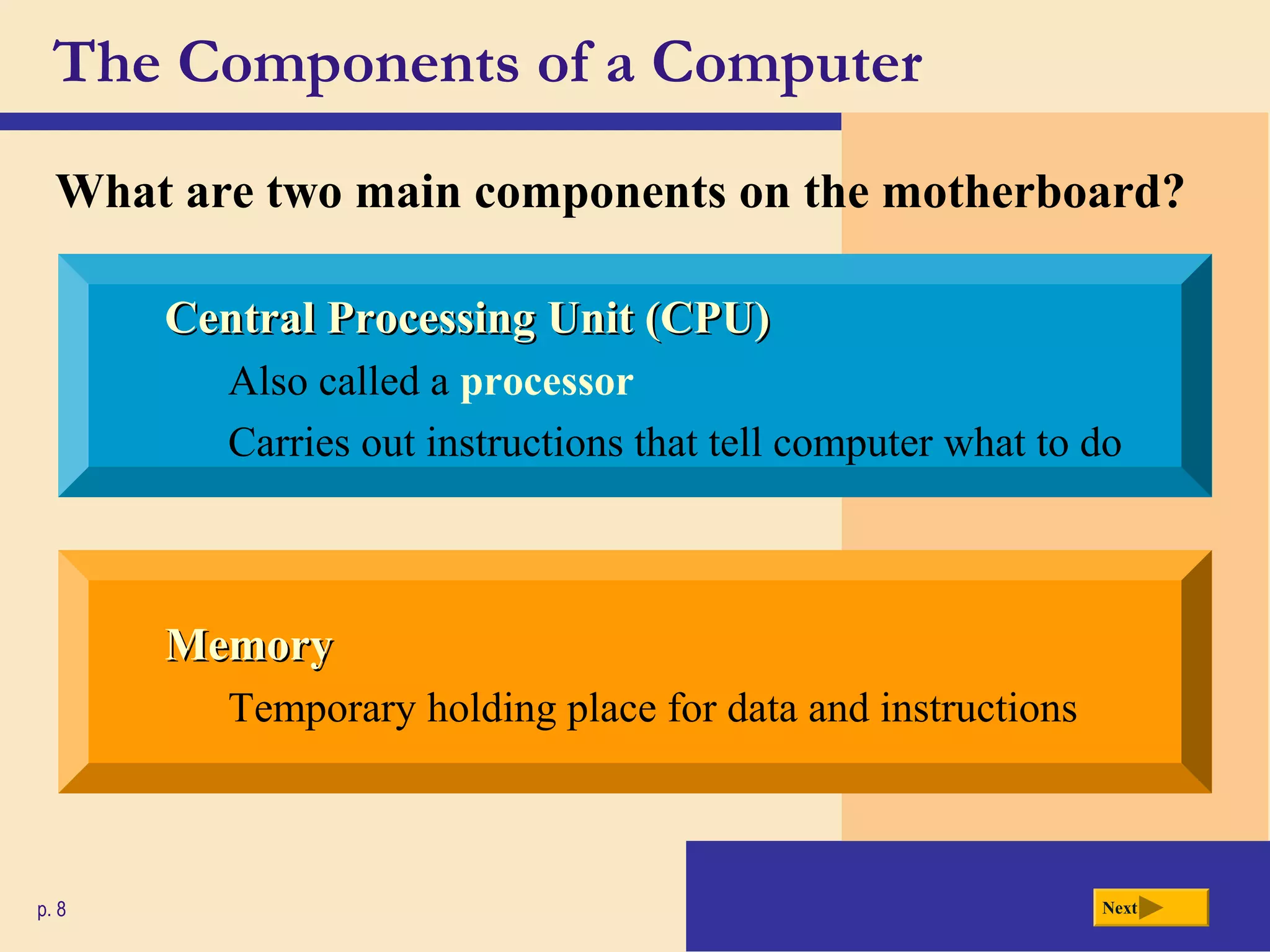
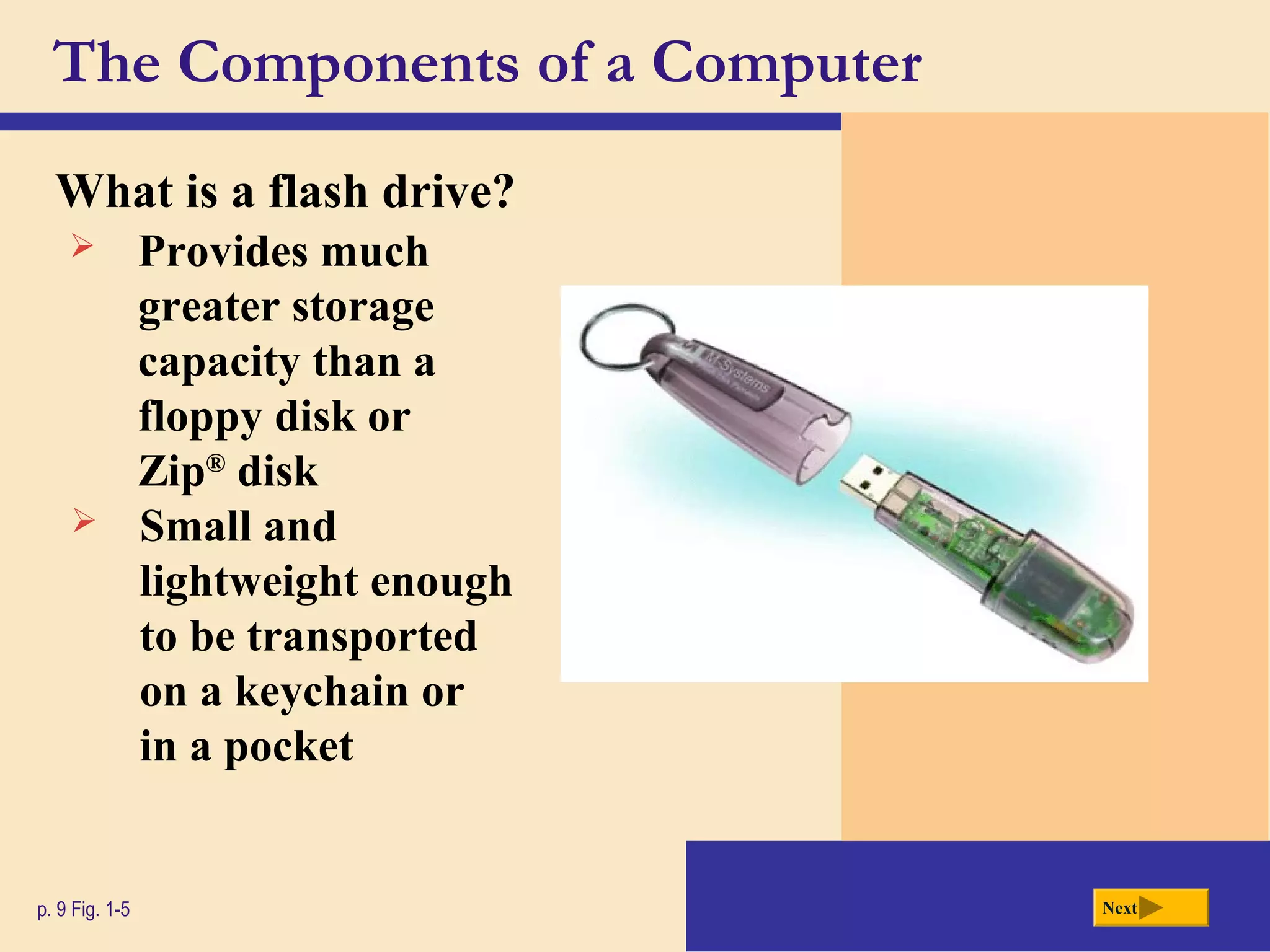
- It defines a computer as an electronic device that processes data according to stored instructions. Computers have input, processing, output, storage, and communication components.
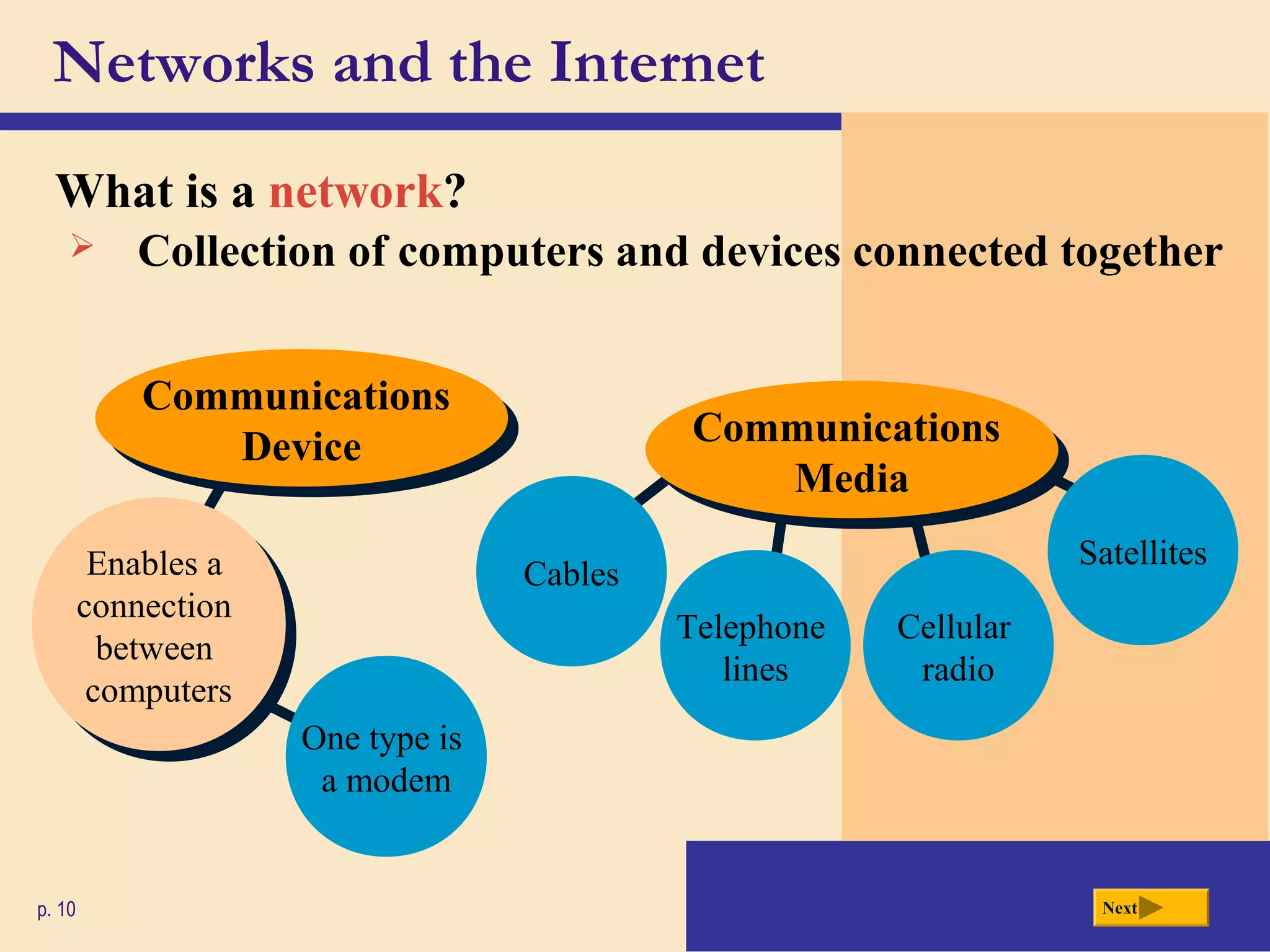
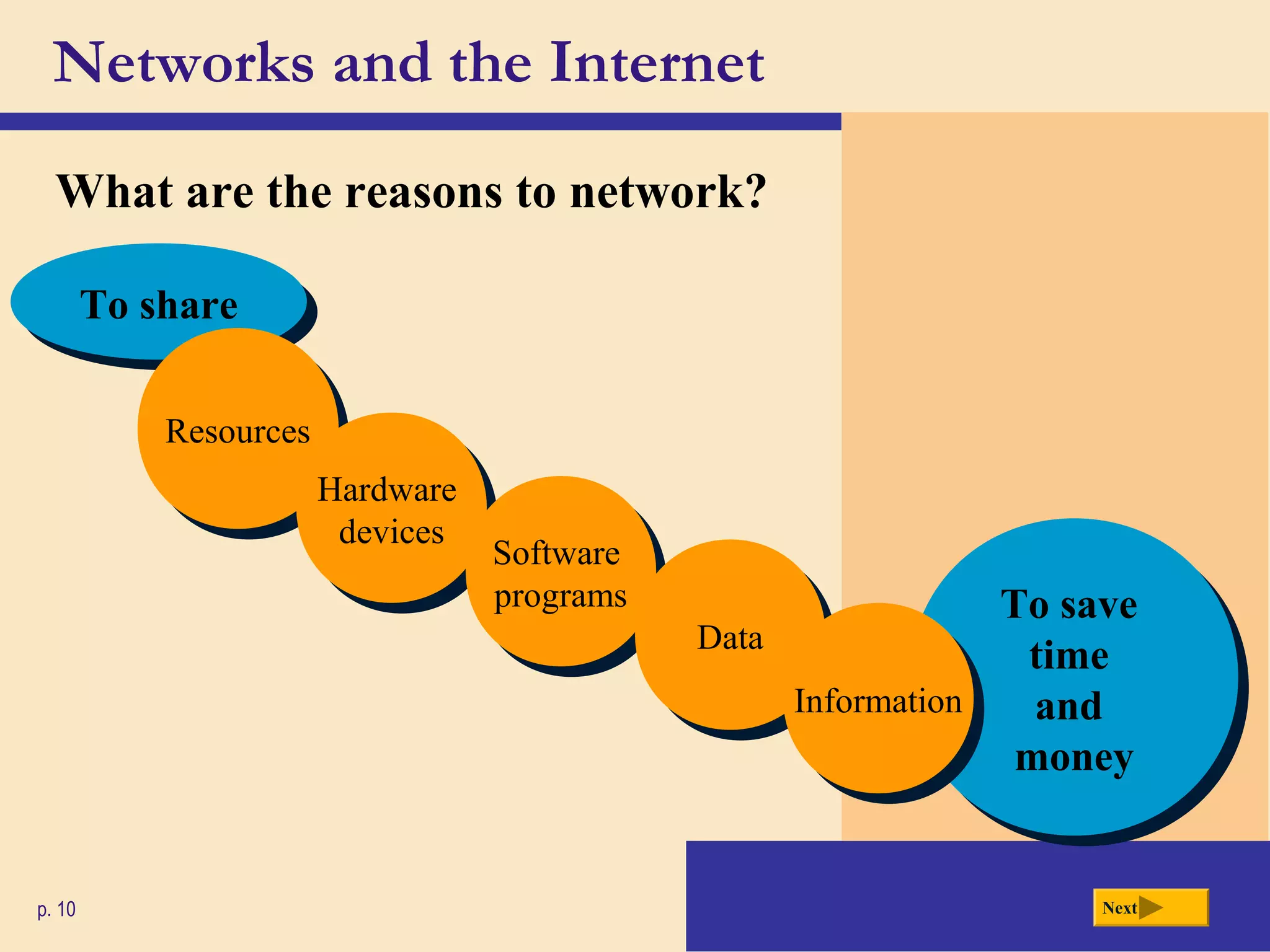
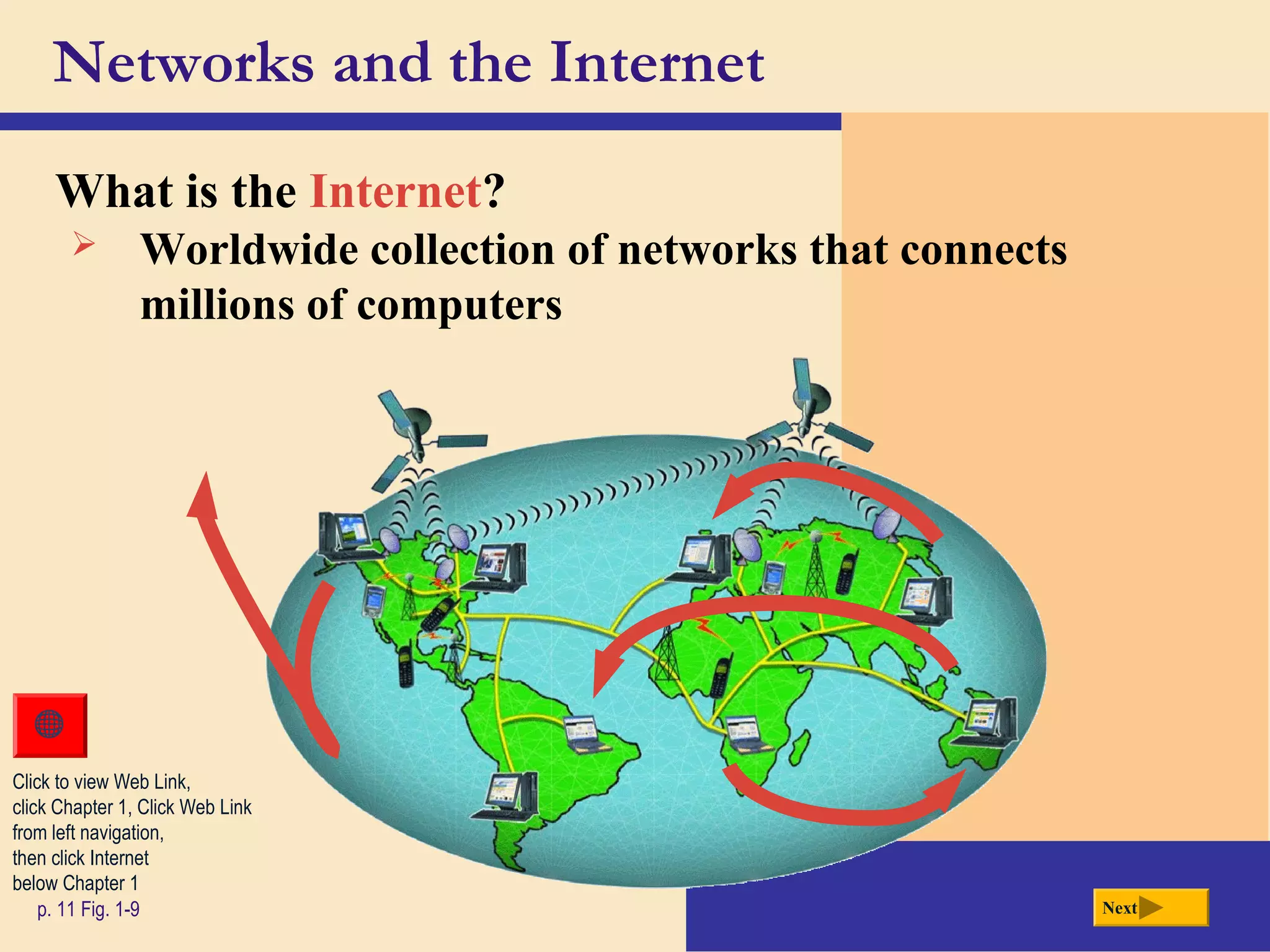
- Networks allow computers to share resources like hardware, software, data and information. The Internet is a worldwide network that connects millions of computers and provides access to billions of web pages.
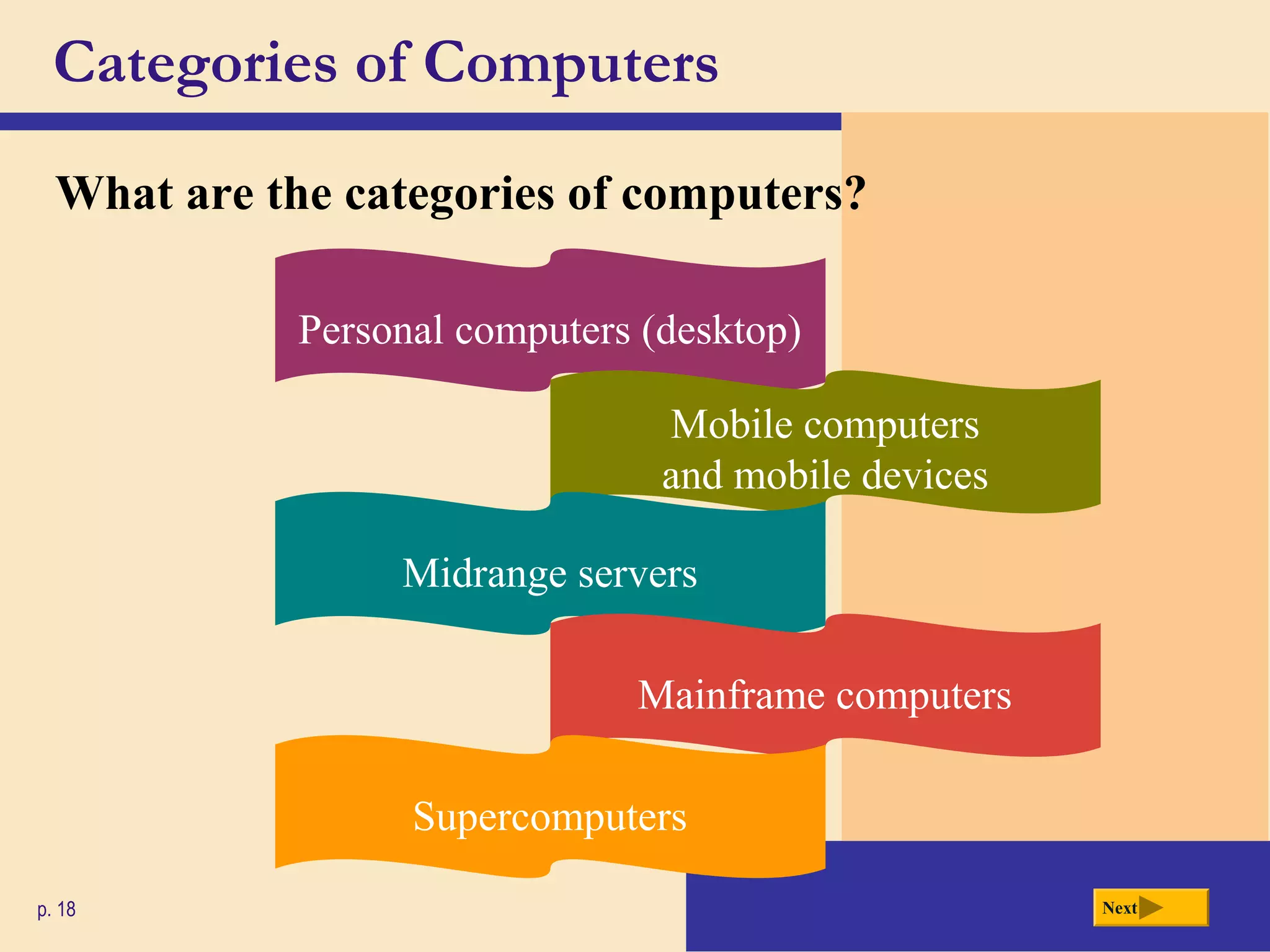
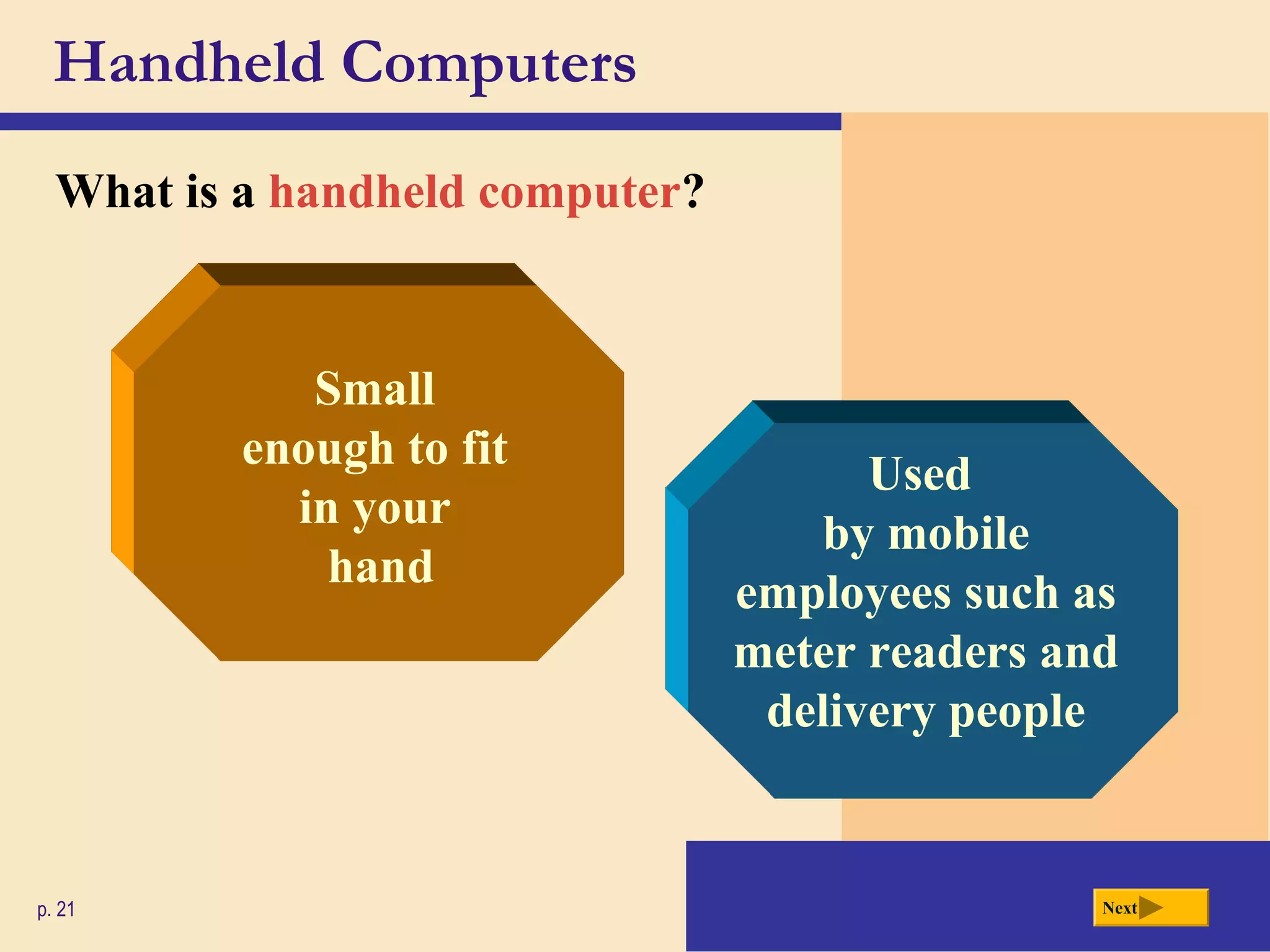
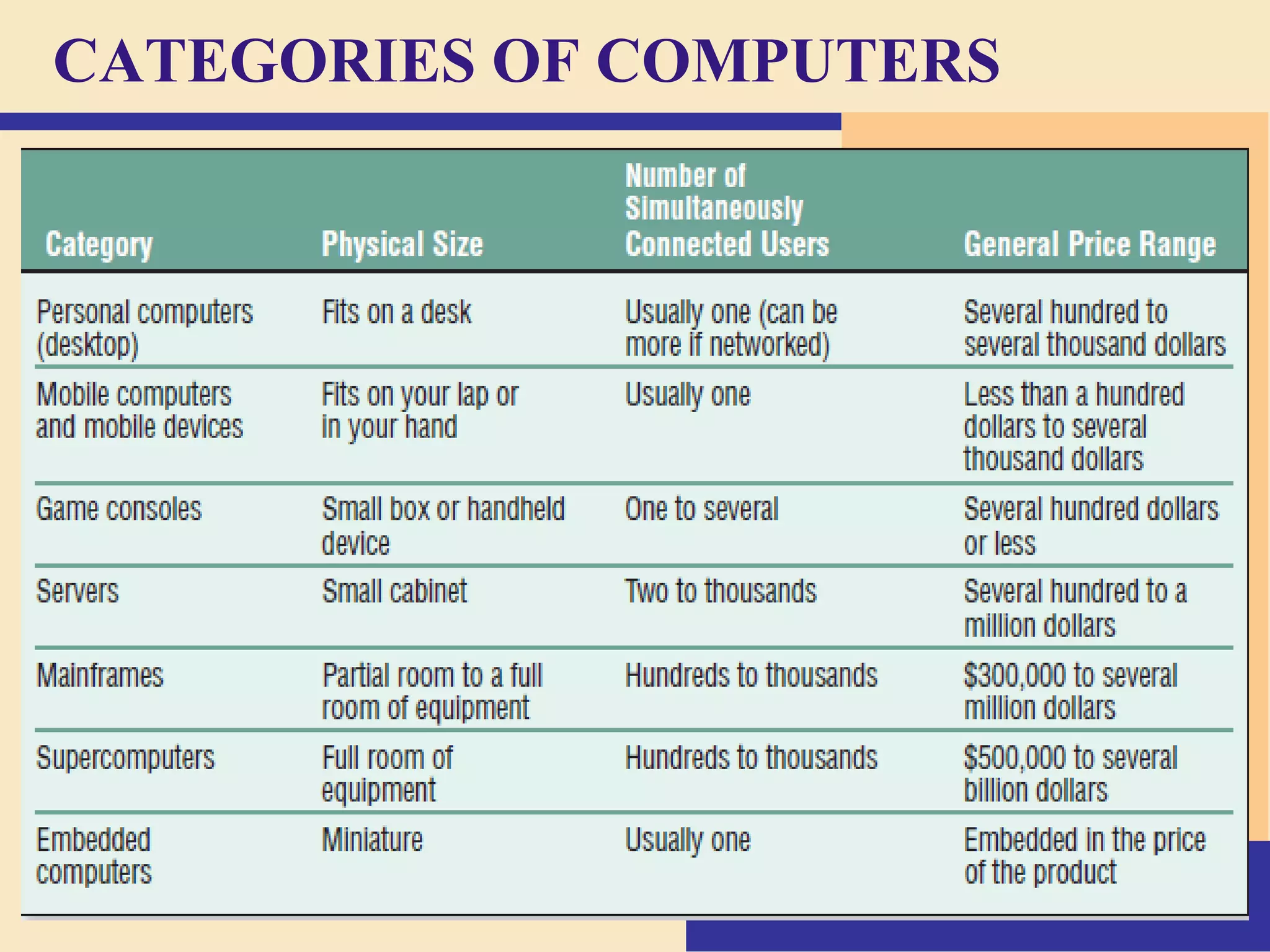
- There are different categories of computers including personal computers, servers, mainframes, and supercomputers. Personal computers can be desktops or laptops.
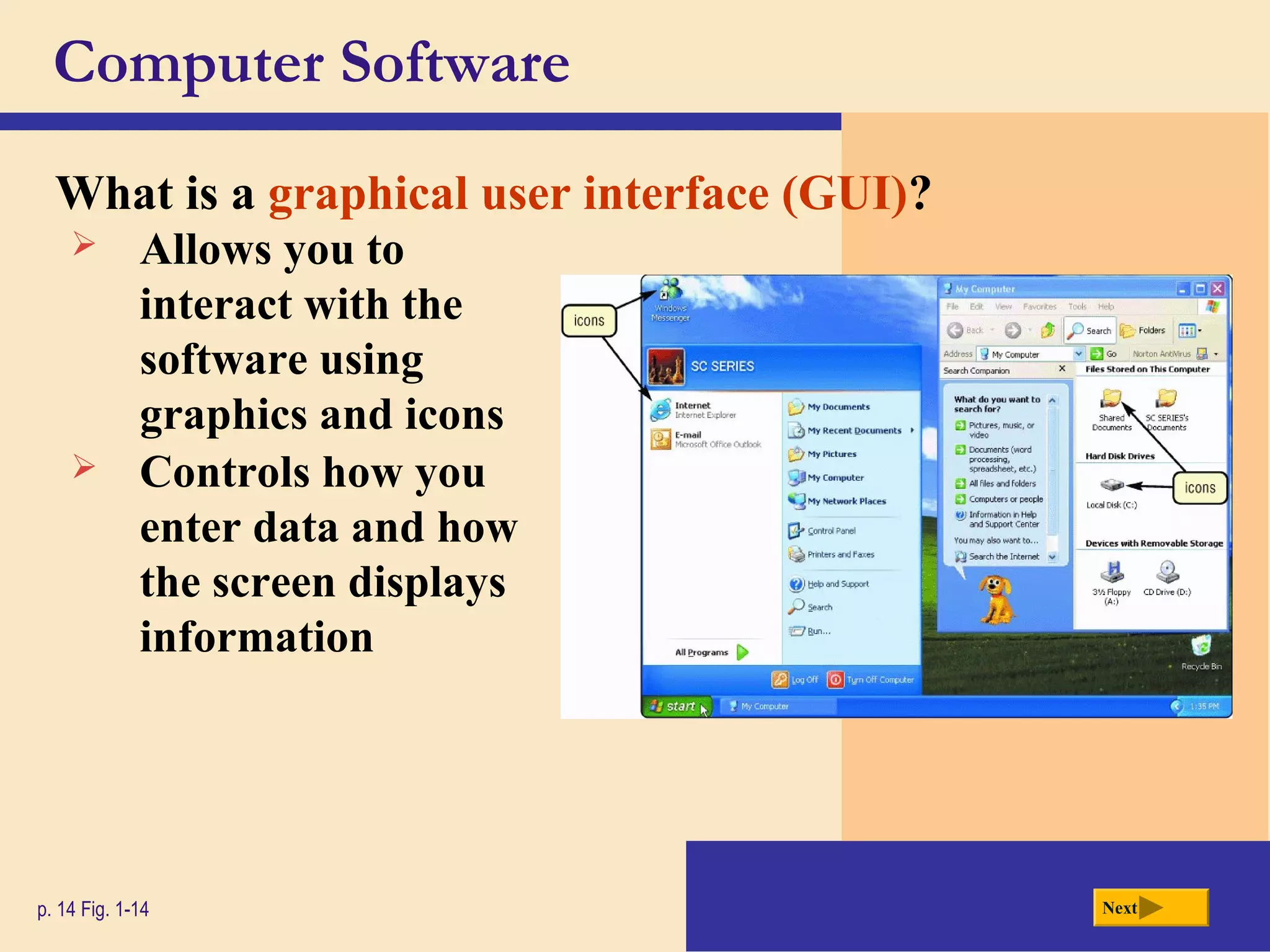
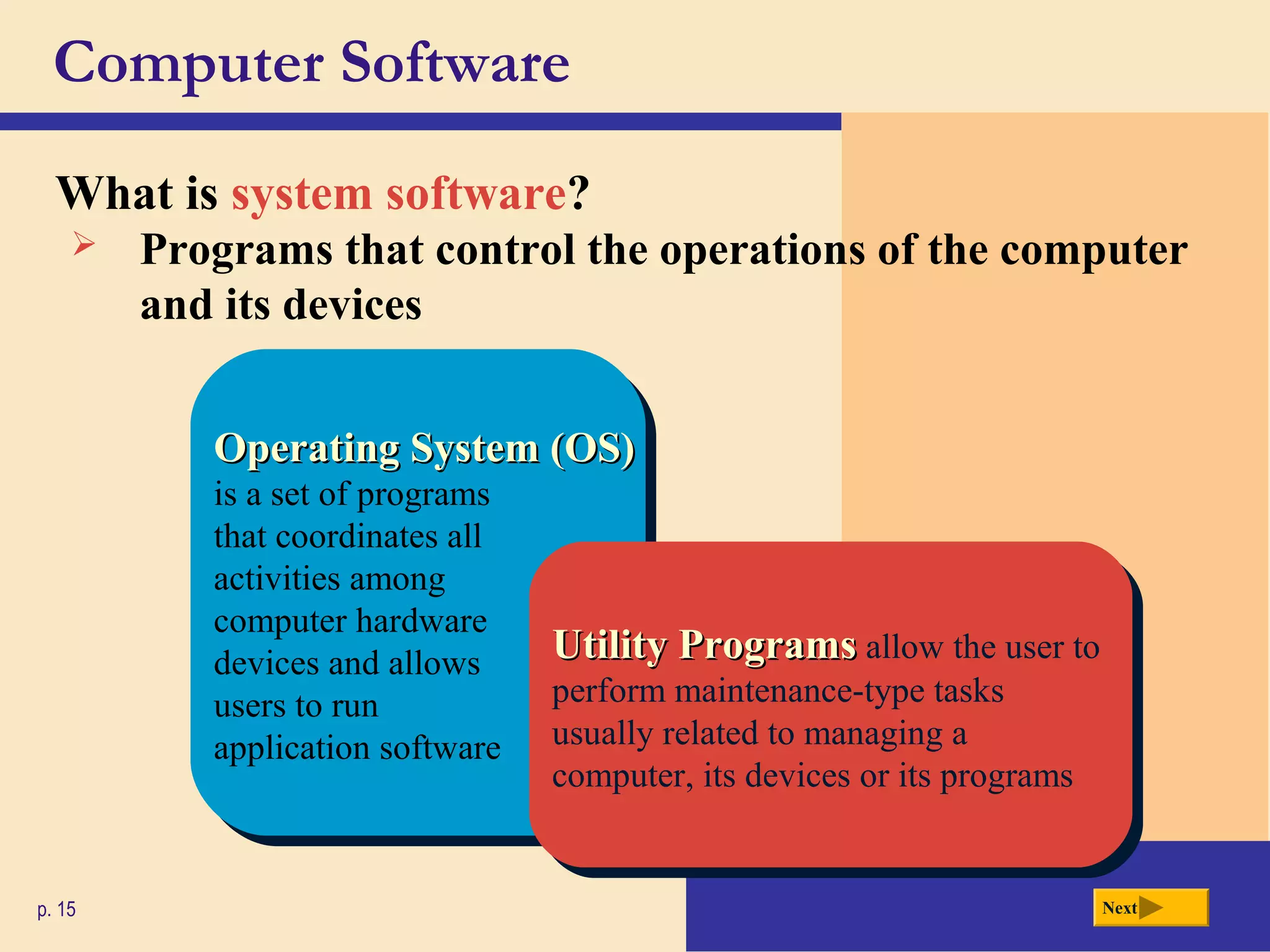
- Software includes system software like operating systems and utility programs, as well as application software for specific tasks.
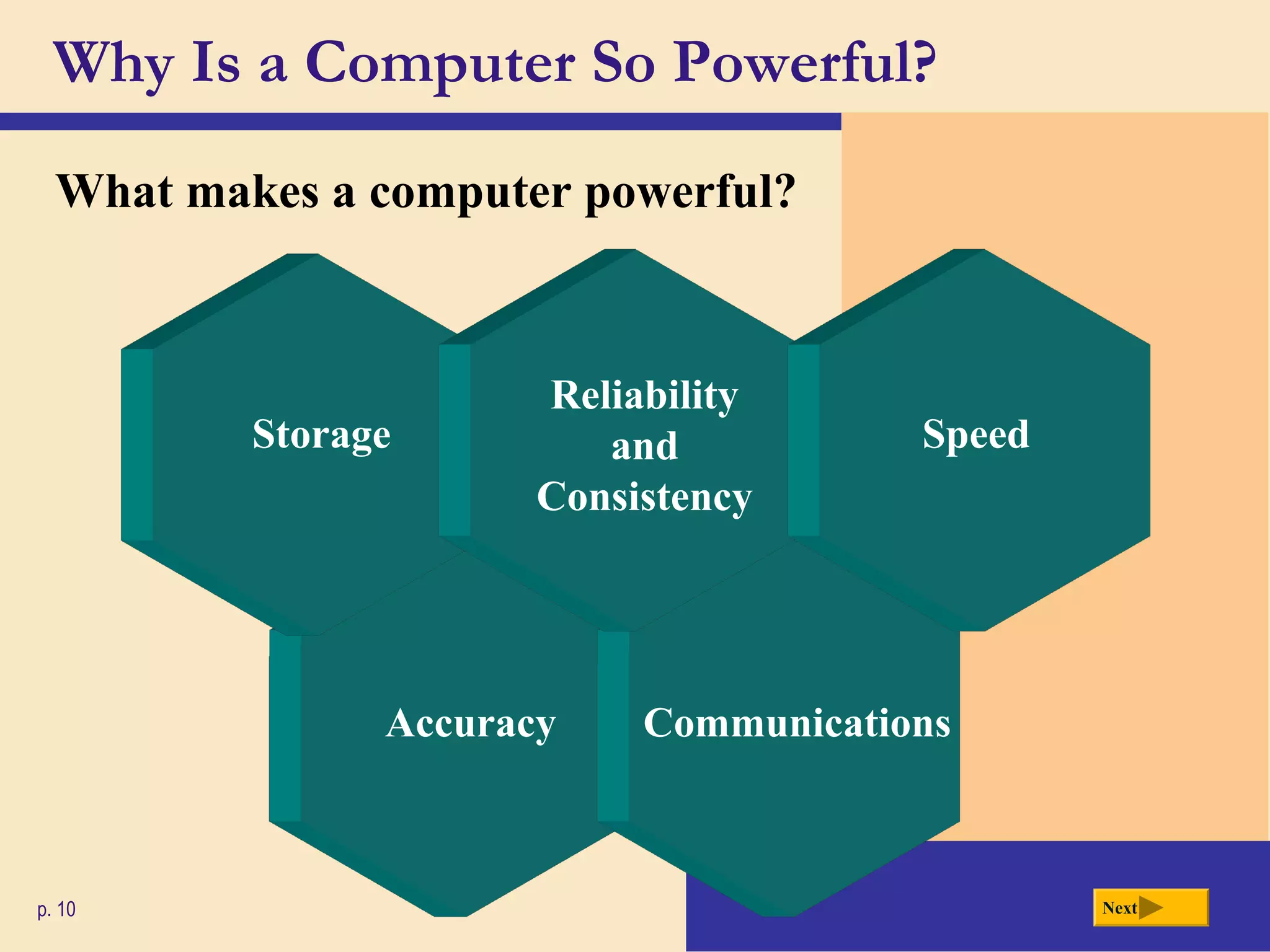
- Computers