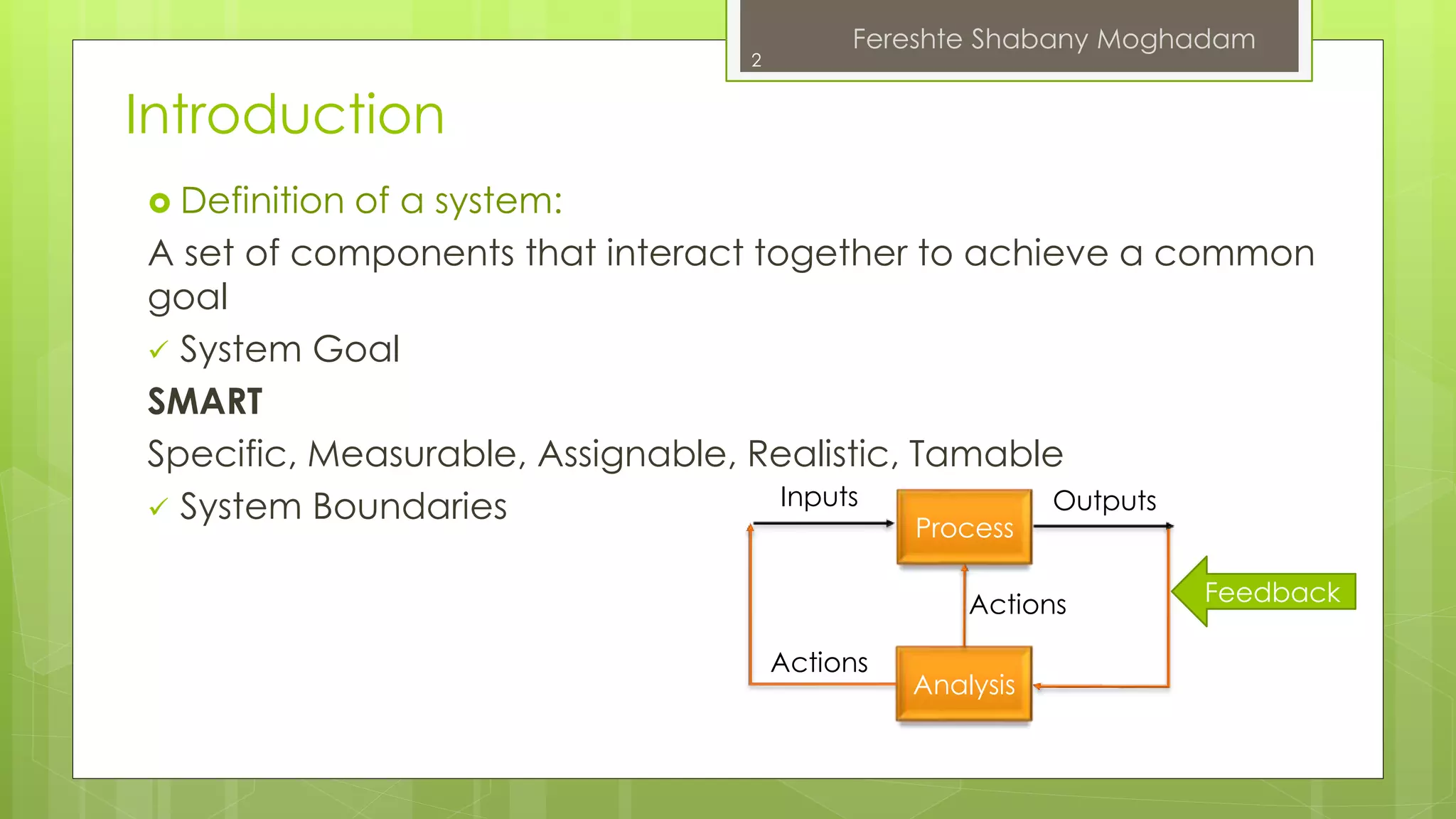
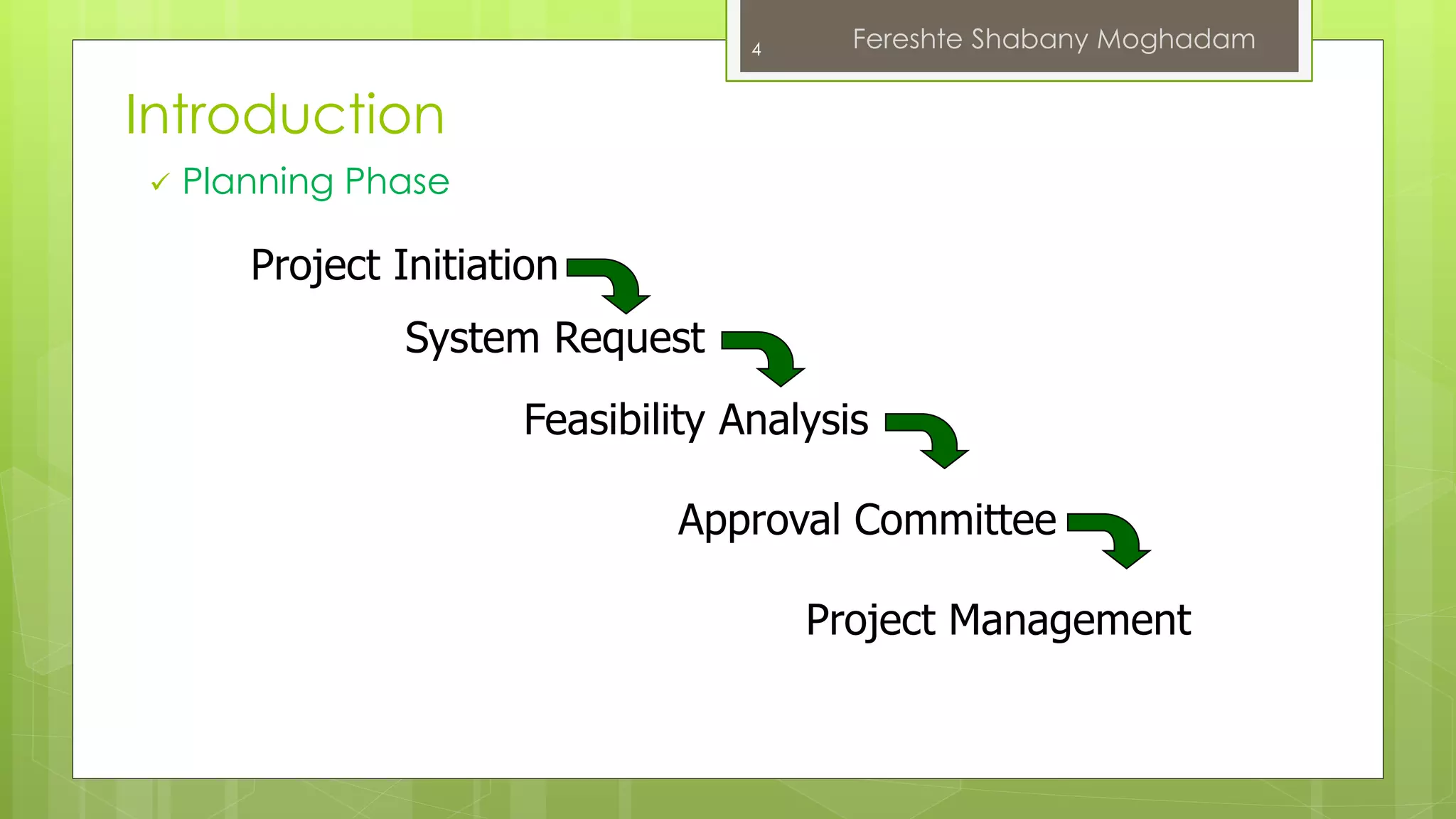
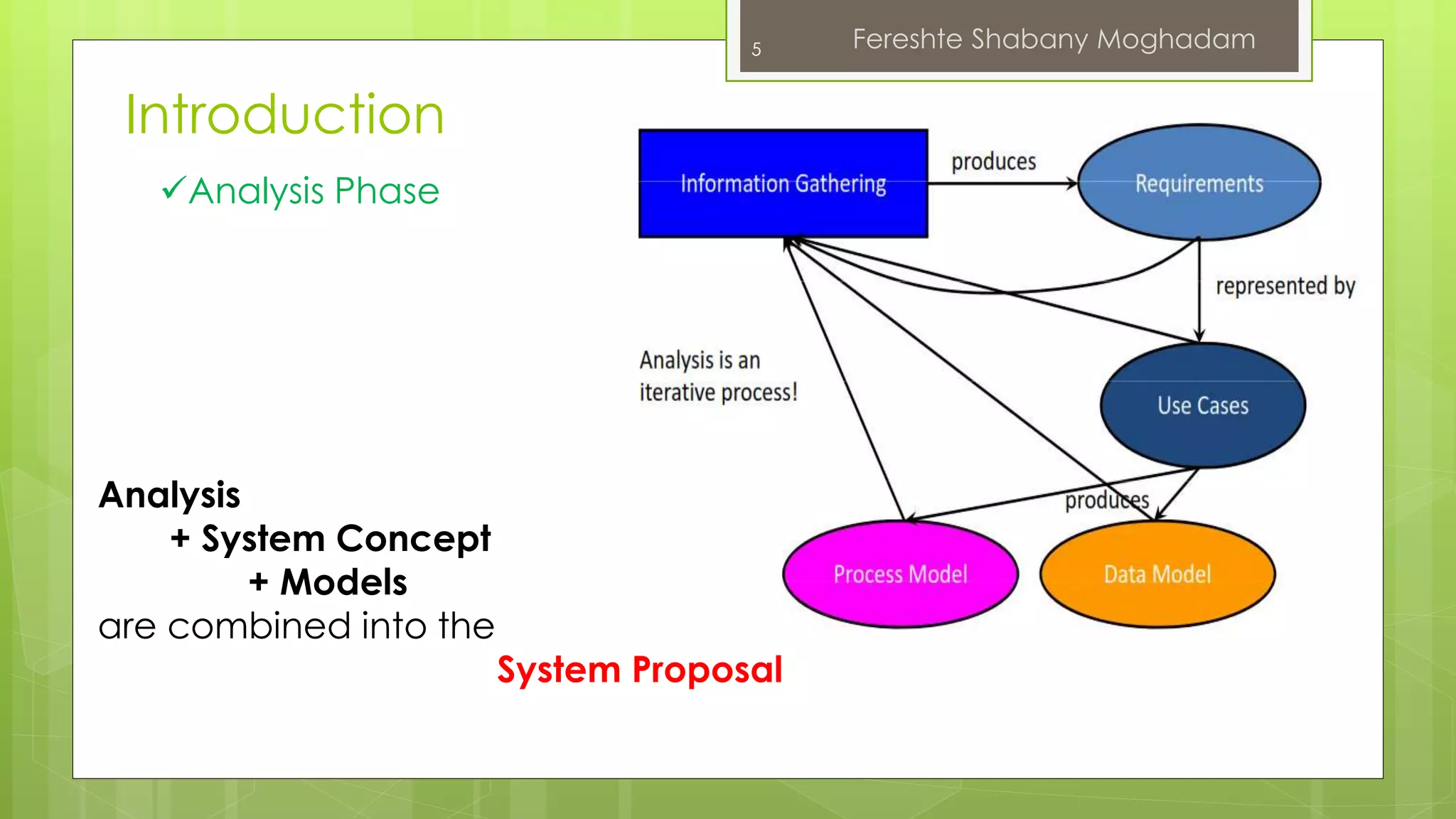
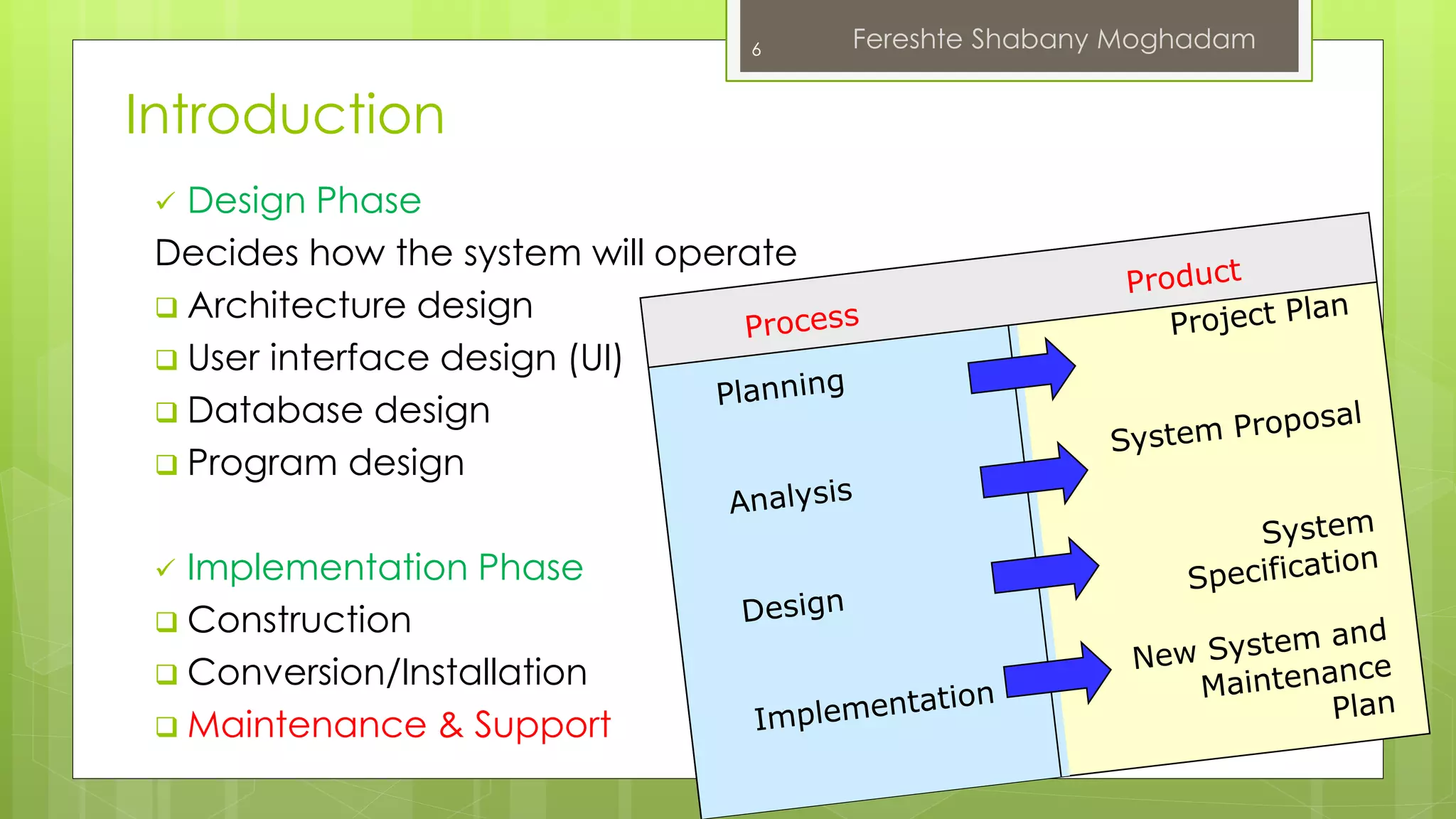
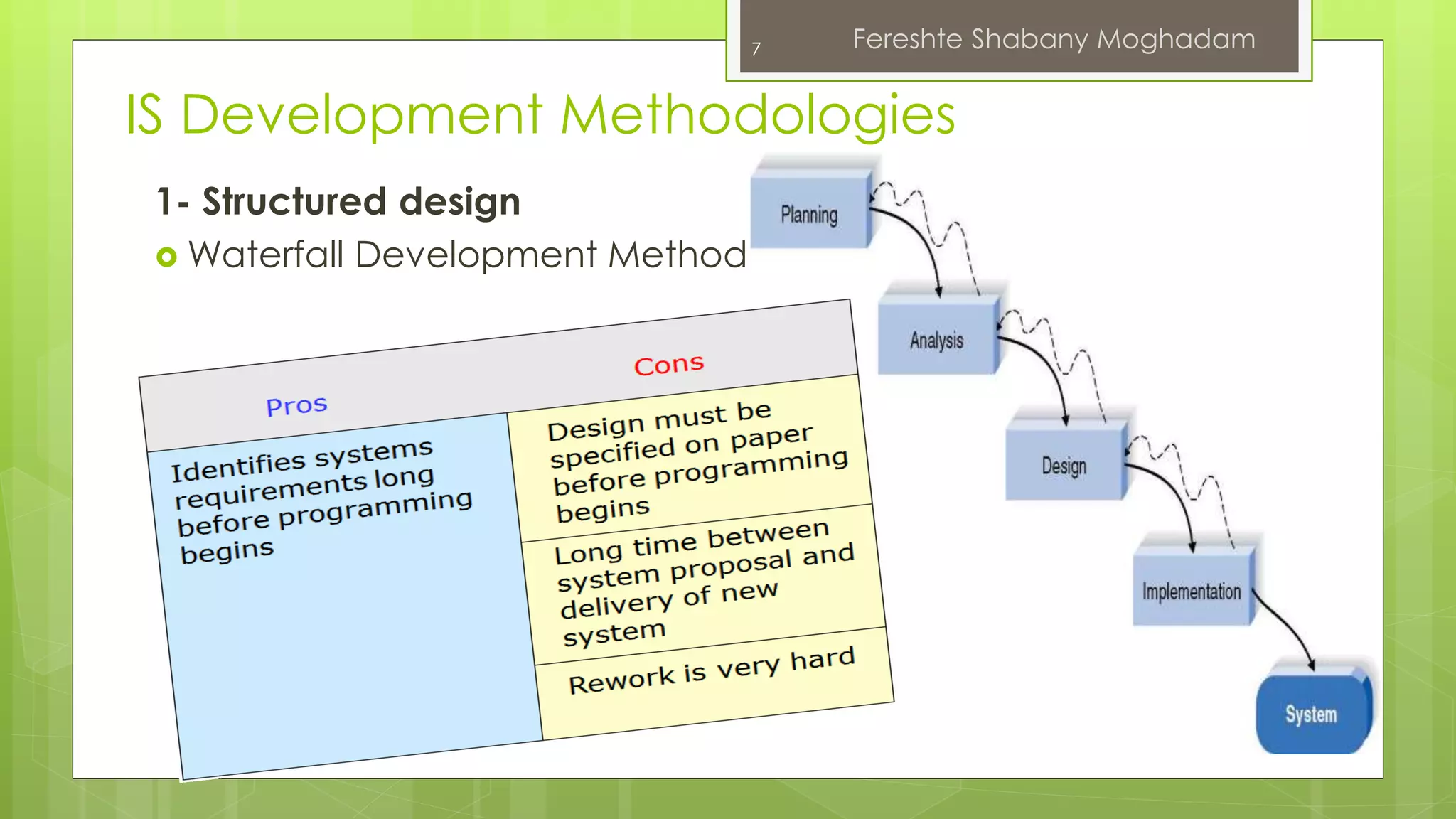
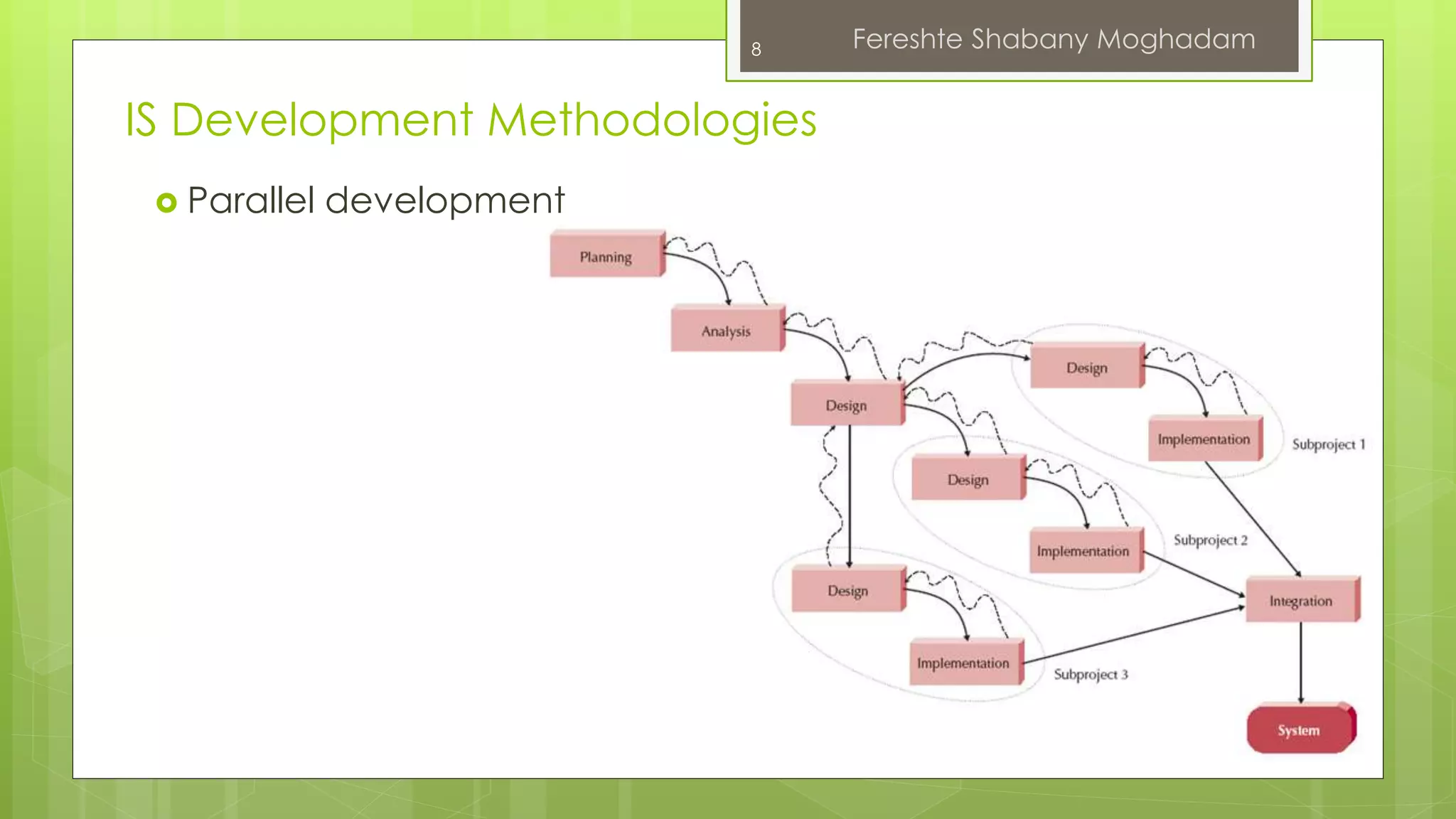
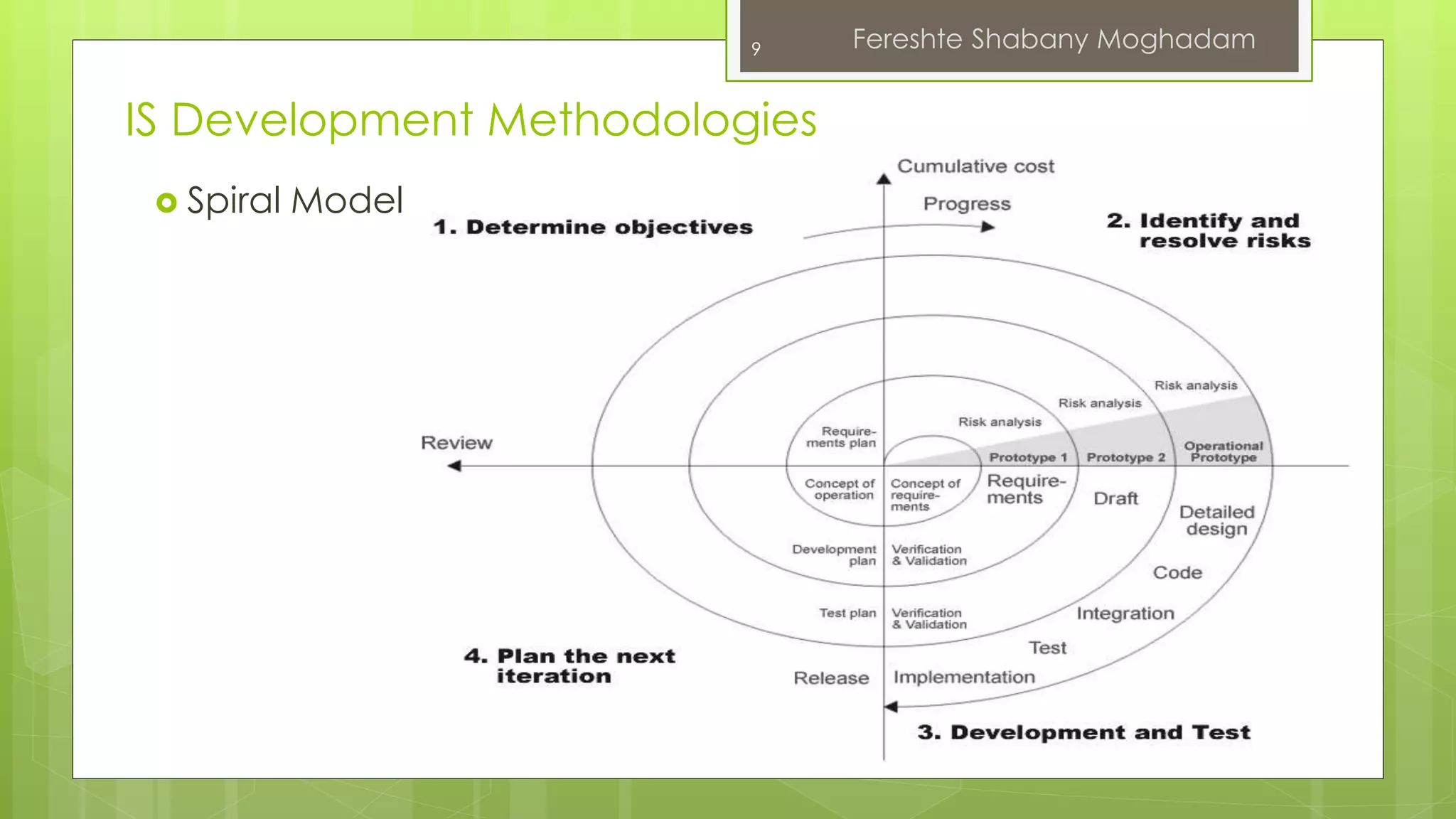
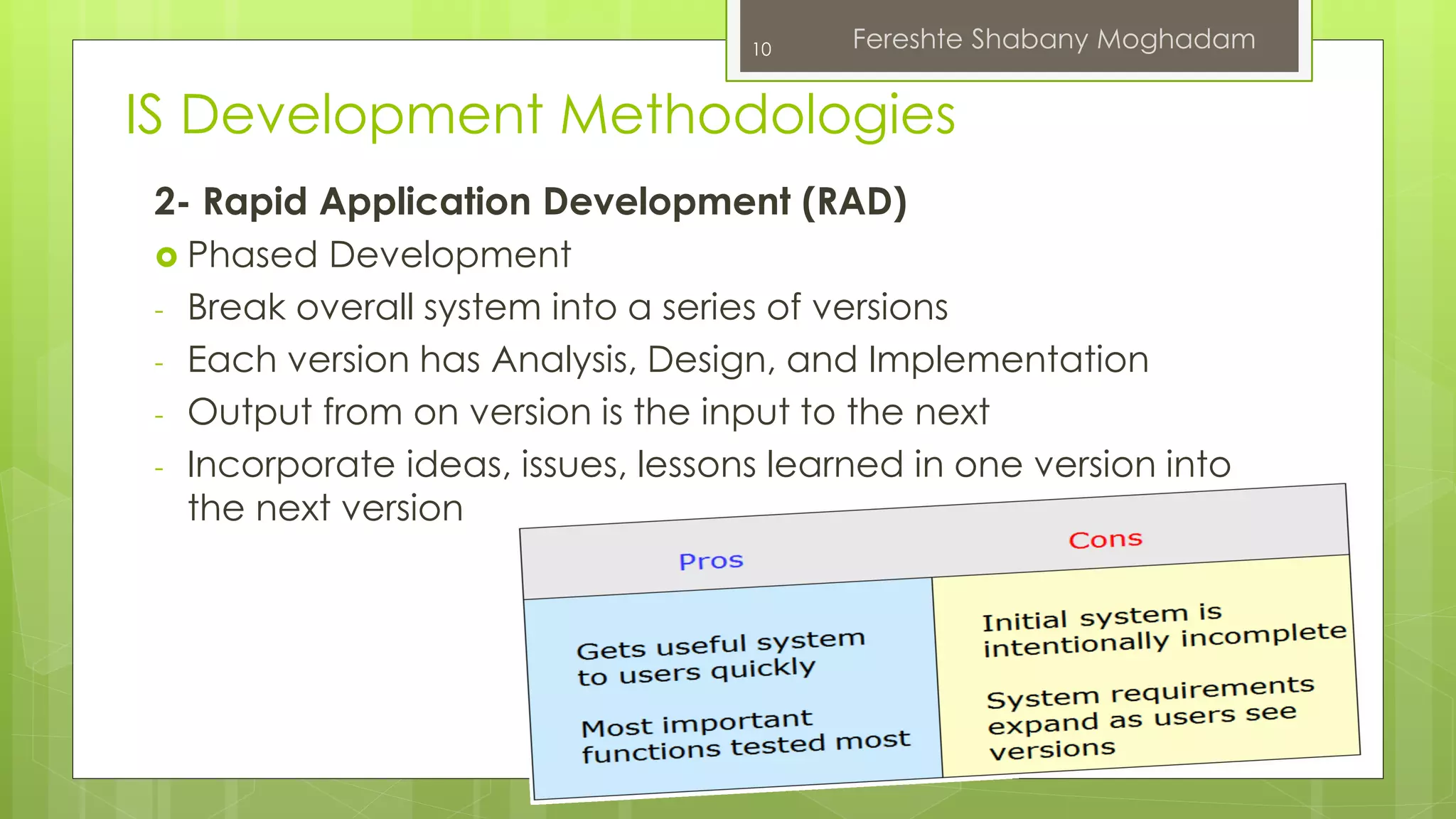
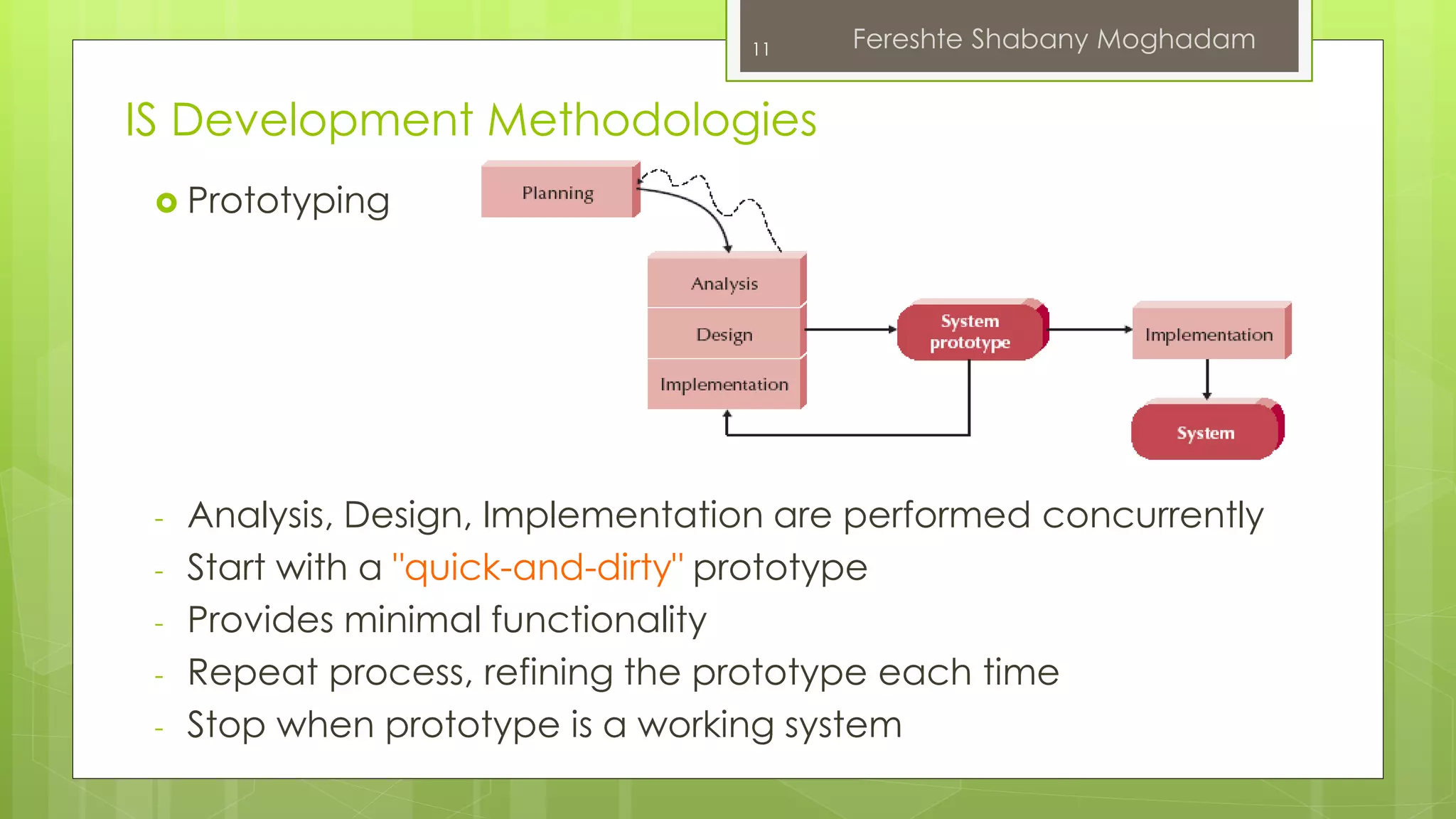
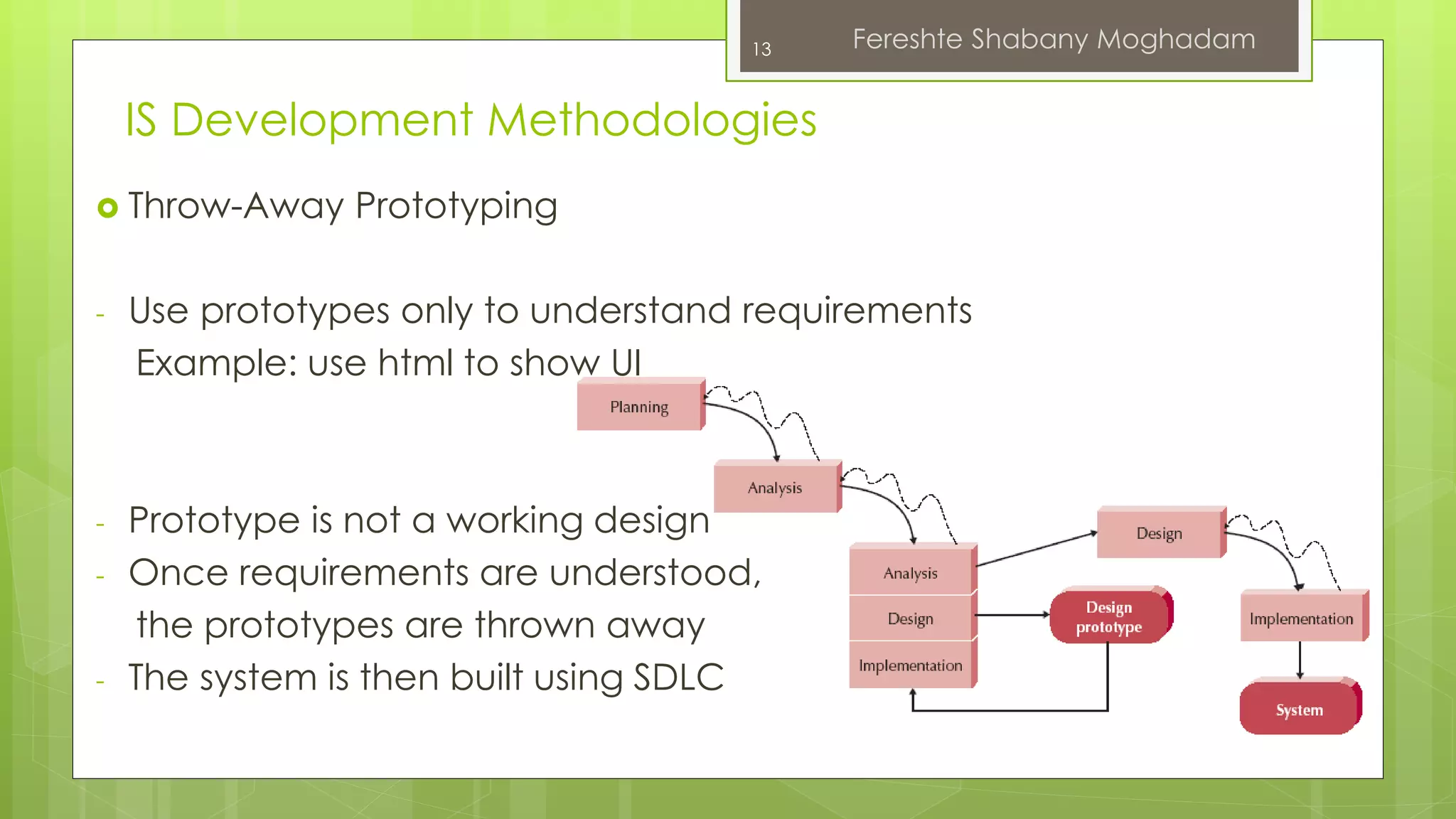
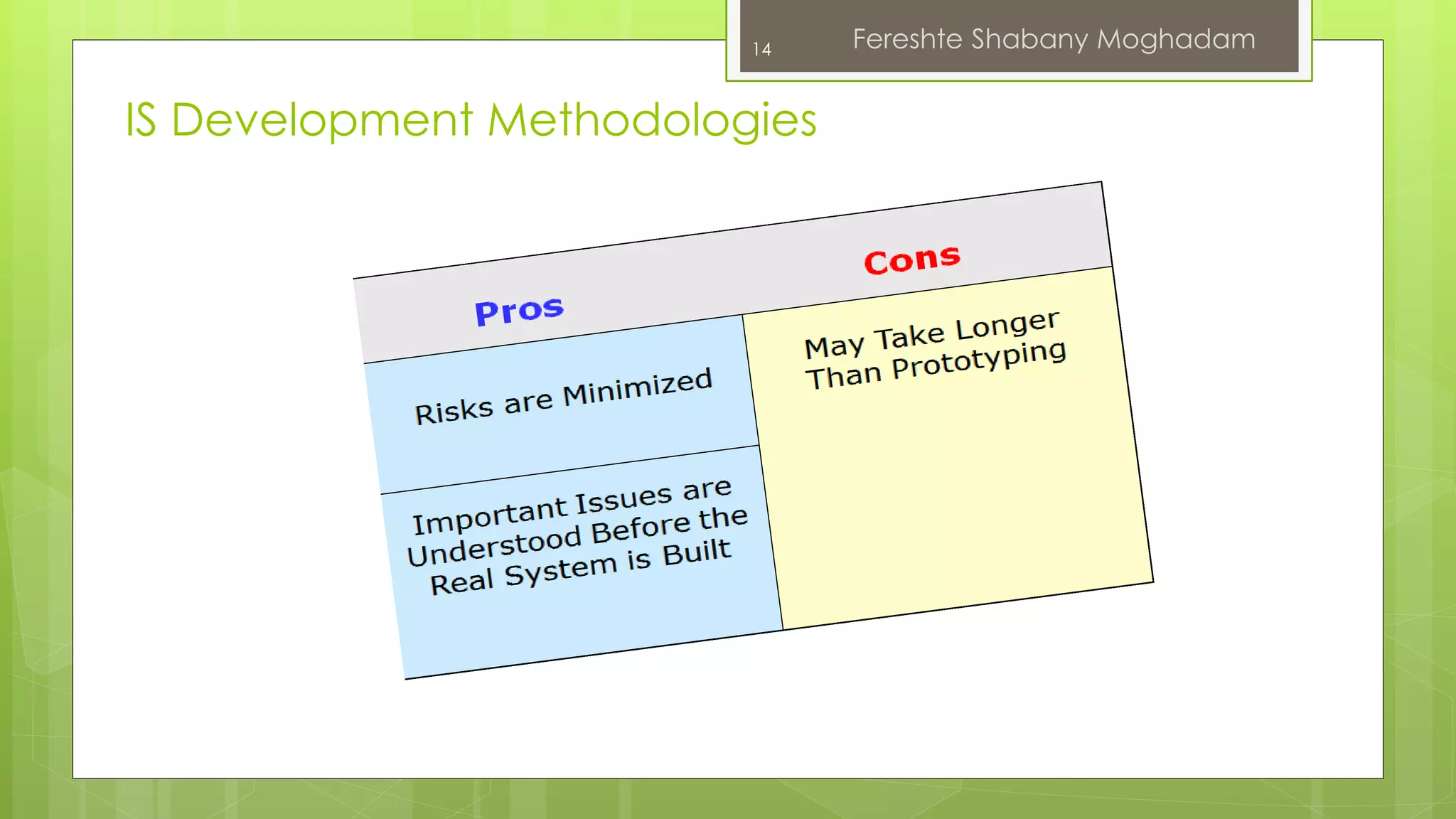
This document outlines the fundamentals of information systems, including their definition, project phases, and various development methodologies such as waterfall, spiral, and agile. It emphasizes the significance of information systems in achieving strategic business objectives and lists different types of information systems along with their roles in organizations. Additionally, it highlights the infrastructure necessary for effective information system implementation, including organizational and technological requirements.